Playing with Constructions
Basic Figures & Tools:
- Ruler and Compass: Tools used to draw accurate geometric shapes.
- Curves: Includes straight lines, circles, etc. Using a compass, you can draw precise curves and circles.
- Circle: The distance between the center of a circle (P) and any point on the circle is called the radius.
Constructing Shapes:
- Person Figure: Challenge is to find where to place the compass tip and what radius to use to draw accurate curves.
- Wavy Line: Central line is usually arbitrary (e.g., 8 cm), and half-circles are drawn using a fixed radius.
Constructing Squares and Rectangles:
- Square Properties:
- All sides are equal.
- All angles are 90°
- Rectangle Properties:
- Opposite sides are equal.
- All angles are 90°
- Construction:
- Use a ruler and compass to mark points, draw perpendiculars, and ensure sides are of the correct length.
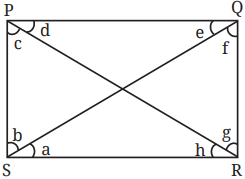
Exploring Rectangles:
- By moving points along a rectangle’s sides, you can observe changes in distances between points and the lengths of diagonals.
- Diagonal Properties: Diagonals of a rectangle divide angles and can be used to explore symmetry.
Rotating Shapes:
- Rotating squares or rectangles doesn’t change their properties. The angles remain 90°, and sides remain equal.
Diagonals of Squares and Rectangles:
- Diagonals divide the angles of squares and rectangles into equal parts.
- You can predict the angle division and confirm with actual measurements.
Advanced Constructions:
- Constructing a square inside a rectangle, dividing a rectangle into smaller squares, or adding curves inside shapes requires precise use of the compass and ruler.
Constructing with Constraints:
- When given side lengths and diagonal measurements, construct rectangles using methods like drawing perpendiculars or arcs with a compass.
- A problem involving a rectangle with one diagonal given as 7 cm and one side as 5 cm can be solved by constructing a circle with the diagonal’s length.
Special Figures:
- You can draw shapes like houses, waves, or symmetric eyes by carefully placing compass points and adjusting radii.
- Estimation and trial are key to achieving symmetry.
Key Concepts:
- Radius: The distance from the center to any point on the circle.
- Square: A shape with four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangle: A shape with opposite sides equal and all right angles.
- Diagonal: A line joining two opposite corners of a rectangle or square.
- Compass: Used to draw arcs and circles, and transfer distances.
- Perpendicular: A line at a 90° angle to another line.
Leave a Reply