Notes For All Chapters – Maths Class 6 Ganita Prakash
What is Mathematics?
- Definition: Mathematics is the search for patterns and the explanations for why those patterns exist.
- Patterns in Daily Life: We see patterns in nature, homes, schools, and even in the motion of celestial bodies like the sun, moon, and stars.
- Importance: Understanding patterns has led to scientific advancements like launching satellites and curing diseases.
- Mathematics as Art and Science: It combines creativity and logic, and finding patterns helps in applications beyond their original context.
Patterns in Numbers
- Number Sequences: A basic concept in mathematics, focusing on whole numbers.
- Key Number Sequences:
- Counting numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,…
- Odd numbers: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13,…
- Even numbers: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14,…
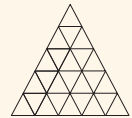
- Triangular numbers: 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28,…
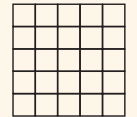
- Square numbers: 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49,…
- Cube numbers: 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216,…
- Virahānka numbers: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21,…
- Powers of 2: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64,…
- Powers of 3: 1, 3, 9, 27, 81, 243, 729,…
Visualising Number Sequences
- Pictorial Representation: Visuals help understand the sequences better.
- Examples:
- Square numbers are represented by square grids.
- Triangular numbers are visualized by arranging dots in triangular shapes.
- Cubes, odd, even, and counting numbers can also be depicted using diagrams.
Relations Among Number Sequences
- Example of Adding Odd Numbers:
- Adding odd numbers gives square numbers:
- 1=1
- 1+3=4
- 1+3+5=9
- This pattern continues forever, and can be explained with pictures.
- Adding odd numbers gives square numbers:
- Adding Counting Numbers Up and Down:
- Adding sequences like 1+2+3+2+1=9 gives square numbers.
Patterns in Shapes
- Shape Sequences: Shapes, like numbers, follow patterns. Examples include:
- Stacked Triangles
- Stacked Squares
- Regular Polygons (like triangles, squares, pentagons, etc.)
- Koch Snowflake: A fractal pattern made by replacing straight lines with zig-zag patterns.
Relations to Number Sequences
- Example: The number of sides in regular polygons follows the counting numbers: 3 (triangle), 4 (square), 5 (pentagon), and so on.
- Stacked Squares and Triangles: The number of little shapes inside larger shapes can be counted to form number sequences.

Ya
Super explanation