Questions Ans For All Chapters – Science Curiosity Class 6
Diversity in the Living World
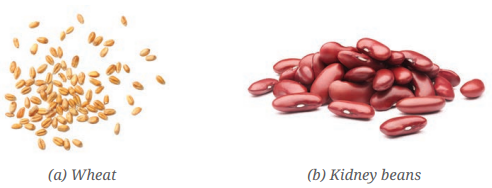
Question 1. Here are two types of seeds. What differences do you find among the roots and leaf venation of their plants?
Answer: Differences between wheat and kidney beans:
| Features | Wheat (Monocot) | Kidney Beans (Dicots) |
|---|---|---|
| (i) Root system | Fibrous root system | Taproot system |
| (ii) Root characteristics | Dense network of thin roots | Central thick taproot with lateral branches |
| (iii) Leaf venation | Parallel venation | Reticulate venation |
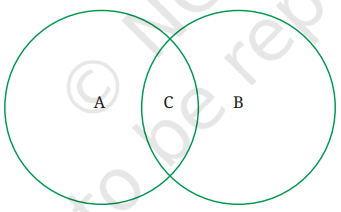
Question 2. Names of some animals are given below. Group them based on their habitats. Write the names of aquatic animals in the area marked ‘A’ and terrestrial animals in the area marked ‘B’. Enter the names of animals living in both habitats in part ‘C’.
Horse, Dolphin, Frog, Sheep, Crocodile, Squirrel, Whale, Earthworm, Pigeon, Tortoise
Answer:
i) A (Aquatic animals): Dolphin, Crocodile, Whale, Tortoise.
ii) B (Terrestrial animals): Horse, Sheep, Squirrel, Earthworm, Pigeon.
iii)C (Both aquatic and terrestrial animals): Frog, Crocodile, Tortoise.
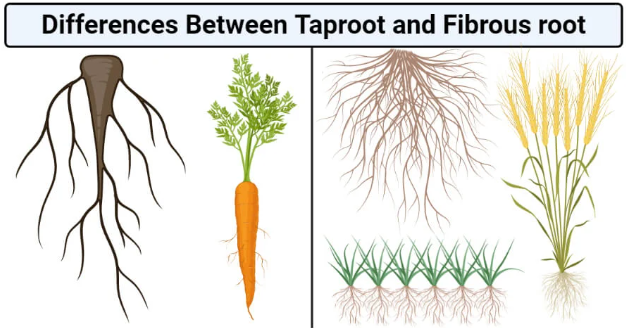
Question 3. Manu’s mother maintains a kitchen garden. One day, she was digging out radish from the soil. She told Manu that radish is a kind of root. Examine a radish and write what type of root it is. What type of venation would you observe in the leaves of radish plant?
Answer:
The radish has a taproot.
The leaves of the radish plant have reticulate venation.
Question 4. Look at the image of a mountain goat and a goat found in the plains. Point out the similarities and differences between them. What are the reasons for these differences?
Answer: Similarities:
- Both are goats and belong to the same family.
- Herbivore diet: Both are herbivores. That is they eat plants including roots, stems, leaves etc.
Differences:
| Mountain Goat | Plains Goat |
|---|---|
| 1. Has thick, long fur to protect against cold mountain temperatures. | 1. Has shorter fur suited for warmer climates. |
| 2. Generally stockier and more muscular, adapted for climbing rocky terrains. | 2. Leaner build suitable for flat, open areas. |
| 3. Specialised hooves with a rough texture for better grip on rocky surfaces. | 3. Hooves more suited for walking on flat, grassy lands. |
Question 5. Group the following animals into two groups based on any feature other than those discussed in the chapter— cow, cockroach, pigeon, bat, tortoise, whale, fish, grasshopper, lizard.
Answer: Group based on flying ability:
- Flying animals: Pigeon, Bat.
- Non-flying animals: Cow, Cockroach, Tortoise, Whale, Fish, Grasshopper, Lizard.
Question 6. As the population grows and people want more comfortable lives, forests are being cut down to meet various needs. How can this affect our surroundings? How do you think we can address this challenge?
Answer:
i) Impact on surroundings:
- Deforestation leads to loss of habitat for many species, reducing biodiversity.
- It contributes to soil erosion, loss of fertile land, and disruption of the water cycle.
- Global warming increases as trees, which absorb carbon dioxide, are cut down.
ii) Addressing the challenge:
- Promoting reforestation and afforestation.
- Sustainable use of resources and limiting urban expansion.
- Raising awareness about the importance of forests for climate regulation and biodiversity.
- Implementing strict laws to protect forests and wildlife.
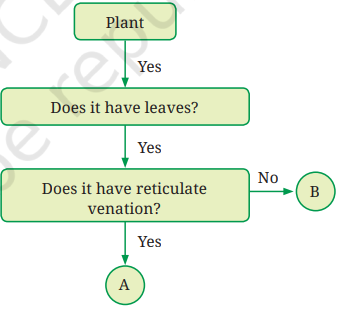
Question 7. Analyse the flowchart. What can be examples of ‘A’ and ‘B’?
Answer:
- Examples of ‘A’: These are plants that have reticulate venation in their leaves. Examples: Mango, Hibiscus, Rose, Chickpea (Chana), Mustard.
- Examples of ‘B’: These are plants that do not have reticulate venation (i.e., they have parallel venation). Examples: Wheat, Maize, Grass.
Question 8. Raj argues with his friend Sanjay that “Gudhal (hibiscus) plant is a shrub”. What questions can Sanjay ask for clarification?
Answer: Sanjay can ask the following questions to clarify:
- What is the height of the Gudhal (hibiscus) plant? Is it medium-sized or tall?
- Does the plant have woody stems branching near the ground, like shrubs?
- Are the stems hard, and do they have multiple branches?
- How is the stem thickness? Does it resemble the features of a shrub?
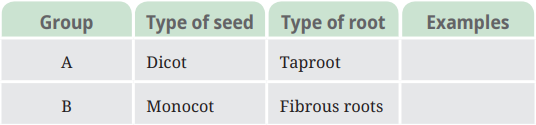
Question 9. Based on the information in the table, find out examples of these plants for each group.
(a) What other similarity do plants of group A have?
(b) What other similarity do plants of group B have?
Answer:
| Group | Type of seed | Type of root | Examples |
| A | Dicot | Taproot | Pea, Rose, Mango |
| B | Monocot | Fibrous roots | Wheat, Maize, Rice |
Answer: (a) Plants in group A (Dicots) generally have reticulate venation in their leaves. This means the veins form a branching pattern.
Answer: (b) Plants in group B (Monocots) typically have parallel venation in their leaves, where the veins run parallel along the length of the leaf.
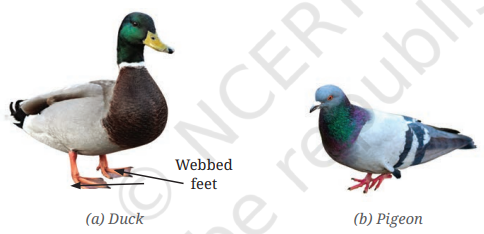
Question 10. Observe the labelled part of a duck in the picture given below. What differences do you observe in the feet of the duck compared to the other birds? Which activity would the duck be able to perform using this part?
Answer:
- Duck: Ducks have webbed feet, which are specially adapted for swimming. The webbing helps them push against water efficiently, making them excellent swimmers.
- Pigeon: Pigeons have normal feet without webbing, which are more adapted for perching and walking. Their feet are suited for gripping branches and walking on solid surfaces.
Activity that the duck can perform using its webbed feet:
Ducks can swim efficiently in water due to their webbed feet, which act as paddles. This helps them to move quickly in aquatic environments.


It’s a very useful website for students. I like it very much.✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
It’s very useful and great
😉😉😉😉 it is V.V.very good