1. MEASUREMENT OF ANGLES
Page 4.12 Ex – 4.1
Q1.
Answer :
We have:π rad =180°∴1 rad=180π°
i 18π5=180π×9π5° =36×9° =324°
ii-5π6=180π×-5π6° =-30×5° =-150°
iii 18π5c=180π×18π5° =36×18° =648°
iv -3c=180π×-3° =18022×7×-3° =-378022° =-1711822° =-171°1822×60′ =-171°49111′ =-171°49’111×60” =-171°49’5.45” ≈-171°49’5”
(v) 11c=180π×11° =18022×7×11° =630°
vi 1c=180π×1° =18022×7×1° =63011° =57311° =57°311×60′ =57°16411′ =57°16’411×60”
=57°16’21.81”≈57°16’22”
Q2.
Answer :
We have:180°=π rad∴1°=π180 rad
i 300°=300×π180=5π3 rad
ii 35°=35×π180=7π36 rad
iii -56°=-56×π180=-14π45 rad
iv 135°=135×π180=3π4 rad
v -300°=-300×π180=-5π3 rad
vi 30’=12°∴7°30’=712°=152°=152×π180=π24 rad
vii 30’=12°∴125°30’=12512°=2512°=2512×π180=251π360 rad
viii 30’=12°∴47°30’=-4712°=-952°=-952×π180=-19π72 rad
Q3.
Answer :
Given:
Difference between two acute angles of a right-angled triangle = 2π5 rad
∵1 rad=180π°
∴2π5 rad=180π×2π5° =36×2° =72°
Now, let one acute angle of the triangle be x°.
Therefore, the other acute angle will be 90°-x°.
Now,
x°-90°-x°=72°⇒x-90+x=72⇒2x=162⇒x=81
Page 4.14 Ex – 4.1
Q4.
Answer :
One angle of the triangle = 23x grad
=23x×910° ∵1 grad=910°=35x°
Another angle = 32x°
∵1 radian=180π°
Third angle of the triangle =xπ75 rad =180π×xπ75° =125x°
Now,
35x+32x+125x=180 (Angle sum property)⇒6x+15x+24×10=180⇒45×10=180⇒x=40
Q5.
Answer :
(i)Sum of the interior angles of the polygon =n-2πNumber of sides in the pentagon=5∴ Sum of the interior angles of the pentagon =5-2π=3πEach angle of the pentagon =Sum of the interior angles of the polygonNumber of sides=3π5radEach angle of the pentagon=3π5×180π°=108°
(ii)Sum of the interior angles of the polygon=n-2πNumber of sides in the octagon=8 ∴ Sum of the interior angles of the octagon =8-2π=6πEach angle of the octagon =Sum of the interior angles of the polygonNumber of sides=6π8 =3π4 radEach angle of octagon=3π4×180π°=135°
(iii)Sum of the interior angles of the polygon=n-2πNumber of sides in the heptagon=7 ∴ Sum of the interior angles of the heptagon =7-2π=5πEach angle of the heptagon =Sum of the interior angles of the polygonNumber of sides=5π7 radEach angle of the heptagon=5π7×180π°=9007°=128°34’17”
(iv)Sum of the interior angles of the polygon =n-2πNumber of sides in the duodecagon=12 ∴ Sum of the interior angles of the duodecagon =12-2π=10πEach angle of the duodecagon =Sum of the interior angles of the polygonNumber of sides=10π12 =5π6 radEach angle of duodecagon=5π6×180π°=150°
Q6.
Answer :
Let the angles of the quadrilateral be a-3d°, a-d°, a+d° and a+3d°.
We know:
a-3d+a-d+a+d+a-2d=360⇒4a=360⇒a=90
We have:
Greatest angle = 120°
Now,
a+3d=120⇒90+3d=120⇒3d=30⇒d=10
Hence, a-3d°, a-d°, a+d° and a+3d° are 60°, 80°, 100° and 120°, respectively.
Angles of the quadrilateral in radians = 60×π180, 80×π180 , 100×π180 and 120×π180
=π3, 4π9, 5π9 and 2π3
Q7.
Answer :
Let the angles of the triangle be a-d°, a° and a+d°.
We know:
a-d+a+a+d=180⇒3a=180⇒a=60
Given:Number of degrees in the least angleNumber of degrees in the mean angle=1120or, a-da=1120or, 60-d60=1120or, 60-d1=12or,120-2d=1or, 2d=119or, d= 59.5
Hence, the angles are a-d°, a° and a+d°, i.e., 0.5°, 60° and 119.5°.
∴ Angles of the triangle in radians = 0.5×π180, 60×π180 and 119.5×π180
= π360, π3 and 239π360
Q8.
Answer :
Let the number of sides in the first polygon be 2x and the number of sides in the second polygon is x.
We know:
Angle of an n-sided regular polygon = n-2nπ radian
∴ Angle of the first polygon = 2x-22xπ=x-1xπ radian
Angle of the second polygon = x-2xπ radian
Thus, we have:
x-1xπx-2xπ=32⇒x-1x-2=32⇒2x-2=3x-6⇒x=4
Thus,
Number of sides in the first polygon = 2x = 8
Number of sides in the first polygon = x = 4
Q9.
Answer :
Let the angles of the triangle be a-d°, a° and a+d°.
We know:
a-d+a+a+d=180⇒3a=180⇒a=60
Given:
Greatest angle=5×Least angleor, Greatest angleLeast angle=5or, a+da-d=5or, 60+d60-d=5or, 60+d=300-5dor, 6d=240or, d= 40
Hence, the angles are a-d°, a° and a+d°, i.e., 20°, 60° and 100°, respectively.
∴ Angles of the triangle in radians = 20×π180, 60×π180 and 100×π180
=π9, π3 and 5π9
Q10.
Answer :
Let the number of sides in the first polygon be 5x and the number of sides in the second polygon be 4x.
We know:
Angle of an n-sided regular polygon = n-2n180°
Thus, we have:
Angle of the first polygon = 5x-25×180°
Angle of the second polygon = 4x-24×180°
Now,
5x-25×180-4x-24×180=9⇒1804(5x-2)-5(4x-2)20x=9⇒20x-8-20x+1020x=9180⇒220x=120⇒2x=1⇒x=2
Thus, we have:
Number of sides in the first polygon = 5x = 10
Number of sides in the second polygon = 4x = 8
Q11.
Answer :
Length of the arc = 40 m
θ=25°=25×π180 =5π36 radian
We know:
θ=ArcRadius⇒5π36=40Radius⇒Radius=405π36=40×36×75×22=91.64 m
So, the radius of the track should be 91.64 m.
Q12.
Answer :
We have:
Radius = 5280 m
Now,
θ=1’=160°=160×π180 radian
We know:
θ=ArcRadius⇒160×π180=Arc5280⇒Arc=5280×2260×180×7=1.5365 m
Q13.
Answer :
Number of revolutions taken by the wheel in 1 minute = 360Number of revolutions taken by the wheel in 1 second=36060=6We know:1 revolution = 2π radians∴ Number of radians the wheel will turn in 1 second=6×2π=12π
Q14.
Answer :
We know:
Radius = 75 cm
(i)
Length of the arc = 10 cm
Now,
θ=ArcRadius=1075=215 radian
(ii)
Length of the arc = 15 cm
Now,
θ=ArcRadius=1575=15 radian
(iii)
Length of the arc = 21 cm
Now,
θ=ArcRadius=2175=725 radian
Q15.
Answer :
Let AB be the chord and O be the centre of the circle.
Here,
AO = BO = AB = 30 cm
Therefore, ∆AOB is an equilateral triangle.
Now,
Radius = 30 cm
θ=60°=60×π180 =π3 radian
θ=ArcRadius⇒π3=Arc30⇒Arc=30π3=10π cm
Q16.
Answer :
Time = 10 seconds
Speed = 66 km/h =66×10003600m/s
We know:Speed = Distance Time⇒66×10003600=DistanceTime⇒Distance =66×10003600×10=11006 m
Now,
Radius of the curve = 1500 m
∴ θ=ArcRadius =110061500 =11001500×6=1190 radian
So, the train will turn 1190 radian in 10 seconds.
Q17.
Answer :
Let PQ be the diameter of the coin and E be the eye of the observer.
Also, let the coin be kept at a distance r from the eye of the observer to hide the moon completely.
Now,
θ=31’=3160°=3160×π180 radians
θ=ArcRadius⇒3160×π180=2Radius⇒Radius=180×60×2×731×22 =221.7 cm or 2.217 m
Q18.
Answer :
Let PQ be the diameter of the Sun and E be the eye of the observer.
Because the distance between the Sun and the Earth is quite large, we will take PQ as arc PQ.
Now,
r = 91×106 km
θ=32’=3260°=3260×π180 radians
θ=ArcRadius⇒3260×π180=d91×106⇒d=32×91×106×2260×180×7=847407.4 km
Q19.
Answer :
Let the angles subtended at the centres by the arcs and radii of the first and second circles be θ1 and r1 and θ2 and r2, respectively.
Thus, we have:
θ1=65°=65×π180 radian
θ2=65°=110×π180 radian
θ1=lr1
⇒r1=l65×π180
θ2=lr2
⇒r2=l110×π180
⇒r1r2=l65×π180l110×π180=11065=2213
Q20.
Answer :
Length of the arc = 22 cm
Radius = 100 cm
Now,
θ=ArcRadius=22100=1150 radian
∴ Angle subtended at the centre by the arc = 1150×180π°=115×1822×7°=635°=12°36′
Page 4.14 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q1.
Answer :
(c) D90=G100=2Rπ
It is the relation between degree, grade and radian.
Q2.
Answer :
(b) π3
Let the angles of the triangle be a-d°,a° and a+d°.
Thus, we have:
a-d+a+a+d=180⇒3a=180⇒a=60
Hence, the angles are a-d°,a° and a+d°, i.e., 60-d°,60° and 60+d°.
60° is the only angle which is independent of d.
∴ One of the angles of the triangle (in radians) = 60×π180 = π3
Q3.
Answer :
(b) 75°
We know that the hour hand of a clock completes one rotation in 12 hours.
∴ Angle traced by the hour hand in 12 hours = 360°
Now,Angle traced by the hour hand in 8 hours 30 minutes, i.e., 172 = 36012×172°=255°
We also know that the minute hand of a clock completes one rotation in 60 minutes.
∴ Angle traced by the minute hand in 60 minutes = 360°
Now, Angle traced by the minute hand in 30 minutes = 36060×30°=180°
∴ Required angle between the two hands of the clock = 255°-180°=75°
Q4.
Answer :
(c) 13π18c
We know that the hour hand of a clock completes one rotation in 12 hours.
∴ Angle traced by the hour hand in 12 hours = 360°
Now,
Angle traced by the hour hand in 3 hours 40 minutes, i.e., 113 = 36012×113°=110°
We also know that the minute hand of a clock completes one rotation in 60 minutes.
∴ Angle traced by the minute hand in 60 minutes = 360°
Now,
Angle traced by the minute hand in 40 minutes = 36060×40°=240°
∴ Required angle between two hands = 240°-110°=130°
And,
Value of the angle (in radians) between the two hands of the clock = 130×π180c=13π18c=13πc18
Page 4.15 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q5.
Answer :
(a) 22:13
Let the angles subtended at the centres by the arcs and radii of the first and second circles be θ1 and r1 and θ2 and r2, respectively.
We have:
θ1=65°=65×π180 radian
θ2=65°=110×π180 radian
θ1=lr1
⇒r1=l65×π180
θ2=lr2
⇒r2=l110×π180
⇒r1r2=l65×π180l110×π180=11065=2213
⇒r1:r2=22:13
Q6.
Answer :
(d) 8π
Angular velocity =DistanceTime=4 revolutions1 second=4×2π1 ∵ 1 revolution = 2π radians=8π radians per second
Q7.
Answer :
(b) 210°
Length of the arc of radius = Circumference of the circle of radius 7 cm = 2πr=14π
Now,
Angle subtended by the arc = ArcRadius=14π12=14π12×180π°=210°
Q8.
Answer :
(b) 20 cm
θ=ArcRadius⇒3π4=15πRadius⇒Radius=603=20 cm
2. TRIGONOMECTRIC FUNCTIONS
Page 5.13 Ex – 5.1
Q1.
Answer :
LHS = sec4 θ-sec2 θ =sec2 θsec2 θ-1 =tan2 θ+1tan2 θ ∵ sec2 θ-tan2 θ = 1 =tan4 θ+tan2 θ =RHSHence proved.
Q2.
Answer :
LHS = sin6θ+cos6θ =sin2θ3+cos2θ3 =sin2θ+cos2θsin2θ2+cos2θ2-sin2θ cos2θ ∵ a3 + b3 = a+ba2+b2-ab =1×sin2θ+cos2θ2-2sin2θ cos2θ-sin2θ cos2θ ∵ sin2θ+cos2θ = 1 and a2 + b2 = a+b2-2ab =12 – 3 sin2θ cos2θ =1-3 sin2θ cos2θ =RHSHence proved.
Q3.
Answer :
LHS = cosec θ-sin θ sec θ-cos θ tan θ+cot θ = 1sin θ-sin θ 1cos θ-cos θsin θcos θ+cos θsin θ =1-sin2θsin θ1-cos2θcos θsin2 θ+cos2θcos θ sin θ =cos2θsin θsin2 θcos θ1cos θ sin θ =1 =RHSHence proved.
Q4.
Answer :
LHS = cosec θ sec θ-1-cot θ 1-cos θ =1sin θ 1cos θ-1-cos θsin θ 1-cos θ =1sin θ 1-cos θcos θ-cos θsin θ 1-cos θ = 1-cos θsin θ1cos θ-cos θ = 1-cos θsin θ1-cos2 θcos θ =1-cos θsin θsin2 θcos θ =1-cos θsin θcos θ =sin θcos θ-sin θ =tan θ-sin θ = RHSHence proved.
Q5.
Answer :
LHS=1-sin A cos Acos A sec A-cosec A×sin2 A-cos2 Asin3 A+cos3 A =1-sin A cos Acos A 1cos A-1sin A×sin A2-cos A2sin A3+cos A3 =1-sin A cos Acos A sin A-cos Acos A sin A×sin A+cos Asin A-cos Asin A+cos Asin A2+cos A2-sin A cos A = sin A1-sin A cos A sin A-cos A×sin A+cos Asin A-cos Asin A+cos Asin A2+cos A2-sin A cos A = sin A1-sin A cos A 1×1×1sin2 A+cos2 A-sin A cos A =sin A1-sin A cos A×11-sinA cos A =sin A =RHSHence proved.
Q6.
Answer :
LHS = tan A1-cot A+cot A1-tan A =sin AcosA1-cos Asin A+cos Asin A1-sin AcosA =sin AcosAsin A-cos Asin A+cos Asin AcosA-sin AcosA =sin AcosA×sin Asin A-cos A+cos Asin A×cosAcosA-sin A =sin AcosA×sin Asin A-cos A+cos Asin A×cosA-sin A-cos A =sin2 AcosAsin A-cos A-cos2Asin Asin A-cos A =sin3 A-cos3Asin A cosAsin A-cos A =sin A-cos Asin2 A+cos2 A+sin Acos Asin A cosAsin A-cos A =1×1+sin Acos Asin A cosA =1+sin Acos Asin A cosA =1sin A cosA+sin Acos Asin A cosA =1sin A ×1cosA+1 =cosec A ×sec A+1 =sec A cosec A+1 =RHSHence proved.
Q7.
Answer :
LHS=sin3 A+cos3 Asin A+cos A+sin3 A-cos3 Asin A-cos A =sin A+cos Asin2 A+cos2 A – sin Acos Asin A+cos A+sin A-cos Asin2 A+cos2 A + sin Acos Asin A-cos A =sin2 A+cos2 A – sin Acos A + sin2 A+cos2 A + sin Acos A =1 – sin Acos A +1 + sin Acos A =2 = RHSHence proved.
Q8.
Answer :
LHS = sec A sec B+tan A tan B2-sec A tan B+tan A sec B2 =sec A sec B2+tan A tan B2-2sec A sec Btan A tan B – sec A tan B2+tan A sec B2-2sec A tan Btan A sec B =sec2 A sec2 B+tan2 A tan2 B-2sec A sec Btan A tan B – sec2 A tan2 B+tan2 A sec2 B-2secA secB tanA tanB =sec2 A sec2 B+tan2 A tan2 B-2sec A sec Btan A tan B – sec2 A tan2 B-tan2 A sec2 B+2secA secB tanA tanB =sec2 A sec2 B- sec2 A tan2 B+tan2 A tan2 B-tan2 A sec2 B =sec2 A sec2 B- tan2 B+tan2 A tan2 B- sec2 B =sec2 A sec2 B- tan2 B-tan2 A sec2 B- tan2 B =sec2 A×1-tan2 A×1 =sec2 A-tan2 A =1 =RHSHence proved.
Q9.
Answer :
RHS=1+cos θ+sin θ1+cos θ-sin θ =1+cos θ+sin θ1+cos θ-sin θ =1+cos θ+sin θ1+cos θ+sin θ1+cos θ-sin θ1+cos θ+sin θ =1+cos θ+sin θ21+cos θ2-sin θ2 =1+cos θ2+sin θ2+21+cos θsin θ12+cos2 θ+2×1×cos θ-sin2 θ =1+cos2 θ+2cos θ+sin2 θ+2sin θ cos θ+2sin θ1+cos2 θ+2cos θ-sin2 θ =1+sin2 θ+cos2 θ+2cos θ+2sin θ cos θ+2sin θ1-sin2 θ+cos2 θ+2cos θ =1+1+2cos θ+2sin θ cos θ+2sin θcos2 θ+cos2 θ+2cos θ =2+2cos θ+2sin θ cos θ+2sin θ2cos2 θ+2cos θ =1+cos θ+sin θ cos θ+sin θcos2 θ+cos θ =11+cos θ+sin θ cos θ+1cos θcos θ+1 =cos θ+11+sin θcos θcos θ+1 =1+sin θcos θ =1+sin θ×cos θcos θ×cos θ =1+sin θ×cos θcos2 θ =1+sin θ×cos θ1-sin2 θ =1+sin θ×cos θ1+sin θ1-sin θ =cos θ1-sin θ =LHSHence proved.
Q10.
Answer :
LHS = 1-sin θ1+sin θ+1+sin θ1-sin θ = 1-sin θ1-sin θ1+sin θ1-sin θ+1+sin θ1+sin θ1-sin θ1+sin θ = 1-sin θ1-sin θ1+sin θ1-sin θ+1+sin θ1+sin θ1-sin θ1+sin θ = 1-sin θ21-sin2 θ+1+sin θ21-sin2 θ =1-sin θ2cos2 θ+1+sin θ2cos2 θ =1-sin θcos θ+1+sin θcos θ =1-sin θ+1+sin θcos θ =2cos θ =-2cos θ ∵ π2<θ<π and in the second quadrant, cosθ is negative =RHSHence proved.
Q11.
Answer :
LHS = tan3 θ1+tan2 θ+cot3 θ1+cot2 θ =tan3 θsec2 θ+cot3 θcosec2 θ =sin3 θcos3 θ1cos2 θ+cos3 θsin3 θ1sin2 θ =sin3 θcos3 θ×cos2 θ1+cos3 θsin3 θ×sin2 θ1 =sin3 θcos θ+cos3 θsin θ =sin4 θ+cos4 θsin θ cos θ =sin2 θ2+cos2 θ2sin θ cos θ =sin2 θ+cos2 θ2-2sin2 θ cos2 θsin θ cos θ =12-2sin2 θ cos2 θsin θ cos θ =1-2sin2 θ cos2 θsin θ cos θ =RHSHence proved.
Q12.
Answer :
1-sin2 θ1+cot θ-cos2 θ1+tan θ=sin θ cos θ
LHS= 1-sin3θsinθ+cosθ-cos3θsinθ+cosθ=sinθ+cosθ-sin3θ+cos3θsinθ+cosθ=sinθ+cosθ1-sin2θ-cos2θ+sinθcosθsinθ+cosθ=1-sin2θ-cos2θ+sinθcosθ=1-1+sinθcosθ=sinθcosθ
= RHS
Hence proved.
Q13.
Answer :
1sec2 θ-cos2 θ+1cosec2 θ-sin2 θ sin2 θ cos2 θ=1-sin2 θ cos2 θ2+sin2 θ cos2 θ
LHS =1sec2θ-cos2θ+1cosec2θ-sin2θsin2θcos2θ=11cos2θ-cos2θ+11sin2θ-sin2θsin2θcos2θ=cos2θ1-cos4θ+sin2θ1-sin4θsin2θcos2θ=cos2θ1-sin4θ+sin2θ1-cos4θ1-cos4θ1-sin4θsin2θcos2θ=1-cos2θsin4θ-cos4θsin2θ1+sin2θ1-sin2θ1+cos2θ1-cos2θsin2θcos2θ=1-cos2θsin4θ-cos4θsin2θ1+sin2θ.cos2θ.1+cos2θ.sin2θsin2θcos2θ=1-cos2θsin4θ-cos4θsin2θ1+sin2θ1+cos2θ =1-cos2θsin2θsin2θ+cos2θ2+sin2θ.cos2θ=1-cos2θsin2θ2+sin2θ.cos2θ
= RHS
Hence proved.
Q14.
Answer :
1+tan α tan β2+tan α-tan β2=sec2 α sec2 β
LHS = 1+tanα tanβ2+tanα-tanβ2 =1+tan2α tan2β+2tanα tanβ+tan2α+tan2β-2tanα tanβ =1+tan2α tan2β+tan2α+tan2β =tan2αtan2β+1+11+tan2β =1+tan2β1+tan2α =sec2α.sec2β = RHS
Hence proved.
Q15.
Answer :
1+cot θ+tan θ sin θ-cos θsec3 θ-cosec3 θ=sin2 θ cos2 θ
LHS=1+cotθ+tanθsinθ-cosθsec3θ-cosec3θ =1+cosθsinθ+sinθcosθsinθ-cosθ1cos3θ-1sin3θ =sinθcosθ+cos2θ+sin2θsinθ-cosθsin2θcos2θsin3θ-cos3θ =1+sinθcosθsinθ-cosθsin2θcos2θsinθ-cosθsin2θ+cos2θ+sinθcosθ =sin2θcos2θ =RHSHence proved.
Q16.
Answer :
LHS = 2sinθcosθ-cosθ1-sinθ+sin2θ-cos2θ =cosθ(2sinθ-1)2sin2θ-sinθ ∵1-cos2θ=sin2θ =cosθ(2sinθ-1)sinθ2sinθ-1 =cotθ =RHSHence proved.
Q17.
Answer :
LHS = cosθtanθ+22tanθ+1 =cosθ2tan2θ+5tanθ+2 =cosθ2sin2θcos2θ+5sinθcosθ+2 =2sin2θ+5sinθcosθ+2cos2θcosθ =2+5sinθcosθcosθ =2secθ+5sinθ = RHSHence proved.
Q18.
Answer :
LHS:asinθ-bcosθasinθ+bcosθDividing by bcosθ:= atanθb-1atanθb+1Substituting the value of tanθ= a2-b2a2+b2= RHS
Hence proved.
Q19.
Answer :
cosec θ-sin θ=a3∴1sin θ-sin =a3⇒1-sin2θsin θ=a3⇒cos2θsin θ=a3 ⇒a=cos2θsin θ13 ….(i)Also, sec θ-cos θ=b3⇒1cos θ-cos =b3⇒1-cos2θcos θ=b3⇒sin2θcos θ=b3 ⇒b= sin2θcos θ13 …..(ii)Now, LHS=a2b2a2+b2=ab2a2+b2=cos2θsin θ13sin2θcos θ132 cos2θsin θ132+sin2θcos θ132=sin θ cos θ23 cos2θ23sin θ23+sin2θ23cos θ23=sin θ cos θ23cos3θ23+sin3θ23sin θ23cos θ23=sin θ cos θ23cos2θ+sin2θsin θ cos θ23=1=RHS
Q20.
Answer :
Given:4m=cotθ1+sinθ and 4n=cotθ1-sinθMultiplying both the equations:⇒16mn=cot2θ1-sin2θ⇒16mn=cot2θ.cos2θ⇒mn=cos4θ16sin2θ 1Squaring the given equation:16m2=cot2θ1+sinθ2 and 16n2=cot2θ1-sinθ2⇒16m2-16n2=cot2θ4sinθ⇒m2-n2=cot2θ.sinθ4Squaring both sides,m2-n22=cot4θ.sin2θ16⇒m2-n22=cos4θ16sin2θ (2)From (1) and (2):m2-n22= mnHence proved.
Q21.
Answer :
(i) LHS:
T3-T5T1=sin3θ+cos3θ-sin5θ+cos5θsinθ+cosθ= sin3θ-sin5θ+cos3θ-cos5θsinθ+cosθ=sin3θ1-sin2θ+cos3θ1-cos2θsinθ+cosθ=sin3θ.cos2θ+cos3θ.sin2θsinθ+cosθ=sin2θ.cos2θsinθ+cosθsinθ+cosθ=sin2θ.cos2θ
RHS:
T5-T7T3=sin5θ+cos5θ-sin7θ+cos7θsin3θ+cos3θ=sin5θ-sin7θ+cos5θ-cos7θsin3θ+cos3θ=sin5θ1-sin2θ+cos5θ1-cos2θsin3θ+cos3θ=sin5θcos2θ+cos5θsin2θsin3θ+cos3θ=sin2θ.cos2θ
LHS = RHS
Hence proved.
(ii) LHS:
2T6-3T4+12sin6θ+cos6θ-3sin4θ+cos4θ+12sin2θ+cos2θsin4θ+cos4θ-sin2θcos2θ-3sin4θ+cos4θ+12.1.sin4θ+cos4θ-sin2θcos2θ-3sin4θ+cos4θ+12sin4θ+2cos4θ-2sin2θcos2θ-3sin4θ-3cos4θ+1-sin4θ+cos4θ-sin2θcos2θ+1-(sin2θ+cos2θ)2+1-1+10
Hence proved.
(iii) LHS:
6T10-15T8+10T6-16sin10θ+cos10θ-15sin8θ+cos8θ+10sin6θ+cos6θ-1
Page 5.14 Ex – 5.1
Q22.
Answer :
sin θ+ cos θ =m (Given)To prove: sin6 θ +cos6 θ =4-3 (m2-1)24 , where m2≤2Proof:LHS: sin6 θ +cos6 θ =sin2 θ3+cos2 θ3=sin2 θ+cos2 θ 3-3sin2 θcos2 θsin2 θ+cos2 θ=1-3sin2 θcos2 θ RHS: 4-3 (m2-1)24 =4-3sin θ+ cos θ 2-124=4-3sin2θ+ cos2 θ+2sinθ cosθ-124=4-3sin2θ-1-cos2 θ+2 sinθ cosθ24=4-3×4 sin2θ cos2 θ4=1-3sin2 θcos2 θ LHS=RHSHence proved
Q23.
Answer :
tan2θ=1-e2⇒sec2θ-1=1-e2⇒sec2θ=2-e2⇒cos2θ=12-e2 (1)LHS:secθ+tan3θ.cosecθ=1cosθ+sin2θcos3θ=cos2θ+sin2θcos3θ=1cos3θ=cosθ-3=12-e2-32 (From(1))=2-e232
Hence proved.
Q24.
Answer :
sinθ=a2-b2a2+b2We know:sin2θ+cos2θ=1cos2θ=1-sin2θ =1-a2-b2a2+b22 =a4+b4+2a2b2-a4+b4-2a2b2a2+b22 =4a2b2a2+b22⇒cosθ = 2aba2+b2
tanθ=sinθcosθ=a2-b2a2+b22aba2+b2=a2-b22absecθ=1cosθ=a2+b22abcosecθ=1sinθ=a2+b2a2-b2
Q25.
Answer :
tanθ=abNow, a+ba-b+a-ba+b=ab+1ab-1+ab-1ab+1=tanθ+1tanθ-1+tanθ-1tanθ+1=tanθ+1+tanθ-1tan2θ-1=2sinθsin2θ-cos2θ
Q26.
Answer :
a=secθ-tanθ And, b=cosecθ+cotθ =1-sinθcosθ And, b=1+cosθsinθNow, we have:ab+a-b+11-sinθcosθ1+cosθsinθ+1-sinθcosθ-1+cosθsinθ+1=1-sinθ+cosθ-sinθcosθ+sinθ-sin2θ-cosθ-cos2θ+sinθcosθsinθcosθ=1-sin2θ-cos2θsinθcosθ=0
Hence proved.
Q27.
Answer :
x = 2sinθ1+sinθ+cosθRationalising the denominator:2sinθ1+sinθ+cosθ×1+sinθ-cosθ1+sinθ-cosθ=2sinθ1+sinθ-cosθ1+sinθ2-cos2θ=2sinθ1+sinθ-cosθ1+sin2θ+2sinθ-cos2θ=2sinθ1+sinθ-cosθ2sin2θ+2sinθ=2sinθ1+sinθ-cosθ2sinθ1+sinθ=1+sinθ-cosθ1+sinθ∴ x=1+sinθ-cosθ1+sinθ
Hence proved.
Page 5.18 Ex – 5.2
Q1.
Answer :
i We have:cotθ = 125 and θ are in the third quadrant. In the third quadrant, tanθ and cotθ are positiveAnd, sinθ, cosθ , secθ and cosecθ are negative.
∴ tanθ = 1cotθ = 1125=512cosecθ = -1 + cot2θ = -1 +1252 = -135sinθ = 1cosecθ = 1- 135 = -513cosθ = -1 – sin2θ = -1 – -5132 = -1213And, secθ = 1cosθ = 1-1213 = -1312
ii We have:cosθ =-12 and θ are in the second quadrant.In the second quadrant, sinθ, and cosecθ are positive.And, tanθ, cotθ , cosθ and secθ are negative.
∴ sinθ = 1 – cos2θ = 1 – -122 = 32tanθ = sinθcosθ = 32-12=-3
cotθ= 1tanθ = 1-3=-13 secθ = 1cosθ = 1-12 = -2cosecθ = 1sinθ = 132 = 23
iii We have:tanθ = 34 and θ are in the third quadrant.In the third quadrant, tanθ, and cotθ are positive.And, sinθ, cosθ , secθ and cosecθ are negative.
∴ cotθ = 1tanθ = 134=43secθ = -1 +tan2θ = -1 +342 = – 54cosθ = 1secθ = 1- 54 = -45sinθ = -1 – cos2θ = -1 – -452 = -35cosecθ = 1sinθ = 1- 35 = -53
iv We have:sinθ =35 and θ are in the first quadrant.In the first quadrant, all six T-ratios are positive.
∴ cosθ = 1 – sin2θ = 1 – 352 = 45tanθ = sinθcosθ = 3545=34cotθ = 1tanθ = 134=43 secθ = 1cosθ = 145 = 54cosecθ = 1sinθ = 135 = 53
Page 5.19 Ex – 5.2
Q2.
Answer :
We have:sinθ = 1213 and θ lie in the second quadrant.In the second quadrant, sinθ and cosecθ are positive and all the other four T-ratios are negative.
∴ cosθ = -1-sin2θ =-1-12132 = -513tanθ = sinθcosθ = 1213-513 =-125And, sec θ = 1cos θ =1-513 = -135∴ secθ + tanθ = -135 + -125 = -5
Q3.
Answer :
We have:
sinθ=35, tanϕ=12 and π2<θ<π<ϕ<3π2,Thus, θ is in the second quadrant and ϕ is in the third quadrant.In the second quadrant, cosθ and tanθ are negative.In the third quadrant, secϕ is negative.
∴ cosθ = -1-sin2 θ = -1-352 = -45tanθ = 35-45 = -34And, secϕ = -1+tan2ϕ = -1+122 = -52∴ 8 tanθ – 5 secϕ = 8×-34 – 5×-52 =-6 + 52=-72
Q4.
Answer :
We have:sinθ + cosθ = 0⇒ sinθ = -cosθ⇒ sinθcosθ = -1⇒ tanθ = -1
Now, θ is in the fourth quadrant.In the fourth quadrant, cosθ and secθ are positive and all the other four T-ratios are negative.
∴ secθ = 1+tan2θ = 1+-12 = 2cosθ = 1secθ = 12And, sinθ = -1-cos2θ = -1-122 = -12∴ sinθ =-12 and cosθ = 12
Q5.
Answer :
We have:cosθ = -35 and π<θ<3π2Thus, θ is in the third quadrant.In the third quadrant, tanθ and cotθ are positiveAnd, all the other four T-ratios are negative.∴ sinθ = -1 – cos2θ = -1 – -352 = -45tanθ = sinθcosθ = -45-35=43cotθ = 1tanθ = 143= 34secθ = 1cosθ=1-35 = -53cosecθ = 1sinθ = 1-45 = -54
Now, cosecθ + cotθsecθ-tanθ = -54+34-53-43 =-24-93 =-12-3 = 16
Page 5.27 Ex – 5.3
Q1.
Answer :
i) We have:5π3 = 53×180° = 300° = 90°×3 + 30°300° lies in the fourth quadrant in which the sine function is negative.Also, 3 is an odd integer.∴ sin5π3 = sin 300° =sin 90°×3 + 30° = -cos30° = -32
ii) We have:3060° = 90°×34 + 0°Clearly 3060° is in the negative direction of the x-axis, i.e. on the boundary line of the II and III quadrants.Also, 34 is an even integer.∴ sin3060° =sin 90°×34 + 0° =-sin 0° =0
iii) We have:11π6 = 116×180° = 330° = 90°×3 + 60°330° lies in the fourth quadrant in which the tangent function is negative.Also, 3 is an odd integer.∴ tan11π6 = tan 330° =tan90°×3 + 60° = -cot 60° = -13
iv) We have:cos -1125° =cos 1125°= cos 90°×12 + 45°1125° lies in the first quadrant in which the cosine function is positive.Also, 12 is an even integer.∴ cos-1125° = cos1125° =cos90°×12 + 45° = cos 45° = 12
v) We have:315° = 90°×3 + 45°315° lies in the fourth quadrant in which the tangent function is negative.Also, 3 is an odd integer.∴ tan 315° = tan 90°×3 + 45° = -cot 45° = -1
vi) We have:510° = 90°×5 + 60°510° lies in the second quadrant in which the sine function is positive.Also, 5 is an odd integer.∴ sin510° = sin 90°×5 + 60° =cos 60° = 12
vii) We have:570° = 90°×6 + 30° 570° lies in the third quadrant in which the cosine function is negative.Also, 6 is an odd integer.∴ cos570° = cos 90°×6 + 30° =-cos 30° = -32
viii) We have:sin -330° =-sin 330°= -sin 90°×3 + 60°330° lies in the fourth quadrant in which the sine function is negative.Also, 3 is an odd integer.∴sin-330° =-sin330° =-sin90°×3 + 60° = –cos60° =– 12 =12
ix) We have:cosec -1200° =-cosec 1200°= -cosec 90°×13 + 30°1200° lies in the second quadrant in which the cosec function is positive.Also, 13 is an odd integer.∴ cosec-1200° = -cosec1200° =-cosec90°×13 + 30° = -sec30° = -23
x) We have:tan -585° =-tan 585°= -tan 90°×6 + 45°585° lies in the third quadrant in which tangent function is positive.Also, 6 is an even integer.∴ tan -585° = -tan 585° =-tan 90°×6 + 45° = -tan 45° = -1
xi) We have:855° = 90°×9 + 45°855° lies in the second quadrant in which the cosine function is negative.Also, 9 is an odd integer.∴ cos855° = cos90°×9 + 45° =-sin45° = -12
xii) We have:1845° = 90°×20 + 45°1845° lies in the first quadrant in which the sine function is positive.Also, 20 is an even integer.∴ sin 1845° = sin 90°×20 + 45° =sin 45° = 12
xiii) We have:1755° = 90°×19 + 45°1755° lies in the fourth quadrant in which the cosine function is positive.Also, 19 is an odd integer.∴ cos1755° = cos90°×19 + 45° =sin 45° = 12
xiv) We have:4530° = 90°×50 + 30°4530° lies in the third quadrant in which the sine function is negative.Also, 50 is an even integer.∴ sin 4530° = sin 90°×50 + 30° =-sin 30° = -12
Page 5.28 Ex – 5.3
Q2.
Answer :
i) LHS = tan225°cot405° + tan765°cot675° =tan 90°×2+45°cot 90°×4+45° + tan 90°×8+45° cot 90°×7+45° =tan 45° cot 45° + tan 45°-tan 45° = 1×1 + 1×-1 = 1-1 = 0 = RHSHence proved.
ii) LHS = sin8π3cos23π6+cos13π3sin35π6 = sin 83×180° cos 236×180°+cos 133×180° sin 356×180° =sin 480° cos 690°+cos 780° sin 1050° =sin 90°×5+30° cos 90°×7+60°+cos 90°×8+60° sin 90°×11+60° =cos 30° sin 60°+cos 60°-cos 60° =32×32+12×-12 =34 – 14 = 24 =12 = RHSHence proved.
iii) LHS = cos 24° + cos 55° + cos 125° + cos 204° + cos 300° = cos 24° + cos 90°-35° + cos 90°×1+35°+ cos 90°×2+24° + cos 90°×3+30° =cos 24° + sin 35° – sin 35°- cos 24° + sin 30° =0 + 0+ 12 = 12 = RHSHence proved.
iv) LHS = tan -225° cot -405° – tan -765° cot 675° =- tan 225°-cot 405° – -tan 765° cot 675° ∵ tan -x = tan x and cot -x = -cot x = tan 225° cot 405° +tan 765° cot 675° =tan 90°×2+45° cot 90°×4+45° + tan 90°×8+45° cot 90°×7+45° =tan 45° cot 45° + tan 45°-tan 45° = 1×1 + 1×-1 = 1-1 = 0 = RHSHence, proved.
v) LHS =cos 570°sin 510° + sin -330°cos -390° =cos 570° sin 510° + -sin 330°cos 390° ∵ sin-x = -sin x and cos-x = cos x =cos 570°sin510° -sin 330° cos 390° =cos 90°×6+30° sin 90°×5+60° -sin 90°×3+60° cos 90°×4+30° =-cos 30° cos 60° –cos 60° cos 30° =-cos 30° cos 60° +cos 30° sin 60° = 0 = RHSHence proved.
vi) LHS = tan11π3-2sin4π6-34cosec2π4+4cos217π6 = tan11π3-2sin4π6-34cosecπ42+4cos17π62 = tan113×180°-2sin46×180°-34cosec180°42+4cos17×180°62 = tan 660°-2sin 120°-34cosec45°2+4cos 510°2 =tan 660°-2sin 120°-34cosec45°2+4cos 510°2 =tan 90°×7+30°-2sin 90°×1+30°-34cosec45°2+4cos90°×5+60°2 =-cot 30°-2cos 30°-34cosec 45°2+4-sin60°2 =-cot 30°-2cos 30°-34cosec45°2+4sin 60°2 =-3-232-3422+4322 =-3-3-32+3 =3-432 = RHSHence proved.
vii) LHS = 3sinπ6secπ3-4sin5π6cotπ4 = 3sin180°6sec180°3-4sin5×180°6cot180°4 =3sin30°sec60°-4sin150°cot45° =3sin30°sec60°-4sin90°×1+60°cot45° =3sin 30°sec 60°-4cos 60° cot 45° =3×12×2 – 4×12×1 =3 – 2 =1 = RHS
Q3.
Answer :
i) LHS = cos2π+θ cosec2π+θ tanπ2+θsec π2+θ cos θ cot π+θ =cos θ cosec θ – cot θ-cosec θcos θ cot θ =-cos θ cosec θ cot θ-cosec θ cos θ cot θ = 1 =RHSHence proved.
ii) LHS =cosec 90°+θ+cot 450°+θcosec 90°-θ+tan 180°-θ + tan 180°+θ+sec 180°-θtan 360°+θ-sec -θ =cosec90°+θ+cot450°+θcosec 90°-θ+tan180°-θ + tan 180°+θ+sec 180°-θtan 360°+θ-sec -θ =cosec90°+θ+cot 90°×5+θcosec90°-θ+tan 90°×2-θ + tan 90°×2+θ+sec 90°×2-θtan90°×4+θ-sec-θ =sec θ+cot 90°×5+θcosec90°-θ+tan 90°×2-θ + tan 90°×2+θ+sec 90°×2-θtan 90°×4+θ-sec -θ =sec θ-tan θsec θ-tan θ + tan θ-sec θtan θ-sec θ =1 + 1 =2 =RHSHence proved.
iii) LHS =sin 180°+θcos90°+θ tan 270°-θcot 360°-θsin 360°-θcos360°+θcosec-θ sin 270°+θ =sin 90×2°+θcos90°×1+θ tan90°×3-θ cot90°×4-θsin90°×4-θcos90°×4+θ cosec -θ sin 90°×3+θ =-sin θ -sin θ cot θ-cot θ-sin θ cos θ -cosec θ-cos θ =sin2θ cot2 θsin θ cosec θ cos θ cos θ =sin2θ ×cos2θsin2θsin θ ×1sin θ×cos2θ =cos2 θcos2 θ =1 =RHSHence proved.
iv) LHS = 1+cot θ-secπ2+θ1+cot θ+secπ2+θ = 1+cot θ–cosec θ 1+cot θ+-cosecθ = 1+cot θ+cosec θ 1+cot θ-cosec θ = 1+cot θ+cosec θ 1+cot θ-cosec θ = 1+cotθ+cosec θ 1+cot θ-cosecθ =1+cot θ2 – cosec θ2
=1+cot2θ+2cot θ-cosec2 θ =2 cot θ ∵1+cot2θ=cosec2θ =RHS Hence proved.
v) LHS =tan 90°-θ sec 180°-θ sin -θsin180°+θcot 360°-θcosec 90°-θ =tan 90°×1-θsec 90°×2-θsin -θsin 90°×2+θcot 90°×4-θcosec 90°×1-θ =cot θ-sec θ-sin θ-sin θ-cot θ sec θ =cot θ sec θ sin θsin θ cot θ sec θ =cos θsin θ×1cos θ×sin θsin θ×cos θsin θ×1cos θ =11 =1 =RHSHence proved.
Q4.
Answer :
LHS = sin2π18 +sin2π9+sin27π18+sin24π9 = sin2π18 +sin22π18+sin27π18+sin28π18 = sin2π18 +sin22π18+sin27π18+sin28π18 = sin2π18 +sin22π18+sin2π2-2π18+sin2π2-π18 = sin2π18 +sin22π18+cos22π18+cos2π18 = sin2π18 +cos2π18+sin22π18+cos22π18 =1+1 =2 =RHSHence proved.
Q5.
Answer :
LHS = sec3π2-θsecθ-5π2+tan5π2+θtanθ-3π2 =sec3π2-θsec-5π2-θ+tan5π2+θtan-3π2-θ =sec3π2-θsec5π2-θ+tan5π2+θ-tan3π2-θ =sec3π2-θsec5π2-θ-tan5π2+θtan3π2-θ =secπ2×3-θsecπ2×5-θ-tanπ2×5+θtanπ2×3-θ =-cosec θcosec θ–cot θcot θ =-cosec2θ+cot2 θ =-cosec2θ-cot2 θ =-1 =RHS Hence proved.
Q6.
Answer :
i) In ∆ABC:A + B + C = π∴ A + B = π-CNow, LHS = cosA + B + cos C = cosπ – C + cos C = -cosC + cos C ∵ cosπ – C = -cosC =0 =RHSHence proved.
ii) In ∆ABC:A + B + C = π⇒A + B = π-C⇒A + B2 = π-C2⇒A + B2 = π2-C2Now, LHS = cosA+B2 = cosπ2-C2 = sin C2 ∵ cosπ2-θ = sin θ =RHSHence proved.
iii) In ∆ABC:A + B + C = π⇒A + B = π-C⇒A + B2 = π-C2⇒A + B2 = π2-C2Now, LHS = tanA+B2 = tanπ2-C2 = cotC2 ∵ tanπ2-θ = cot θ =RHSHence proved.
Q7.
Answer :
A, B, C and D are the angles of a cyclic quadrilateral.∴ A + C = 180° and B + D = 180°⇒A = 180 -C and B = 180 -DNow, LHS = cos180°-A + cos180°+B + cos180°+C -sin90°+D = -cosA + -cos B + -cosC -cosD = -cosA -cos B -cosC -cosD = -cos180°-C -cos180°-D -cosC -cosD = –cos C –cos D -cos C -cos D = cos C +cos D -cosC -cos D =0 =RHS
Hence proved.
Q8.
Answer :
i) We have: cosec90°+θ + x cos θ cot90°+θ = sin90°+θ⇒ sec θ + x cos θ -tan θ = cos θ⇒ sec θ – x cosθ tanθ = cos θ⇒ sec θ – x cosθ×sin θcos θ = cos θ⇒ sec θ – x sin θ = cos θ⇒ sec θ – cos θ = x sin θ⇒ 1cos θ – cosθ = x sin θ⇒ 1 – cos2 θcos θ = x sin θ⇒ sin2θcosθ = x sin θ⇒ sin2 θcos θ sin θ = x⇒ sin θcos θ = x⇒ tan θ = x∴ x =tan θ
ii) We have: x cot90°+θ +tan90°+θ sin θ +cosec90°+θ =0⇒ x -tan θ +-cot θ sin θ +sec θ =0⇒ – x tan θ -cot θ sin θ +sec θ =0 ⇒ – x×sin θcos θ -cos θ sin θ × sin θ +1 cos θ=0 ⇒ – x×sin θcos θ -cos θ +1 cos θ =0 ⇒ – x sin θ-cos2 θ+1cos θ =0
⇒-x sin θ-cos2θ+1=0⇒-xsin θ+sin2θ=0⇒xsin θ=sin2θ⇒x=sin2 θsin θ⇒x=sin θ
Q9.
Answer :
i) LHS = tan720° -cos270° – sin150° cos120° = tan90°×8+0° -cos90°×3+0° – sin90°×1+60° cos90°×1+30° = tan0° -sin0° – cos60° -sin30° = tan0° -sin0° + cos60° sin30° = 0-0 + 12× 12 = 14 =RHS Hence proved.
ii) LHS = sin 780° sin 480° + cos 120° sin150° =sin 90°×8+60° sin 90°×5+30° + cos 90°×1+30° sin 90°×1+60° = sin 60° cos 30° + -sin 30° cos 60° =sin 60° cos 30° – sin 30° cos60° = 32×32-12×12 =34-14 = 12 =RHS Hence proved.
iii) LHS = sin780° sin120° + cos240° sin390° =sin90°×8+60° sin90°×1+30° + cos90°×2+60° sin90°×4+30° = sin 60° cos 30° + -cos 60° sin 30° =sin 60° cos 30° -cos 60°sin 30° = 32×32-12×12 =34-14 = 12 =RHS Hence proved.
iv) LHS = sin 600°cos 390°+cos 480° sin 150° =sin 90°×6+60° cos90°×4+30°+cos90°×5+30° sin90°×1+60° = -sin 60° cos30°+ -sin 30° cos 60° =-sin 60° cos30° -sin 30° cos 60° = -32×32-12×12 =-34- 14 = -1 =RHS Hence proved.
v) LHS = tan 225°cot 405°+tan 765° cot 675° = tan90°×2+45°cot90°×4+45°+tan90°×8+45° cot90°×7+45° =tan 45°cot 45°+tan 45° -tan45° =tan 45°cot 45°-tan 45° tan 45° =1×1-1×1 =1-1 = 0 =RHS Hence proved.
Page 5.29 (Very Short Answers)
Q1.
Answer :
We know: -1≤ cos x ≤1Also, cos-θ = cosθWhen the angle increases from 0 to π2, the value of cosθ decreases.∴Maximum value of coscosx = cos0= 1’And, minimum value of coscosx = cos1
Q2.
Answer :
We know:-1≤ sin x ≤1Also, sin-θ = -sinθWhen the angle increases from 0 to π2, the value of sinθ also increases.∴Maximum value of sinsinx = sin1And, minimum value of sinsinx = sin-1 = -sin1
Q3.
Answer :
We know:-1≤ cos x ≤1Also, sin-θ = -sinθWhen the angle increases from 0 to π2, the value of sinθ also increases.∴ Maximum value of sincos x = sin1
Q4.
Answer :
We have: sinx = cos2x 1∴ cos2x 1+cos2x=sinx1+sinx Using 1=sinx +sin2x=sinx +1-cos2x=sinx +1-sinx Using 1=1
Q5.
Answer :
We have:sinx + cosecx = 2⇒sinx + 1sinx = 2⇒sin2x +1sinx=2
⇒sin2x+1 = 2 sinx⇒sin2x+1-2sin x = 0⇒sin x-12 =0⇒sin x -1 = 0⇒sin x = 1And, cosec x = 1sin x = 1∴ sinnx+cosecnx = 1n+1n = 1+1 = 2
Q6.
Answer :
We have:sinx + sin2x = 1 1⇒sinx = 1 – sin2x⇒sinx = cos2x 2Now, taking cube of 1:sinx + sin2x = 1⇒ sinx + sin2x 3= 13⇒ sinx 3 + sin2x3 + 3sinx 2 sin2x+3sinx sin2x2=1⇒ sinx 3 + sinx6 + 3sinx 4 +3sinx 5=1⇒ sinx6 +3sinx 5 + 3sinx 4 + sinx 3=1⇒ cos2x6 +3cos2x5 + 3cos2x 4 + cos2x 3=1⇒ cos12x+3cos10x + 3cos8x + cos6x =1
Q7.
Answer :
We have:sinx + sin2x=1 1⇒sinx=1-sin2x⇒sinx=cos2x 2Now, taking square of 1:⇒ sinx+sin2x 2=12⇒ sinx 2+sin2x2+2sinx sin2x=1⇒ sinx 2+sinx4+ 2sinx 3=1⇒ sinx2+2sinx 3+sinx 4=1⇒ cos2x2+2cos2x3+cos2x 4=1⇒ cos4x+2cos6x+cos8x=1∴ cos8x+2cos6x+cos4x=1
Q8.
Answer :
Sine function can take the maximum value of 1.
If, sinθ1+sinθ2+sinθ3=3, then we have:
sinθ1 = 1
⇒ θ1=π2
Similarly, θ2=θ3=π2
⇒cosθ1=cosθ2=cosθ3=0⇒cosθ1+cosθ2+cosθ3=0
Q9.
Answer :
sin10°+sin20°+…+sin170°+sin180°+sin360°-170°+sin360°-160°+…+sin360°-20°+sin360°-10°+sin360°=sin10°+sin20°+…+sin180°-sin170°-sin160°-…-sin20°-sin10°+sin360° ∵ sin360°-x=- sinx=sin180°+sin360°=0+0=0
Q10.
Answer :
Circumference of the circle of radius 15 cm:
2πr=2×3.14×15 cm= 94.2 cm
Now, 94.2 cm will be the length of arcl for the circle with radius 120 cm.
We know:
l=rθHere, θ is measured in radians.∴ 94.2 = 120×θ⇒θ=0.785 radians
45° = π4=227×4=0.785 radians
Therefore, the angle subtended by it at the centre of the loop is 45°.
Q11.
Answer :
2sin6θ+cos6θ-3sin4θ+cos4θ+1=2sin2θ+cos2θsin4θ+cos4θ-sin2θ.cos2θ-3sin4θ+cos4θ+1=2.1sin4θ+cos4θ-sin2θ.cos2θ-3sin4θ+cos4θ+1=2sin4θ+cos4θ-2sin2θ.cos2θ-3sin4θ+cos4θ+1=-sin4θ+cos4θ-2sin2θ.cos2θ+1=-sin4θ+cos4θ+2sin2θ.cos2θ+1=-sin2θ+cos2θ2+1=-1+1=0
Q12.
Answer :
cos1°+cos2°+cos3°+…+cos180°=cos1°+cos2°+cos3°+…+cos88°+cos89°+cos90°+cos180-89°+cos180-88°+…+cos180-1°+ cos180° cos180°-θ=-cos θ=cos1°+cos2°+cos3°+…+cos88°+cos89°+cos90°-cos89°-cos88°-…-cos1°+ cos180°=cos90°+cos180°=0-1=-1
Q13.
Answer :
cot α+β=0⇒α+β=π2 1β=π2-α 2α=π2-β 3Now, sinα+2β = sinα+β+β =sinπ2+π2-α =sinπ-α =sin αNow, sinα+2β = sinα+2β =sinπ2-β+2β =sinπ2+β =cos β
Q14.
Answer :
tanA+cotA=4Squaring both the sides:tan2A+cot2A+2=16⇒tan2A+cot2A=14Squaring both the sides again:tan4A+cot4A+2=196⇒tan4A+cot4A=194
Q15.
Answer :
We know:
cos θ can take the minimum value of -1.
cos2 θ + sec2 θ
=cos4θ+1cos2θ=-14+1-12=2
Q16.
Answer :
If θ = 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°, 360°, then sin14θ+cos20θ will always be 1.
The smallest interval in which the value of x lie is (0,1].
Q17.
Answer :
3 sin θ +5 cos θ =5 GivenSquaring both the sides: 9 sin2 θ +25 cos2 θ+30 sin θ cos θ=2530 sin θ cos θ=25-9 sin2 θ -25 cos2 θ (1)We have to find the value of 5 sin θ-3 cos θ.5 sin θ-3 cos θ2=25 sin2 θ +9 cos2 θ -30 sin θ cos θ5 sin θ-3 cos θ2=25 sin2 θ +9 cos2 θ -25-9 sin2 θ -25 cos2 θ From (1)5 sin θ-3 cos θ2=34 sin2θ+34 cos2 θ-255 sin θ-3 cos θ2=34-25 ∵ sin2θ+cos2 θ=15 sin θ-3 cos θ2=95 sin θ-3 cos θ=±3
Page 5.30 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q1.
Answer :
(a) -2x,12x
We have,tanθ = x – 14x⇒sec2θ = 1 + tan2θ⇒ sec2θ= 1 +x – 14×2⇒sec2θ =x2 +116×2+12⇒sec2θ =x + 14×2∴secθ =± x + 14x⇒secθ – tanθ = x + 14x – x – 14x or -x + 14x – x – 14x =12x or -2x
Q2.
Answer :
(b) 2x,12x
We have,secθ = x + 14x⇒sec2θ = =x2 +116×2+12⇒1+tan2θ = 1+x2 +116×2-12⇒tan2θ = x2 +116×2-12 ⇒ tan2θ=x – 14×2∴tanθ =± x – 14x⇒secθ – tanθ = x + 14x – x – 14x or x + 14x — x – 14x =12x or 2x
Q3.
Answer :
(c) tan θ − sec θ
1-sinθ1+sinθ =1-sinθ1-sinθ1+sinθ1-sinθ=1-sinθ21-sin2θ=1-sinθ2cos2θ=1-sinθ-cosθ as,π2<θ<3π2, so cosθ will be negative=-secθ -tanθ =-secθ +tanθ
Q4.
Answer :
(d) −cosec θ − cot θ
1+cosθ1-cosθ =1+cosθ1+cosθ1-cosθ1+cosθ=1+cosθ21-cos2θ=1+cosθ2sin2θ=1+cosθ-sinθ as,π<θ<2π, so sinθ will be negative=-cosecθ +cotθ =-cosecθ -cotθ
Q5.
Answer :
(b) tanθ2
We have:y+11-y=1+sinθ1-sinθ ⇒y+11-y=cos2θ2+sin2θ2+2sinθ2cosθ2cos2θ2+sin2θ2-2sinθ2cosθ2⇒y+11-y=cosθ2+sinθ22cosθ2-sinθ22⇒y+11-y=cosθ2+sinθ2cosθ2-sinθ2 ∵ 0<θ<π2⇒0<θ2<π4, 0 to π4 cos θ is greater than sin θ⇒y+11-y=cosθ2cosθ2+sinθ2cosθ2cosθ2cosθ2-sinθ2cosθ2 ⇒1+y1-y=1 + tanθ21 – tanθ2 Comparing both the sides:y = tanθ2
Q6.
Answer :
(b) −2 sec θ
1-sinθ1+sinθ +1+sinθ1-sinθ=1-sinθ1-sinθ1+sinθ1-sinθ+1+sinθ1+sinθ1-sinθ1+sinθ=1-sinθ21-sin2θ+1+sinθ21-sin2θ=1-sinθ2cos2θ+1+sinθ2cos2θ=1-sinθ-cosθ +1+sinθ-cosθ π2<θ<π, so cosθ will be negative.=-secθ -tanθ -secθ +tanθ=-2secθ
Q7.
Answer :
(a) θ, ϕ
We have:
x = r sin θ cos ϕ , y = r sin θ sin ϕ and z = r cos θ,
∴ x2 + y2 + z2
= r sinθ cosϕ2+r sinθ sinϕ2+ r cosθ2= r2 sin2θ cos2ϕ+r2 sin2θ sin2ϕ + r2 cos2θ = r2 sin2θ cos2ϕ+sin2ϕ + r2 cos2θ = r2 sin2θ×1 + r2 cos2θ= r2 sin2θ + r2 cos2θ= r2 sin2θ +cos2θ= r2 ×1=r2 Thus, x2 + y2 + z2 is independent of θ and ϕ.
Q8.
Answer :
(c) π6
We have:tanθ + secθ = 3 0 < θ<π⇒ secθ + tanθ= 3⇒1cosθ+sinθcosθ = 3⇒1 + sinθ = 3cosθ
⇒1+sinθ2 =3 cosθ2⇒1+sin2θ+2sinθ = 3cos2θ⇒1+sin2θ+2sinθ = 3(1-sin2θ)⇒4 sin2θ+2sinθ =2⇒2 sin2θ+sin θ -1=0⇒sinθ = -1, 12Since 0<θ<π, sinθ cannot be negative.∴ sinθ=12∴ θ=π6
Q9.
Answer :
(a) 56
In the fourth quadrant, cosθ and secθ are positive.cosθ = 1secθ =1sec2θ =11+tan2θ =1 1 + -152 =1 65 =56
Q10.
Answer :
(d) −1 −cot α
We have: 2cotα+1sin2α = 2cosαsinα+1sin2α= 2sin αcos α+1sin2α= 2sin αcosα+sin2α+cos2αsin2α= sinα + cosα2sin2α= 1+cot α2= 1+cot α=-1+cot α When 3π4<α<π, cot α<-1⇒cot α +1<0=-1-cot α
Q11.
Answer :
(b) 1
We have:sin6A + cos6A + 3sin2A cos2A=sin2A3 + cos2A3 + 3sin2A cos2A×1=sin2A3 + cos2A3 + 3sin2A cos2Asin2A+cos2A=sin2A+cos2A3=13=1
Q12.
Answer :
(b) 35
We have: cosecθ – cotθ = 12 1⇒1cosecθ – cotθ = 2⇒cosec2θ – cot2θcosecθ – cotθ = 2⇒cosecθ + cotθcosecθ – cotθcosecθ- cotθ = 2∴ cosecθ + cotθ= 2 2Adding 1 and 2:2cosecθ =12+2⇒2cosecθ =52⇒cosecθ =54⇒1sinθ =54⇒sinθ = 45
Now, 0<θ<π2∴ cosθ = 1-sin2θ =1-452 =35
Q13.
Answer :
(c) 44117
We have: cosecθ+ cotθ = 112 1⇒1cosecθ + cotθ = 211⇒cosec2θ – cot2θcosecθ + cotθ = 211⇒cosecθ + cotθcosecθ – cotθcosecθ + cotθ = 211∴ cosecA – cotθ= 211 2Subtracting 2 from 1:2cotθ =112-211⇒2cotθ=121-422⇒2cotθ=11722⇒cotθ =11744⇒1tanθ =11744⇒tanθ =44117
Page 5.31 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q14.
Answer :
(b) x = y, x ≠ 0
We have:sec2θ=4xy(x+y)2⇒4xy(x+y)2≥1 ∵sec2θ≥1⇒4xy ≥(x+y)2
⇒4xy ≥ x2+y2+2xy⇒2xy ≥ x2+y2⇒x-y2 ≤0⇒x-y ≤0⇒ x= yFor x = 0, sec2θ will not be defined, ⇒x ≠ 0∴ x=y
Q15.
Answer :
(a) 3/4
We have:tanθ = 17∴ tan2θ =17Now, dividing the numerator and the denominator of cosec2θ-sec2θcosec2θ+sec2θ by cosec2 θ:
1-tan2θ1+tan2θ= 1-171+17= 68 = 34
Q16.
Answer :
(c) 9.5
We have:sin25° + sin210° + sin215° + …+ sin285° + sin290°=sin25° + sin210° + sin215° + …+ sin290° -10°+ sin290° -5°+ sin290°=sin25° + sin210° + sin215° + …+cos210°+ cos25°+ sin290°=sin25°+ cos25° + sin210° +cos210°++ sin215° +cos215°+ sin220° +cos220°+ sin225° +cos225°+ sin230° +cos230° + sin235° +cos235°+ sin240° +cos240° +sin245° + sin290°=1+1+1+1+1+1+1+1+122+12 ∵ sin2θ+cos2θ = 1=8+12+1=9.5
Q17.
Answer :
(c) 2
We have: sin2π18 +sin2π9+sin27π18+sin24π9= sin2π18 +sin22π18+sin27π18+sin28π18= sin2π18 +sin22π18+sin27π18+sin28π18= sin2π18 +sin22π18+sin2π2-2π18+sin2π2-π18= sin2π18 +sin22π18+cos22π18+cos2π18= sin2π18 +cos2π18+sin22π18+cos22π18=1+1=2
Q18.
Answer :
(d) 194
We have:tan A + cot A = 4Squaring both the sides:tan A + cot A2 = 42⇒ tan2A + cot2A +2 tan Acot A = 16⇒ tan2A + cot2A +2 = 16⇒ tan2A + cot2A = 14Squaring both the sides again: tan2A + cot2A2 = 142⇒ tan4A + cot4A +2 tan2Acot2A = 196⇒ tan4A + cot4A +2 = 196⇒ tan4A + cot4A= 194
Q19.
Answer :
(c) 8
We have:x sin 45° cos2 60° = tan2 60° cosec 30°sec45°cot230°⇒x× 12 × 122 = 3 2 × 22 × 32⇒x42 = 632 ⇒ x = 632 ×42⇒x=8
Q20.
Answer :
(d) 35
We have: cosec θ – cot θ = 12 1⇒1cosecθ – cotθ = 2⇒cosec2θ – cot2θcosec θ + cot θ = 2⇒cosec θ + cot θcosec θ – cot θcosec θ+ cot θ = 2∴ cosec θ – cot θ= 2 2Adding 1 and 2:2cosec θ =12+2⇒2cosec θ =52⇒cosec θ =54⇒1sin θ =54⇒sin θ = 45
Now, 0<θ<π2∴ cos θ = 1-sin2θ =1-452 =35
Q21.
Answer :
(c) 44117
We have: cosec A+ cot A = 112 1⇒1cosec A + cot A = 211⇒cosec2A – cot2Acosec A + cot A = 211⇒cosec A + cot Acosec A – cot Acosec A + cot A = 211∴ cosec A – cot A= 211 2Subtracting 2 from (1):2cot A =112-211⇒2cot A =121-422⇒2cot A =11722⇒cot A =11744⇒1tan A =11744⇒tan A =44117
Q22.
Answer :
(b) 2ex+e-x
We have: tan θ +sec θ = ex sec θ+ tan θ = ex 1⇒1secθ + tanθ = 1ex⇒sec2 θ – tan2θsec θ + tan θ = 1ex⇒sec θ + tan θsec θ – tan θsec θ + tan θ = 1ex∴ sec θ – tan θ= 1ex 2Adding 1 and 2:2sec θ =ex + 1ex⇒2sec θ =ex2 + 1ex⇒sec θ =e2x + 12ex⇒sec θ =12×e2x + 1ex⇒sec θ =12×ex + e-x⇒1cos θ =ex + e-x2⇒cos θ =2ex + e-x
Q23.
Answer :
(b) 2kk2+1
We have:sec θ + tan θ = k 1⇒1sec θ + tan θ = 1k⇒sec2 θ – tan2 θsec θ + tan θ = 1k⇒sec θ + tan θsec θ – tan θsec θ + tan θ = 1k∴ sec θ – tan θ= 1k 2Adding 1 and 2:2sec θ =k + 1k⇒2sec θ =k2 + 1k⇒secθ =k2 + 12k⇒1cos θ =k2 + 12k⇒cos θ =2kk2 + 1
3. GRAPHS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
Page 6.3 Ex – 6.1
Q1.
Answer :
(i)
Step I- We find the value of c and a by comparing y = 2 sin 2x with y = c sin ax, i.e. c = 2 and a = 2.
Step II- Then, we draw the graph of y = sin x and mark the point where it crosses the x-axis.
Step III- Divide the x-coordinates of the points where y = sin x crosses x-axis by 2 (i.e. a = 2) and mark the maximum value (i.e. c = 2) and minimum value (i.e.-c = -2).
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(ii)
Step I- We find the value of c and a by comparing y = 3 sin x with y = c sin ax, i.e. c = 3 and a = 1.
Step II- Then, we draw the graph of y = sin x and mark the point where it crosses the x-axis.
Step III- Divide the x-coordinates of the points where y = sin x crosses x-axis by 1 (i.e. a = 1) and mark the maximum value (i.e. c = 3) and minimum value (i.e.-c = -3).
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(iii)
y=2sinx-π4⇒ y-0=2sinx-π4 …(i)On shifting the origin at π4,0, we get:x=X+π4 and y=Y+0On substituting the values in (i), we get:Y=2sinXThen, we draw the graph of Y=2sinX and shift it by π4 to the right.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(iv)
y=2sin2x-1⇒ y-0=2sin2x-12 …(i)On shifting the origin at 12,0, we get:x=X+12 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=2sin2XThen, we draw the graph of Y=2sin1X and shift it by 12 to the right.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(v)
y=3sin3x+1⇒ y-0=2sin3x+13 …(i)On shifting the origin at -13,0, we get:x=X-13 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=3sin3XThen, we draw the graph of Y=3sin3X and shift it by 13 to the left.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(vi)
y=3sinx-π4⇒y-0=3sin2x-π8 …(i)On shifting the origin at π8,0, we get:x=X+π8 and y=Y+0On substituting the values in (i), we get:Y=3sin2XThen. we draw the graph of Y=3sin2X and shift it by π8 to the right.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
Page 6.4 Ex – 6.1
Q2.
Answer :
(i)
First, we draw the graph of y = sin x.
Then, let us draw the graph of y=sinx+π4.
y=sinx+π4⇒ y-0=sinx+π4 …(i)On shifting the origin at -π4,0, we get:x=X-π4 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=sinXThen, we draw the graph of Y=sinX and shift it by π4 to the left.
Then, we will obtain the following graph:
(ii)
First, we draw the graph of y = sin x.
Let us now draw the graph of y = sin 3x.
Step I- We find the value of c and a by comparing y = sin 3x with y = c sin ax, i.e. c = 1 and a =3.
Step II – Then, we draw the graph of y = sin x and mark the point where it crosses the x-axis.
Step III – Divide the x-coordinates of the points where y = sin x crosses x-axis by 3 (i.e. a =3) and mark the maximum value (i.e. c = 1) and minimum value (i.e.-c = -1).
Then, we obtain the following graph:
Page 6.6 Ex – 6.2
Q1.
Answer :
(i)
y=cosx+π4⇒ y-0=cosx+π4 …(i)On shifting the origin at -π4,0, we get:x=X-π4 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=cosXThen, we draw the graph of Y=cosX and shift it by π4 to the left.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(ii)
y=cosx-π4⇒ y-0=cosx-π4 …(i)On shifting the origin at π4,0, we get:x=X+π4 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i) we get:Y=cosXThen, we draw the graph of Y=cosX and shift it by π4 to the right.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(iii)
y=3cos2x-1⇒ y-0=3cos2x-12 …(i)On shifting the origin at 12,0, we have:x=X+12 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=3cos2XThen, we draw the graph of Y=3cos2X and shift it by 12 to the right.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
(iv)
y=2cosx-π2⇒ y-0=2cosx-π2 …(i)On shifting the origin at π2,0, we get:x=X+π2 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=2cosXThen, we draw the graph of Y=cosX and shift it by π2 to the right.
Then, we obtain the following graph:
Q2.
Answer :
(i)
First, we draw the graph of y = cos x.
Let us now draw the graph of y=cosx-π4.
y=cosx-π4⇒ y-0=cosx-π4 …(i)On shifting the origin at π4,0, we get:x=X+π4 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=cosXThen, we draw the graph of Y=cosX and shift it by π4 to the right.
Then, we will obtain the following graph:
(ii)
First, we draw the graph of y = cos 2x.
Let us now draw the graph of y=cos2x-π4.
y=cos2x-π4⇒ y-0=cos2x-π4 …(i)On shifting the origin at π4,0, we get:x=X+π4 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=cos2XThen, we draw the graph of Y=cos2X and shift it by π4 to the right.
Then, we will obtain the following graph:
(iii)
First, we draw the graph of y = cos x.
Let us now draw the graph of y=cosx2.
⇒ y=cos12x
Then, we will obtain the following graph:
Page 6.7 Ex – 6.3
Q1.1
Answer :
The obtained graph of y = sin2 x is given below.
Q1.2
The obtained graph of y = cos2 x is given below.
Q1.3
Answer :
y=sin2x-π4y-0=sin2x-π4………………(i)On shifting the origin at π4,0, we will have:x=X+π4 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=sin2XThen, we draw the graph of Y=sin2X and shift it by π4to the right.
The obtained graph is given below.
Q1.4
Answer :
Step I- We find the value of c and a by comparing y = 2 tan 2x with y = c tan ax, i.e. c = 1 and a = 2.
Step II- Then, we draw the graph of y = tan x and mark the point where it crosses the x-axis.
Step III- Divide the x-coordinates of the points where y = tan x crosses x-axis by 2(i.e. a = 2) and mark the maximum value (i.e. c = 1) and minimum value (i.e.-c = -1).
Then , we obtain the following graph:
Q1.5
Answer :
Step I- We find the value of c and a by comparing y = 2 tan 3x with y = c tan ax, i.e. c = 2 and a = 3.
Step-II- Then, we draw the graph of y = tan x and mark the point where it crosses the x-axis.
Step-III- Divide the x-coordinates of the points where y = tan x crosses x-axis by 3(i.e. a = 3) and mark the maximum value (i.e. c = 2) and minimum value (i.e.-c = -2).
Then , we obtain the following graph:
Q1.6
Answer :
Step I- We find the value of c and a by comparing y = 2 cot 2x with y = c cot ax, i.e. c = 2 and a = 2.
Step II- Then we draw the graph of y = cot x and mark the point where it crosses the x-axis.
Step III- Divide the x-coordinates of the points where y = cot x crosses x-axis by 2 (i.e. a = 2) and mark the maximum value (i.e. c =2) and minimum value (i.e.-c = -2).
Then, we obtain the following graph:
Q2.1
Answer :
(ii)
First, we draw the graph of y = cos 2x.
Then, let us draw the graph of y=cos2x-π4.
y=cos2x-π3⇒ y-0=cos2x-π6 … (i)On shifting the origin at π6,0, we have:x=X+π6 and y=Y+0On subsitituting the values in (i), we get:Y=cos2XThen, we draw the graph of Y=cos2X and shift it by π6to the right.
Then, we will obtain the following graph:
Q2.2
Answer :
First, we draw the graph of y = sin2 x.
Then, we draw the graph of y = sin x.
Then, we will obtain the following graph.
Q2.3
Answer :
First, we draw the graph of y = tan x.
Then, we draw the graph of y = tan2 x.
Then, we will obtain the following graph:
Q2.4
Answer :
To draw the graph of y = tan 2x, we will follow the steps given below.
Step I- We find the value of c and a by comparing y = tan 2x with y = c tan ax, i.e. c = 1 and a = 2.
Step II- Then, we draw the graph of y = tan x and mark the point where it crosses the x-axis.
Step III- Divide the x-coordinates of the points where y = tan x crosses x-axis by 2(i.e. a = 2) and mark the maximum value (i.e. c = 1) and minimum value (i.e.-c = -1).
Then, we will draw the graph of y = tan x.
TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS OF COMPOUND ANGLES
Page 7.19 Ex – 7.1
Q1.
Answer :
Given: sinA = 45 and cosB = 513We know that cosA = 1 – sin2A and sinB = 1 – cos2B , where 0 < A , B < π2⇒ cosA = 1 – 452 and sinB = 1 – 5132⇒ cosA =1 – 1625 and sinB = 1 – 25169⇒ cosA =925 and sinB = 144169⇒ cosA =35 and sinB = 1213
Now,
(i) sinA+B = sinA cosB + cosA sinB =45×513 + 35×1213 =2065 + 3665 =5665
(ii) cosA+B = cosA cosB – sinA sinB =35×513 – 45×1213 =1565 – 4855 =-3365
(iii) sinA-B = sinA cosB – cosA sinB =45×513 – 35×1213 =2065 – 3665 =-1665
(iii) sinA-B=sinA cosB-cosA sinB =45×513-35×1213 =2065-3665 =-1665
iv cosA-B = cosA cosB + sinA sinB =35×513 + 45×1213 =1565 + 4865 =6365
Q2.
Answer :
a Given:sinA = 1213 and sinB = 45When, π2 < A < π and 0 < B < π2,cosA = -1 – sin2A and cosB = 1 – sin2B As cosine function is negative in second qudrant and positive in first quadrant
⇒ cosA =- 1 – 12132 and cosB = 1 – 452⇒ cosA =- 1 – 144169 and cosB = 1 – 1625⇒ cosA =- 25169 and cosB = 925⇒ cosA = -513 and cosB = 35Now,
(i) sinA+B = sinA cosB + cosA sinB =1213×35 + -513×45 =3665 + -2065 =1665ii cosA+B = cosA cosB – sinA sinB =-513×35 – 1213×45 =-1565 – 4865 =-6365
b Given: sinA =35 and cosB = -1213and that A and B both lie in second qudrant.We know that in second quadrant sine function is positive and cosine function is negative.Therefore, cosA =- 1 – sin2A and sinB = 1 – cos2B ⇒ cosA =- 1 – 352 and sinB = 1 – -12132 ⇒ cosA =- 1 -925 and sinB = 1 – 144169⇒ cosA =- 1625 and sinB = 2569⇒ cosA = -45 and sinB = 513Now, sinA+B = sinA cosB + cosA sinB =35×-1213 + -45×513 =-3665 – 2065 =-5665
Q3.
Answer :
Given:cosA =-2425 and cosB = 35and π<A<3π2 and 3π2<B<2π.That is, A is in third quadrant and B is in fourth qudrant.We know that sine function is negative in third and fourth quadrants.Therefore,sinA =- 1 – cos2A and sinB =- 1 – cos2B⇒sinA = 1 – -24252 and sinB = -1 – 352⇒sinA =- 1 – 576625 and sinB = -1 – 925⇒sinA =- 49625 and sinB =-1625⇒sinA = -725 and sinB = -45
Now,i sinA+B = sinA cosB + cosA sinB =-725×35 + -2425×-45 =-21125+96125 =75125
=35
ii cosA+B = cosA cosB – sinA sinB =-2425×35 – -725×-45 =-72125 – 28125 =-100125 =-45
Page 7.20 Ex – 7.1
Q4.
Answer :
Given:tanA = 34 and cosB = 941Here, π< A < 3π2 and 0 < B < π2.That is, A is in third quadrant and B is in first qudrant.We know that tan function is positive in first and third quadrants,and in the first quadrant, sine function is also positive.Therefore, sinB = 1 – cos2B =1 – 9412 =1 – 811681 =16001681 =4041And tanB = sinBcosB =4041941=409Therefore, tanA+B = tanA + tanB1-tanA tanB =34+4091-34×409 =18736-8436 =-18784
Q5.
Answer :
Given:sinA = 12 and cosB = 1213Here, π2 < A < π and 3π2< B < 2π.That is, A is in the second quadrant and B is in the fourth quadrant.We know that in the second quadrant, sine function is positive and cosine and tan functions are negative.In the fourth quadrant, sine and tan functions are negative and cosine function is positive. Therefore,cosA =- 1 – sin2A =- 1 – 122 = -1-14 = -34 = -32tanA = sinAcosA=12-32 = -13sinB =- 1 – cos2B =- 1 – 12132 =- 1 – 144169 =- 25169 = -513tanB = sinBcosB = -5131213 = -512Now, tanA-B = tanA -tanB1 + tanA tanB =-13–5121+-13×-512 =-12+53123123+5123=53-125+123
Q6.
Answer :
Given: sinA = 12 and cosB = 32Here, π2<A<π and 0<B<π2.That is, A is in the second quadrant and B is in the first quadrant.We know that in the second quadrant, sine function is positive and cosine and tan functions are negativeIn the first quadrant, all T-functions are positive.Therefore,cosA = -1-sin2A = -1-122 =-1-14 =-34 =-32tanA = sinAcosA = 12-32 = -13sinB = 1-cos2A = 1-322 = 1-34 = 14 = 12tanB = sinBcosB = 1232 = 13
Now,i tanA+B = tanA + tanB1 – tanA tanB =-13+131–13×13 =01+13= 0
ii tanA-B = tanA – tanB1+tanA tanB =-13-131+-13×13 =-231-13 =-2323 =-3
Q7.
Answer :
i sin78°cos18° – cos 78° sin 18° = sin78°-18° Using sinA cosB – cosA sinB = sinA-B = sin60° = 32ii cos47°cos13° -sin47° sin13° =cos47°+13° Using cosA cosB – sinA sinB = cosA+B = cos60° = 12iii sin36°cos9° + cos 36° sin9° = sin36°+9° Using sinA cosB+ cosA sinB = sinA+B = sin45° = 12iv cos80°cos20° +sin80° sin20° =cos80°-20° Using cosA cosB + sinA sinB = cosA-B = cos60° = 12
Q8.
Answer :
Given:cosA = -1213 and cotB = 247A lies in the second quadrant and B lies in the third quadrant.We know that sine function is positive in the second quadrant and in the third quadrant, both sine and cosine functions are negative.Therefore,sinA = 1-cos2A = 1–12132 = 1-144169 = 25169 = 513sinB = -11+cot2B = -11+2472 = -11+57649=-162549=-725cosB = -1-sin2B = -1–7252 =- 1-49625 =- 576625=-2425Now,i sinA+B = sinA cosB + cosA + sinB = 513×-2425 + -1213×-725 =-120325+84325 =-36325ii cosA+B=cosA cosB – sinA sinB =-1213×-2425 – 513×-725 =288325 + 35325 =323325iii tanA+B=sinA+BcosA+B =-36325323325 =- 36323
Q9.
Answer :
LHS = cos105o + cos15o
= cos(90o + 15o) + cos(90o – 75o)
= – sin 15o + sin 75o [As cos(90o+A) = – sin A and cos(90o – B) = sin B]
= sin 75o – sin 15o
= RHS
Hence proved.
Q10.
Answer :
LHS = tanA + tanBtanA – tanB =sinAcosA+sinBcosBsinAcosA-sinBcosB =sinA cosB+cosAsinBcosA cosBsinA cosB – cosA sinBcosA cosB =sinA cosB + cosA sinBsinA cosB -cosA sinB =sinA+BsinA-B =RHS Hence proved.
Q11.
Answer :
LHS= cos11° + sin11°cos11° – sin11° =cos11°cos11°+sin11°cos11°cos11°cos11° – sin11°cos11° Dividing numerator and denominator by cos11° =1+tan11°1-tan11° =1+tan11°1-1×tan11° =tan45° + tan11°1 – tan45° tan11° As tan45° = 1 = tan45°+11° As tanA + tanB1 – tanA tanB = tanA+B = tan56° = RHS Hence proved.
Q12.
Answer :
i LHS = cos9° + sin9°cos9° – sin9° =cos9°cos9° + sin9°cos9°cos9°cos9° – sin9°cos9° Dividing the numerator and denominator by cos9 =1 + tan9°1 – tan9° =1 + tan9°1 + 1× tan9° =tan45°+ tan9°1 – tan45°× tan9° As tan45° = 1 = tan45° + 9° As tanA+tanB1 – tanA tanB = tanA+B = tan54° = RHS Hence proved.
ii LHS = cos8° – sin8°cos8° + sin8° =cos8°cos8° – sin8°cos8°cos8cos8 +sin8cos8 Dividing numeraor and denominator by cos8° =1-tan8°1+tan8° =1- tan8°1+1×tan8° =tan45° – tan8°1 + tan45° tan8° As tan 45° = 1 =tan45°-8° As tanA-tanB1+tanA tanB=tanA+B =tan37° =RHS Hence proved.
Q13.
Answer :
LHS = sin60°-θ cos30°+θ +cos60°-θ sin30°+θ =sin60°-θ+30°+θ Using the formula sinA cosB + cosA sinB = sinA+B and taking A =60°-θ and B =30°+θ =sin90° =1 = RHS Hence proved.
Q14.
Answer :
LHS = tan69°+tan66°1-tan69°tan66° =tan69°+66° Using the formula tanA+tanB1-tanAtanB=tanA+B =tan135° =tan180°-45° =-tan45° tan180-A = -tanA = -1 = RHS Hence proved.
Q15.
Answer :
We have:tanA = 56 and tanB = 111Therefore, tanA+B = tanA+tanB1-tanA tanB ⇒ tanA+B = tanA +tanB1 – tanA tanB ⇒tanA+B = 56+1111 – 56×111 ⇒tanA+B =61666166 ⇒tanA+B =1 ⇒tanA+B =tanπ4 Therefore, A + B = π4.Hence proved.
Q16.
Answer :
LHS = cos245° – sin215° = cos45°+15° cos45°-15° cosA+BcosA-B = cos2A – sin2B = cos60°×cos30° =12×32 = 34 = RHSHence proved.
Q17.
Answer :
i LHS= sinA+B+sinA-BcosA+B +cosA-B =sinA cosB +cosA sinB + sinA cosB – cosA sinBcosA cosB -sinA sinB +cosA cosB +sinA sinB =2sinA cosB2cosA cosB =sinAcosA =tanA = RHSHence proved.
ii LHS = sinA-BcosA cosB+sinB-CcosB cosC + sinC-AcosC cosA =sinA cosB – cosA sinBcosA cosB + sinB cosC -cosB sinCcosB cosC +sinC cosA-cosC sinAcosC cosA =sinA cosBcosA cosB – cosA sinBcosA cosB +sinB cosCcosB cosC – cosB sinCcosB cosC +sinC cosAcosC cosA -cosC sinAcosC cosA =sinAcosA – sinBcosB +sinBcosB – sinCcosC +sinCcosC-sinAcosA =tanA – tanB + tanB -tanC +tanC -tanA = 0 =RHSHence proved.
iii LHS = sinA-BsinA sinB +sinB-CsinB sinC + sinC-AsinC sinA =sinA cosB -cosA sinBsinA sinB + sinB cosC -cosB sinCsinB sinC+sinC cosA -cosC sinAsinC sinA =sinA cosBsinA sinB – cosA sinBsinA sinB + sinB cosCsinB sinC – cosB sinCsinB sinC + sinC cosAsinC sinA – cosC sinAsinC sinA =cosBsinB – cosAsinA + cosCsinC-cosBsinB +cosAsinA – cosCsinC = cotB – cotA + cotC -cotB+cotA-cotC =0 =RHSHence proved.
iv RHS= sin2A + sin2A-B -2sinA cosB sinA-B = sin2A + sinA-B sinA-B -2sinA cosB = sin2A + sinA-B sinA cosB – cosA sinB – 2sinA cosB = sin2A + sinA-B -sinA cosB – cosA sinB = sin2A – sinA-B sinA cosB + cosA sinB = sin2A – sinA-B sinA+B = sin2A – sin2A – sin2B = sin2A – sin2A + sin2B = sin2B = LHSHence proved.
v LHS = cos2A + cos2B -2cosA cosB cosA+B = cos2A + 1 – sin2B – 2cosA cosB cosA+B =1 + cos2A – sin2B – 2cosA cosB cosA+B =1 + cos2A – sin2B – 2cosA cosB cosA+B =1 + cosA+BcosA-B – 2cosA cosB cosA+B =1 + cosA+BcosA-B – 2cosA cosB =1 + cosA+BcosA cosB + sinA sinB – 2cosA cosB =1 + cosA+B-cosA cosB + sinA sinB =1 – cosA+BcosA cosB – sinA sinB =1 – cosA+BcosA+B =1 – cos2A+B = sin2A+B = RHSHence proved.
vi LHS =tanA+BcotA-B =tanA+B1tanA-B = tanA+B × tanA-B = tanA +tanB1-tanA tanB×tanA -tanB1+tanAtanB =tanA+tanBtanA -tanB1-tanA tanB1 + tanA tanB =tanA2-tanB212-tanA tanB2 =tan2A -tan2B1 – tan2A tan2B = RHSHence proved.
Q18.
Answer :
i We know that 8θ = 6θ + 2θTherefore, tan8θ = tan6θ + 2θ⇒ tan8θ =tan6θ+tan2θ1 – tan6θ tan2θ⇒tan8θ – tan8θ tan6θ tan2θ = tan6θ + tan2θ⇒tan8θ – tan6θ – tan2θ =tan8θ tan6θ tan2θHence proved.
ii We know that 45° = 15° + 30°Therefore,tan45° = tan15°+30°⇒1 = tan15° + tan30°1 – tan15° tan30°⇒ 1 – tan15° tan30° = tan15° + tan30° ⇒ 1 = tan15° + tan30° + tan15° tan30°⇒ tan15° + tan30° + tan15° tan30°= 1Hence proved.
iii We know that 36° + 9° = 45°Therefore, tan36° + 9° = tan45°⇒tan36° + tan9°1 – tan36° tan9° = 1⇒tan36° + tan9° = 1 – tan36° tan9°⇒tan36° + tan9° + tan36° tan9° = 1Hence proved.
iv We know that 13θ = 9θ + 4θTherefore, tan13θ = tan9θ + 4θ⇒tan13θ = tan9θ + tan4θ1 – tan9θ tan4θ⇒tan13θ – tan13θ tan9θ tan 4θ = tan9θ + tan4θ⇒tan13θ – tan9θ – tan4θ = tan13θ tan9θ tan4θ Hence proved.
Page 7.21 Ex – 7.1
Q19.
Answer :
LHS = sin2n+1A – sin2nA =sinn+1A+nA sinn+1A-nA Using the formula sin2X – sin2Y = sinX+Y sinX-Y and taking X = n+1A and Y = nA =sinn+1+nA sin n+1-nA =sin2n +1A sinA = RHS Hence proved.
Q20.
Answer :
tan(2A)=tan(A+A) =tan(A+B+A-B) =tan(A+B)+tan(A-B)1-tan(A+B)tan(A-B) =x+y1-xy
tan 2B= tan B+B =tan B+A+B-A = tan A+B+tan B-A1-tanA+BtanB-A =tanA+B-tanA-B1+tanA+BtanA-B tan-θ=-tan θ =x-y1+xy
Q21.
Answer :
RHS= m2+n2-2= cos A +sin B2+sin A+cos B 2-2=cos2A+sin2B+2cosAsinB+sin2 A+cos 2 B +2sinAcos B-2=1+1+2cosAsinB+2sinAcos B-2=2cos AsinB+sinA cos B=2sinA+B=LHS Hence proved.
Q22.
Answer :
LHS =tan22θ-tan2θ1-tan22θtan2θ=(tan2θ+tanθ)(tan2θ-tanθ)1-tan22θtan2θ Using A2-B2=A+BA-B tan3θ=tan(2θ+θ) and tanθ=tan(2θ-θ).=tan3θ1-tan2θtanθ×tanθ1+tan2θtanθ1-tan22θtan2θ ∵ tan 2θ+tan θ=tan3θ1-tan2θtanθ & tan 2θ -tanθ =tanθ1+tan2θtanθ=tan3θtanθ (1-tan22θtan2θ)1-tan22θtan2θ=tan3θtanθ
=RHS Hence proved.
Q23.
Answer :
Given:
cot A + cot B = b⇒1tanA+1tanB=b⇒tanA+tanBtanAtanB=bNow,RHS = 1a-1b = 1tan A +tan B-tan A tan Btan A +tan B = 1-tan A tan Btan A + tan B = cot (A+B) = LHS Hence proved.
Q24.
Answer :
LHS = sin(A-B)sin(A+B) = sin A cos B – cos A sin Bsin A cos B + cos A sin B Dividing numerator and denominator by cos A cos B: tan A -tan Btan A + tan B =xtan B-tan Bxtan B+tan B (Since tan A = x tan B ) =tan B x-1tan B x+1 = x-1x+1 = RHS Hence proved.
Q25.
Answer :
Given: 0<θ<π2Now, sin θ = 1-cos2θ = 1-64289=1517LHS = cosπ6+θ +cosπ4-θ+cos2π3-θ = cos(30+θ) +cos(45-θ)+cos(120-θ) =cos 30° cos θ -sin30° sin θ +cos 45° cos θ+sin 45° sin θ + cos120° cos θ+sin120° sin θ Using formulas of cos(A+B) and cos(A-B) = cos θ(cos 30°+cos 45°+cos120) +sin θ(-sin 30° +sin 45° +sin120°) = 81732+12-12 +1517-12+12+32 =8173-12+12+15173-12+12 =23173-12+12 = RHS Hence proved.
Q26.
Answer :
Given:tan x +tanx+π3+tanx+2π3 = 3⇒tanx+tan x+tanπ31-tan x tan π3+tan x+tan2π31-tan x tan2π3=3⇒tanx+tan x+31-3tan x +tan x-31+3tan x =3 tan120°=-3⇒tan x(1-3tan2x)+tan x+3+3tan2x+3tan x+tan x-3-3tan2x+3tan x1-3tan2x=3 ⇒9tan x-3tan3x1-3tan2x=3⇒3tan x-tan3x1-3tan2x=1 Hence proved.
Q27.
Answer :
Given:sin (α+β)=1 and sin (α-β)=12⇒α+β=90° …(1) and α-β=30° …(2) By adding eq (1) and eq (2) we get: 2α=120°⇒α=60°By subtracting eq (2) from eq (1), we get: 2β=60°⇒ β=30°Therefore, tan(α+2β)=tan 60°+2×30°=tan 120°=-3tan(2α+β)=tan 2×60°+30°=tan 150° = -13
Q28.
Answer :
We know thattan(A-B)=tan A-tan B1+tan Atan B =mm-1-12m-11+m(m-1)(2m-1) =2m2-m-m+12m2-m-2m+1+m =2m2-2m+12m2-2m+1 =1⇒A-B =tan-1(1) ⇒A-B =π4
Q29.
Answer :
Given:6 cosθ+8 sinθ=9⇒6 cosθ=9-8 sinθ⇒36cos2θ=(9-8 sinθ)2⇒361-sin2θ=81+64sin2θ -144sinθ⇒100sin2θ -144sinθ+45 =0Now, α and β are the roots of the given equation; therefore, cos α and cos β are the roots of the above equation.⇒sinα sinβ=45100 (Product of roots of a quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 is ca.)Again, 6 cosθ+8 sinθ=9⇒8 sinθ=9-6 cosθ⇒64sin2θ=(9-6 cosθ)2⇒64(1-cos2θ)=81+36cos2θ-108cos θ⇒100cos2θ-108cosθ+17=0Now, α and β are the roots of the given equation; therefore, sinα and sinβ are the roots of the above equation.Therefore, cosα cosβ=17100Hence, cos(α+β)=cosα cosβ-sinα sinβ =17100-45100 =-28100 =-725
sin α+β =1-cos2α+β =1–7252 =576625 =2425
Q30.
Answer :
(i)
a2+b2=sinα+sinβ2+(cosα+cosβ)2⇒a2+b2=sin2α+sin2β+2sinαsinβ+cos2α+cos2β+2cosαcosβ⇒a2+b2=sin2α+cos2α+sin2β+cos2β+2sinαsinβ+cosαcosβ⇒a2+b2=2+2 cos(α-β) …(1)
Now,
b2-a2=(cosα+cosβ)2-sinα+sinβ2⇒b2-a2 = cos2α+cos2β -sin2α-sin2β +2cosαcosβ-2sinαsinβ⇒b2-a2 =(cos2α-sin2β)+(cos2β-sin2α)-2cos(α+β) ⇒b2-a2 =2cos(α+β)cos(α-β)+2cos(α-β) ⇒b2-a2 =cos(α+β)(2+2 cos(α-β)) …(2)
From (1) and (2), we have
b2-a2 =cos(α+β)a2+b2 ⇒b2-a2a2+b2 =cos(α+β)
⇒sinα+β =1-cos2(α+β)⇒sinα+β=1-b2-a2b2+a22 =b4+a4-b4-a4+4a2b2b2+a22 ⇒sinα+β=2aba2+b2
(ii)
a2+b2=sinα+sinβ2+(cosα+cosβ)2 =sin2α+sin2β+cos2α+cos2β+2sinαsinβ+2cosαcosβ =2+2 cos(α-β)⇒b2-a2=(cosα+cosβ)2-sinα+sinβ2⇒b2-a2 = cos2α+cos2β -sin2α-sin2β +2cosαcosβ-2sinαsinβ⇒b2-a2 =(cos2α-sin2β)+(cos2β-sin2α)-2cos(α+β) ⇒b2-a2 =2cos(α+β)cos(α-β)+2cos(α-β) ⇒b2-a2 =cos(α+β)(2+2 cos(α-β)) ⇒b2-a2 =cos(α+β)a2+b2 b2-a2a2+b2 =cos(α+β)
Q31.
Answer :
(i) RHS = cotx-a -cot(x-b)sin(a-b) = cos(x-a)sin(x-a)-cos(x-b)sin(x-b)sin(a-b) = sin(x-b) cos(x-a) -sin(x-a) cos(x-b)sin(x-a) sin(x-b) sin(a-b) =sin(x-b -x +a)sin(x-a) sin(x-b) sin(a-b) = sin(a-b)sin(x-a) sin(x-b) sin(a-b) = 1sin(x-a)sin(x-b) =LHSHence proved.
(ii) RHS = cot(x-a) + tan(x-b)cos(a-b) = cos(x-a)sin(x-a)+sin(x-b)cos(x-b)cos(a-b) = cos(x-b) cos(x-a) + sin(x-a) sin(x-b)cos(a-b) sin(x-a) cos(x-b) =cos(x-b-x+a)cos(a-b) sin(x-a) cos(x-b) ( Using cos(A-B) = cos A cosb B+sin A sin B) =cos(a-b)cos(a-b) sin(x-a) cos(x-b)= 1 sin(x-a) cos(x-b) = RHSHence proved.
(iii) RHS = tan(x-b) -tan(x-a)sin(a-b) =sin(x-b)cos(x-b)-sin(x-a)cos(x-a)sin(a-b) = sin(x-b) cos(x-a) -sin(x-a) cos(x-b)sin(a-b) cos(x-a) cos(x-b) = sin(x-b-x+a)sin(a-b) cos(x-a) cos(x-b) ( Using sin(A-B) = sin Acos B -cos Asin B) =sin(a-b)sin(a-b) cos(x-a) cos(x-b) = 1cos(x-a) cos(x-b) =LHSHence proved.
Q32.
Answer :
Given:
sinα sinβ − cosα cosβ + 1 = 0⇒-(cosα cosβ-sinα sinβ) +1 = 0⇒-cos(α+β) +1 = 0⇒cos(α+β) = 1Therefore, sin(α+β) = 0 ….(1) (Since sinθ = 1-cos2θ ) Hence ,1+cotα tanβ = 1 +cosα sinβ sinα cosβ = sinαcosβ +cosαsinβsinα cosβ = sin(α+β)sinαcosβ = 0 …From eq (1) Hence proved.
Q33.
Answer :
LHS = 2cot(α-β) =2(1+tanαtanβ)tanα-tanβ
=2+2x+1x-1x+1-x+1 =2+2×2-22 =2×22 =x2 =RHS Hence proved.
Page 7.26 Ex – 7.2
Q1.
Answer :
(i)
Let fθ =12 sin θ – 5 cosθWe know that-122+(-5)2≤12 sin θ – 5 cosθ≤122+(-5)2-144+25≤12 sin θ – 5 cosθ≤144+25-13≤12 sinθ – 5 cosθ≤13Hence the maximum and minumun values of fθ are 13 and -13, respectively .
(ii)
Let f(θ) = 12 cosθ +5 sinθ +4We know that-122+52≤12 cosθ +5 sinθ ≤122+52 for all θ⇒-169≤12 cosθ +5 sinθ ≤169⇒-13≤12 cosθ +5 sinθ ≤13⇒-9≤12 cosθ +5 sinθ +4≤17Hence, the maximum and minimum vaues of fθ are 17 and -9, respectively.
(iii)
Let fθ=5 cosθ +3 sinπ6-θ +4Now fθ = 5cosθ+3sin30°cosθ -cos30°sinθ+4 =5cosθ +32cosθ -332sinθ +4 =132cosθ-332sinθ +4We know that-1322+-3322≤132cosθ-332sinθ≤1322+-3322 for all θTherefore,-169+274 ≤132cosθ-332sinθ ≤169+274⇒-142+4≤132cosθ-332sinθ +4≤142+4⇒-3≤132cosθ-332sinθ +4≤11Hence, maximum and minimun values of fθ are 11 and -3, respectively .
(iv)
Let fθ =sinθ-cosθ+1We know that-12+(-1)2≤sinθ-cosθ≤12+(-1)2 for all θ⇒-2≤sinθ-cosθ≤2⇒-2+1≤sinθ-cosθ +1≤2+1Hence maximum and minimum values of f(θ) are 1+2 and 1-2 , respectively .
Q2.
Answer :
(i) Let fθ =3 sinθ – cosθDividing and multiplying by3+1 , i.e. by 2, we get: fθ =232 sinθ -12 cosθ⇒f(θ)= 2cosπ6sinθ-sinπ6cosθ⇒f(θ) = 2sinθ-π6Again, fθ =232 sinθ -12 cosθ⇒ fθ =2sinπ3 sinθ -cosπ3 cosθ⇒fθ =-2cosπ3+θ
(ii) Let fθ=cosθ-sinθDividing and multiplying by 12+12, i.e. by2, we get : fθ=212cosθ-12sinθ⇒ fθ=2(cos45°cosθ-sin45°sinθ) ⇒ fθ=2cosπ4+θAgain, fθ=212cosθ-12sinθ⇒ fθ=2(sin45°cosθ-cos45°sinθ)⇒f(θ) =2 sinπ4-θ
(iii) Let f(θ) =24 cosθ + 7sinθDividing and multiplying by 242+72, i.e.by 25, we get: f(θ) =252425 cosθ +725sinθ⇒f(θ) =25(sinα cosθ+ cosα sinθ), where sinα =2425 and cosα =725⇒f(θ) =25 sin(α+θ), where tanα = 247 .Again, f(θ) =252425 cosθ +725sinθ⇒f(θ) =25(cosα cosθ+ sinα sinθ), where cosα=2425, sinα= 725.⇒f(θ) =25 cos(α-θ), where tanα =724.
Q3.
Answer :
Let fθ = sin100° – sin10°Multiplying and dividing by 12+12 , i.e. by 2 , we get: 212sin100°-12sin10° =2cos45°sin(90°+10°) -sin45°sin10° =2cos45°cos10°-sin45°sin10° =2 cos(45°+10°) =2co s55° , which is positive since cos is positive in the first quadrant.
Q4.
Answer :
Let fθ =(23+3) sinθ +23cosθWe know that,-23+32+232≤fθ≤23+32+232⇒-12+9+123+12≤fθ≤12+9+123+12⇒-33+123 ≤fθ≤33+123Disclaimer : Instead of -23+15 and 23+15, it should be -33+123and 33+123.
Page 7.27 (Very Short Answers)
Q1.
Answer :
Given:γ=-π-(α+β)Also,λ=sin2α+sin2β-sin2-(π-(α+β)sinα sinβ cos(-(π-(α+β)) =sin2α+sin2β-(sin(α+β))2-(sinα sinβcos(α+β)) sin π-θ=sin θ and cosπ-θ=-cos θ = sin2α+sin2β-sin2α cos2β-cos2α sin2β-2sinα sinβ cosα cosβ-(sinα sinβ cosα cosβ-sin2α sin2β) =sin2α(1-cos2β)+sin2β(1-cos2α)-2sinα sinβ cosα cosβsin2α sin2β -sinα sinβ cosα cosβ =2sin2α sin2β-2sinα sinβ cosα cosβsin2α sin2β-sinα sinβ cosα cosβ =2
Q2.
Answer :
Given:x cosθ =ycosθcos2π3-sinθ sin2π3=zcosθcos4π3-sinθ sin4π3⇒xcosθ =y-12cosθ-32sinθ =z-12cosθ+32sinθ ⇒x=y2-1-3tanθ=z2-1+3tanθx=y2-1-3tanθz=y-1-3tanθ-1+3tanθNow,1x+1y+1z =2y-1-3tanθ+1y+-1+3tanθy-1-3tanθ =2+-1-3tanθ+-1+3tanθy-1-3tanθ =0
Q3.
Answer :
Let fx =3 cos x +4 sin x +5We know that-32+42≤3 cosx +4 sinx≤32+42⇒-5≤3 cosx +4 sinx≤5⇒-5+5≤3 cosx +4 sinx+5≤5+5⇒0≤f(x)≤10Hence, maximum and minimum vales of f(x) are 0 and 10 respectively .
Q4.
Answer :
Let fθ=12sinθ -9 sin2θ =-9sin2θ-12 sin θ = -3sin θ2-2.3 sin θ.2+22-4 =-3 sinθ-22-4 =4-3 sinθ-22Minimum value of 3 sinθ-22 is 0.Therefore, maximum value of 4-3 sinθ-22 would be 4.
Q5.
Answer :
Let fθ=12sinθ -9 sin2θ =-9sin2θ-12 sin θ = -3sin θ2-2.3 sin θ.2+22-4 =-3 sinθ-22-4 =4-3 sinθ-22Minimum value of 3 sinθ-22 is 0.Therefore, maximum value of fθ= 4-3 sinθ-22 is 4.We are given that 12sinθ -9 sin2θ will attain its maximum value at θ=α.∴ 12sinα -9 sin2α =4⇒-9sin2α+12sinα-4=0⇒9sin2α-12 sinα+4=0⇒9sin2α-6sinα-6sinα+4=0⇒3sinα3sinα-2-23sinα-2=0⇒3sinα-23sinα-2=0∴ sinα=23
Q6.
Answer :
Let fθ=5 cosθ+3 cosθ+π3+3 =5 cosθ+3(cosθ cos60° -sinθ sin60°) +3 =5 cosθ+32cosθ-332sinθ +3 =132cosθ-332sinθ +3We know that-1322+3322≤132cosθ-332sinθ≤1322+3322-1694+274≤132cosθ-332sinθ≤1694+274⇒-142≤132cosθ-332sinθ≤142⇒-7+3≤132cosθ-332sinθ+3≤7+3Hence, f(θ) lies in the interval -4,10.
Q7.
Answer :
tan 2B = tan(B+B) =tan(A+B-(A-B)) = tan(A+B) – tan(A-B) 1+tan(A+B)tan(A-B) =p-q1+pq ∵tan(A+B)=p and tan(A-B)=q
Q8.
Answer :
cos(x-y)cos(x+y)=mn⇒cosx cosy+ sinx sinycosx cosy – sinx siny=mn⇒1+tanx tany1- tanx tany=mn Dividing numerator and denominator of LHS by cosx cosy⇒n+ntanx tany =m-mtanx tany⇒tanxtany(m+n)=m-n⇒tanx tany =m-nm+n
Q9.
Answer :
a=b cos120°=c cos 240°⇒a =-12b=-12cTherefore,ab+bc+ca =-12b×b +b×b +b×-12b =-b2+b2 =0
Q10.
Answer :
tanA tanB tanC =tanA tanB tan(A+B) Using A+B=C =tanA tanB×tanA+tanB1-tanA tanB =tan2AtanB+ tanA tan2B1-tanA tanB =tan2AtanB+ tanA tan2B+tanA+tanB-tanA-tanB1- tanA tanB =-tanA(1-tanAtanB)-tanB(1-tanAtanB)+tanA+tanB1-tanA tanB =-(1-tanAtanB)tanA+tanB+tanA+tanB1-tanA tanB =tanA+tanB1-tanA tanB-tanA-tanB =tan(A+B)-tanA-tanB =tanC-tanA-tanB
Q11.
Answer :
cos(α+β) =cosαcosβ -sinα sinβ =2cosαcosβ -2sinα sinβ +2-22
=sin2α +cos2α+sin2β +cos2β+2cosαcosβ -2sinα sinβ-22
=(sinα-sinβ)2+(cosα+cosβ)2-22
=a2+b2-22
Q12.
Answer :
tan(α+β) =tanα+tanβ1-tanαtanβ =11+2-x+11+2x+11-1(1+2-x)(1+2x+1) =1+2x+1+1+2-x1+2x+1+2-x+2-x+x+1-1 =2+2x+1+2-x2+2x+1+2-x =1Therefore, α+β =tan-1(1)=π4.
Page 7.27 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q1.
Answer :
(b) 32
sin275°-sin215° =sin275°-cos275° sin90°-θ=cosθ Now, sin75° =sin(45°+30°) =sin45°cos30°+cos45°sin30° =12×32+12×12 =3+122cos75° =cos(45°+30°) =cos45° cos30° -sin45° sin30° =12×32-12×12 =3-122Hence ,sin275°-cos275°=3+1222-3-1222 =3+1+23-3-1+238 =438 =32
Q2.
Answer :
(b) −1
secAcosBcosC-sinBsinC=cosBcosπ-A+B-sinBsinπ-A+BcosA
We know that, cosπ-θ=-cosθ and sinπ-θ=sinθ,
∴secAcosBcosC-sinBsinC=cosBcosA+B-sinBsinA+BcosA
Now, using the identities cosA+B=cosAcosB-sinAsinB and sinA+B=sinAcosB+cosAsinB, we get
secAcosBcosC-sinBsinC=-cosAcosB2+cosBsinAsinB-sinBsinAcosB-sin2BcosAcosA
⇒secAcosBcosC-sinBsinC=-cosAcos2B+sin2BcosA⇒secAcosBcosC-sinBsinC=-cosAcosA=-1
Q3.
Answer :
(c) 3
tan20°+tan40°+3tan20° tan40°=tan 60°(1-tan20°tan40°) +tan60°tan20°tan40° Using tan60°=tan20+tan401-tan20tan40 and tan60°=3=tan60°-tan60°tan20°tan40°+tan60°tan20°tan40°=tan60° =3
Page 7.28 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q4.
Answer :
(d) π4
tan(A+B) =tanA+tanB1-tanAtanB =aa+1+12a+11-aa+1(2a+1) = 2a2+a+a+12a2+3a+1-a =2a2+2a+12a2+2a+1 =1Therefore, A+B = tan-1(1) = π4.
Q5.
Answer :
(a) 0
3 sin θ +4 cos θ =535sin θ +45cos θ =1Let cos α=35 and sin α=45.∴ cos α sin θ +sinαcos θ =1⇒ sin α+θ =sinπ2⇒α+θ =π2⇒θ =π2-α ….(1)We have to find the value of 4 sin θ -3 cos θ. 4 sinπ2-α -3 cosπ2-α …{From eq (1)} =4cos α-3sinα =4 × 35-3×45 ∵ cos α=35 and sin α=45 =0
Q6.
Answer :
(c) 16
In triangle ABC,
A+B+C=πWe know that tanA+B+ C=tan A+tan B+tan C-tanA tanB tan C1-tan A tan B-tan B tanC-tan C tan Aand tan π=0.∴ tan A+tan B+tan C-tanA tanB tan C=0tan A+tan B+tan C=tanA tanB tan C
If tan A+tan B+tan C =6,
tan A tan B tan C =6
⇒1tanA tanB tanC=16⇒cotA cotB cotC =16
Q7.
Answer :
(a) tan 3A tan 2A tan A
3A=2A+A⇒tan 3A=tan(2A+A) =tan2A+tanA1-tan2AtanA⇒tan 3A-tan3A tan2A tanA =tan 2A+tanA⇒tan 3A-tan 2A- tanA=tan3A tan2A tanA
Q8.
Answer :
(c) 1
Using tan(180-A) = -tan A, we get:
C=π-(A+B)Now,tanA+tanB+tanCtanA tanB tanC=tanA+tanB+tanπ-(A+B)tanA tanB tanπ-(A+B)=tanA+tanB-tan(A+B)-tanA tanB tan(A+B)=tanA+tanB-tan A+tan B1-tanA tanB-tanA tanB×tan A+tan B1-tanA tanB
= tanA+tanB-tan2AtanB-tanA tan2B-tanA-tanB-tan2A tanB-tanA tan2B=-tan2AtanB-tanA tan2B-tan2AtanB-tanA tan2B=1
Q9.
Answer :
(b) 60⁰
cosP=17 , cosQ=1314
Therefore, sin P =1-149=437and sinQ =1-169196=3314
Hence, tan P =43, tan Q =3313
cos(P-Q) =cosP cosQ + sinP sinQ
=17×1314+437×3314=13+3698
=4998
∴ cos P-Q=12⇒ P-Q=cos-112⇒ P-Q=60°
Q10.
Answer :
(a) sin α
Given:cot(α+β) =0⇒cos(α+β)sin(α+β)=0⇒cos(α+β)=0⇒α+β=π2
Therefore, sinα+2β=sin α+α+β=sin α
Q11.
Answer :
(a) tan 55°
cos10°+sin10°cos10°-sin10°=1+tan10°1-tan10° Dividing the numerator and denominator by cos 10°=tan45°+tan10°1-tan45°×tan10°=tan(45°+10°) Using tan(A+B) =tanA+tanB1-tanA tanB= tan55°
Q12.
Answer :
(a) 12cos 2θ
cos2π6+θ-sin2π6-θ=cosπ6+θ+π6-θ cosπ6+θ-π6+θ Using cos(A+B) cos(A-B) =cos2A- sin2B=cos2π6cos2θ=12cos2θ As cosπ3=12
Q13.
Answer :
(a) 1+k1-k
cos(θ1-θ2)cos(θ1+θ2)=cosθ1cosθ2+sinθ1 sin θ2cosθ1cosθ2-sinθ1 sin θ2Dividing numerator and denominator by cos θ1cos θ2 , we get:
1+tanθ1tanθ21-tanθ1tanθ2=1+k1-k
Q14.
Answer :
(c) ±13sin π cos θ=cos π sin θAs we know that sin θ =-cos π2+θ⇒ -cos π2+π cos θ=cos π sin θ⇒-π2-π cos θ=π sin θ⇒π sin θ-π cos θ=π2⇒ sin θ- cos θ=12Squaring both sides we get, sin2θ+cos2θ-2 sinθ cosθ=14⇒1-sin 2θ=14⇒sin 2θ =13And we know that sin θ=cos π2-θ⇒cos π2-π cos θ=cos π sin θ⇒π2-π cos θ=π sin θ⇒π sin θ+π cos θ=π2⇒ sin θ+cos θ=12Squaring both sides we get, ⇒sin 2θ+cos 2θ+2sin θ cos θ=14⇒1+sin 2θ=14⇒sin 2θ=13Therefore, sin 2θ=±13
Q15.
Answer :
(c) cos 2A
2sin2B+4cos(A+B) sinA sinB+cos2(A+B)=2sin2B+4cosAcosB sinA sinB-4sin2A sin2B+cos(A+B+A+B)=2sin2B+4cosAcosB sinA sinB-4sin2A sin2B+cos2(A+B)-sin2(A+B) Using cos(x+x)=cos2x-sin2x=2sin2B+4cosAcosB sinA sinB-4sin2A sin2B+cos2Acos2B+sin2A sin2B-2cosA cosB sinA sinB-sin2A cos2B-cos2A sin2B-2sinA sinB cos A cos =sin2B+sin2B-3 sin2A sin2B+cos2Acos2B-sin2A cos2B-cos2A sin2B=1-cos2B-3sin2A sin2B+sin2B+cos2A cos2B-sin2A cos2B-cos2A sin2B=1+sin2B(1-cos2A)-3sin2A sin2B-cos2B(1-cos2A)-sin2A cos2B=1+sin2B sin2A-3sin2A sin2B-sin2A cos2B-cos2B sin2A=1-2 sin2A(sin2B+cos2B)=1-2 sin2A=cos2A-sin2A= cos2A
Q16.
Answer :
(b) cos 2A
cos(36°-A)cos(36°+A)+cos(54°+A)cos(54°-A)=cos(36°-A) cos(36°+A) +sin90°-(54°+A) sin90°-(54°-A) Since sin(90°-θ)= cosθ=cos(36°-A)cos(36°+A)+sin(36°-A)sin(36°+A)=cos(36°+A-36°+A) Using cos(A-B) formula=cos 2A
Page 7.29 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q17.
Answer :
(c) a2-2
Given:tanπ4+θ+tanπ4-θ =a⇒tanπ4+θ+tanπ4-θ2=a2⇒tan2π4+θ+tan2π4-θ+2 tanπ4-θ tanπ4+θ =a2⇒tan2π4+θ+tan2π4-θ=a2-2 tanπ4-θ tanπ4+θ ⇒tan2π4+θ+tan2π4-θ=a2-2tan45°-tanθ1+tan45° tanθ×tan45°+tanθ1-tan45° tanθ ⇒tan2π4+θ+tan2π4-θ=a2-21°-tanθ1+ tanθ×1+tanθ1- tanθ⇒tan2π4+θ+tan2π4-θ=a2-21-tan2θ1-tan2θ⇒tan2π4+θ+tan2π4-θ=a2-2
Q18.
Answer :
(b) 19 π24
Given:tan(A-B)=1 and sec(A+B) =23⇒A-B=π4…(1) and A+B=π6…(2)Adding these equations we get: 2A=π4+π6⇒A=5π24⇒Smallest possible value of B=π-5π24=19π24.
Q19.
Answer :
(a) 2
tan(A-B)=tanπ4⇒tanA-tanB1+tanA tanB=1⇒tanA-tanB=1+tanAtanB …(1) Now,(1+tanA)(1-tanB ) =1+tanA-tanB-tanA tanB =1+1+tanAtanB-tanA tanB Using eq (1) = 2
Q20.
Answer :
(b) 32
Let f(θ) =sin2(90+30+θ)+ sin2(90+30-θ) =cos(30+θ)2+cos(30-θ)2 Using sin(90+A) = cosA =32cosθ-12sinθ2+32cosθ+12sinθ2 = 34cos2θ+14sin2θ-32cosθ sinθ+ 34cos2θ+14sin2θ+32cosθ sinθ =32cos2θ+12sin2θ =321-sin2 θ+12sin2θ =32-32sin2 θ+12sin2θ =32-sin2θFor f(θ) to be maximum, sin2 θ must have minimum value, which is 0.∴ 32 is the maximum value of fθ.
Q21.
Answer :
(a) 15
tanA tanB = sinA sinBcosA cosB=2 Given …(1)
Also,cos(A-B)=35⇒cosA cosB+sinA sinB=35
∴ sin A sinB =35-cos Acos B …(2) Substituting eq (2) in eq (1), we get:
⇒35-cosA cosBcosA cosB=2
⇒3cosA cosB=35
⇒cosA cosB =15
Q22.
Answer :
(c)-12
tan135° =tan(90°+45°) = -tan45° = -1Or, tan(69°+66°)=tan69°+tan66°1-tan69° tan66°⇒-1 =tan69°+tan66°1-tan69° tan66°⇒tan69°+tan66°-tan69°tan66°=-1Therefore,2k=-1⇒k=-12
5. TRANSFORMATION FORMULAE
Page 8.7 Ex – 8.1
Q1.
Answer :
(i) 2sin 3θ cos θ=sin 3θ+θ+sin 3θ-θ ∵2sin A cos B=sin(A+B)+sin(A-B)=sin 4θ + sin 2θ
(ii) 2cos 3θ sin 2θ=sin 3θ+2θ-sin 3θ-2θ ∵2 cos A sin B=sin(A+B)-sin(A-B)=sin 5θ – sin θ
(iii) 2sin 4θ sin 3θ=cos 4θ-3θ-cos 4θ+3θ ∵2 sin A sin B=cos(A-B)-cos(A+B)=cos θ – cos 7θ
(iv) 2cos 7θ cos 3θ=cos 7θ+3θ+cos 7θ-3θ ∵2 cos A cos B=cos(A+B)+cos(A-B)=cos 10θ + cos 4θ
Q2.
Answer :
(i) LHS = 2sin 5π12 sin π12 = cos 5π12 – π12 – cos 5π12 + π12 ∵2 sin A sin B = cos (A – B) – cos (A + B)= cos π3 – cos π2= 12 – 0= 12RHS = 12Hence, LHS = RHS
(ii) LHS = 2cos 5π12 cos π12 = cos 5π12 + π12 + cos 5π12 – π12 ∵2 cos A cos B = cos (A+B) + cos (A-B)= cos π2 + cos π3= 0 + 12= 12RHS = 12Hence, LHS = RHS
(iii) LHS = 2sin 5π12 cos π12 = sin 5π12 + π12 + sin 5π12 – π12 ∵2 sin A cos B = sin (A + B) + sin (A – B)= sin π2 + sin π3= 1 + 32= 2 + 32RHS = 2 + 32 Hence, LHS = RHS
Q3.
Answer :
(i) LHS = 2 sin 50° cos 85°= sin 50° + 85° + sin 50° – 85°2 ∵sin A cos B=12sin (A + B) + sin (A – B)= sin 135° + sin -35°2= sin 135° – sin 35°2= cos 45° – sin 35°2 ∵sin 90° + 45° = cos 45°= 1212 – sin 35°= 121 – 2sin 35°2= 1 – 2sin 35°22RHS = 1-2sin 35°22Hence, LHS = RHS
(ii) LHS = 2sin 25° cos 115°= sin 25°+115° + sin 25°-115°2 ∵sin A cos B = 12sin (A + B) + sin (A – B)= sin 140° + sin -90°2= sin 140° – sin 90°2= sin 140° – 12 RHS = sin 140°-12Hence, LHS = RHS
Q4.
Answer :
LHS = 4cos θ cos π3 + θ cos π3 – θ= 2cos θ2 cos π3 + θ cos π3 – θ= 2cos θcos π3 + θ + π3 – θ + cos π3 + θ – π3 + 2θ ∵2cos A cos B = cos (A + B) + cos (A – B)= 2cos θcos 2π3 + cos 2θ= 2cos θ-12 + cos 2θ= -cos θ + 2cos θ cos 2θ= -cos θ + cos θ + 2θ + cos θ – 2θ= -cos θ + cos 3θ + cos-θ= -cos θ + cos 3θ + cos θ= cos 3θRHS = cos 3θHence, LHS = RHS
Q5.
Answer :
(i) LHS = cos 10° cos 30° cos 50° cos 70°= 12 2cos 10° cos 50° cos 30° cos 70°= 12 cos 10° + 50° + cos 10° – 50° cos 30° cos 70° ∵2cos A cos B = cosA + B – cos A – B= 12 cos 60° + cos -40° cos 30° cos 70°= 12 12 + cos 40°32×cos 70° = 34cos 70°12 + cos 40°= 38cos 70° + 34cos 70° cos 40°= 38cos 70° + 382cos 70° cos 40°= 38cos 70° + 38cos 70° + 40° + cos 70° – 40°= 38cos 70° + 38cos 110°+cos 30°= 38cos 70° + 38cos 180° – 70° + 32= 32cos 70° – 38cos 70° + 316 ∵cos 180° – 70° = -cos 70°= 316 = RHS
(ii) LHS = cos 40° cos 80° cos 160°= 122cos 40° cos 80° cos 160°= 12cos 40° + 80° + cos 40° – 80° cos 160°= 12cos 120° + cos -40° cos 160°= 12cos 160°-12 + cos 40°= -14cos 160° + 12cos 160° cos 40° = -14cos 160° + 142cos 160° cos 40°= -14cos 160° +14cos 160° + 40° + cos 160° – 40°= -14cos 160° + 14cos 200° + cos 120°= -14cos 160° + 14cos 360°-160° -12= -14cos 160° + 14cos 160° – 18 ∵cos 360° – 160° = cos 160°= -18 = RHS
(iii) LHS = sin 20° sin 40° sin 80°=122sin 20° sin 40°sin 80°=12cos 20° – 40° – cos 20° + 40° sin 80°=12cos 20° – 12 sin 80°=12sin 80°cos 20° – 12=12sin 80° cos 20° – 14sin 80°=12sin 90° – 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°=12cos 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80° = 142cos 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°=14cos 10° + 20° + cos 10° – 20° – 14sin 80°=14cos 30° + cos -10° – 14sin 80°=14cos 30° + cos 90°-80° -14sin 80°=38+14sin 80° – 14sin 80° ∵cos 90° – 80° = sin 80°=38 = RHS
(iv) LHS = cos 20° cos 40° cos 80°=122cos 20° cos 40° cos 80°=12cos 20° + 40° + cos20° – 40° cos 80°=12cos 60° + cos -20° cos 80°=12cos 80°12 + cos 20°=14cos 80° + 12cos 80° cos 20° = 14cos 80° + 142cos 80° cos 20°= 14cos 80° + 14cos 80° + 20° + cos 80° – 20°= 14cos 80° + 14cos 100° + cos 60°= 14cos 80° + 14cos 180° – 80° + 12= 14cos 80° – 14cos 80° + 18 ∵cos 180° – 80° = -cos 80°= 18 = RHS
(v) LHS = tan 20° tan 40° tan 60° tan 80° =tan 60°sin 20° sin 40° sin 80°cos 20° cos 40° cos 80°=3 × 122sin 20° sin 40°sin 80°122cos 20° cos 40°cos 80°=3×12cos 20° – 40° – cos 20° + 40° sin 80°12cos 20° + 40° + cos20° – 40° cos 80°=3×12cos -20° – cos 60° sin 80°12cos 60° + cos-20° cos 80°=3×12sin 80°cos 20° – 1212cos 80°12 + cos 20°=3×12sin 80° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 12cos 80° cos20°=3×12sin 90° – 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 12cos 80° cos 20°=3×12cos 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 12cos 80° cos 20°
= 3×142cos 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 142cos 80° cos 20°= 3×14cos 10° + 20° + cos 10°-20°-14sin 80°14cos 80° + 14cos 80° + 20° + cos 80° – 20°= 3×14cos 30° + cos -10° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 14cos 100° + cos 60°= 3×14cos 30° + cos 90° – 80° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 14cos 180° – 80° + 12= 3×38 + 14sin 80° – 14sin 80° 14cos 80° – 14cos 80° + 18 cos 90° – 80° = sin 80°, and cos180°-80°=-cos80°= 3×3818= 3 = RHS
(vi) LHS = tan 20° tan 30° tan 60° tan 80° =tan 30°sin 20° sin 40° sin 80°cos 20° cos 40° cos 80°=13×122sin 20° sin 40°sin 80°122cos 20° cos 40°cos 80°=13×12cos 20° – 40° – cos 20° + 40°sin 80°12cos 20° + 40° + cos 20° – 40°cos 80°=13×12cos 20° – 12sin 80°12cos 60° + cos -20°cos 80°=13×12sin 80°cos 20°- 1212cos 80°12 + cos 20°=13×12sin 80° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 12cos 80° cos 20°=13×12sin 90° – 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 12cos 80° cos 20°=13×12cos 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 12cos 80° cos 20°
=3×142cos 10° cos 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 142cos 80° cos 20°=3×14cos 10° + 20° + cos 10° – 20° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 14cos 80° + 20° +cos 80° – 20°=3×14cos 30° + cos -10° -14sin 80°14cos 80°+14cos 100° + cos 60°=3×14cos 30° + cos 90° -80° – 14sin 80°14cos 80° + 14cos 180° – 80° + 12=3×38 + 14sin 80° – 14sin 80° 14cos 80° -14cos80°+18 ∵cos 90° – 80° = sin 80°, cos 180° – 80° =-cos 80°=3×3818= 3 = RHS
(vii) LHS = sin 10° sin 50° sin 60° sin 70°=12sin 60° 2sin 10° sin 50°sin 70°=12×32cos 10° – 50° – cos 10° + 50°sin 70°=34cos -40° – 12sin 70°=34sin 70°cos 40° – 12=34sin 70° cos 40° – 38sin 70°=34sin 90° – 20° cos 40° – 38sin 70°=34cos 20° cos 40° – 38sin 70° =382cos 20° cos 40° – 38sin 70°=38cos 20° +40° + cos 20° – 40° – 38sin 70°=38cos 60° + cos -20° -38sin 70°=38cos 60° + cos 90° – 70° – 38sin 70°=316+38sin 70° – 38sin 70° ∵cos 90° – 70° = sin 70°=316=RHS
(viii) LHS = sin 20° sin 40°sin 60° sin 80°=12sin 60° 2sin 20° sin 40°sin 80°=12×32cos 20° – 40° – cos 20° + 40°sin 80°=34cos 20° – 12sin 80°=34sin 80°cos 20° – 12=34sin 80° cos 20° – 38sin 80°=34sin 90°-10°cos 20°-38sin 80°=34cos 10° cos 20° – 38sin80° =382cos 10° cos 20° – 38sin 80°=38cos 10° + 20° + cos 10° – 20° -38sin 80°=38cos 30° + cos -10° – 38sin 80°=38cos 30° + cos 90°-80°-38sin 80°=316+38sin 80° -38sin 80° ∵cos 90° – 80° = sin 80°=316 = RHS
Q6.
Answer :
(i) Consider LHS:sin A sin B- C + sin B sin C -A + sin C sin A – B= 122sin A sin B – C + 122sin B sin C – A + 122sin C sin A – B= 12cos A – B – C – cos A + B – C + 12cos B – C – A – cos B + C – A + 12cos C – A – B -cos C + A – B= 12cos A – B + C – cos A + B – C + 12cos B – C + A – cosB + C – A + 12cosC – A + B – cosC + A – B= 12cosA – B + C – 12cos A + B- C + 12cos B – C + A – 12cos B + C – A + 12cos C – A + B – 12cosC + A – B= 12cosA – B + C – 12cosA + B – C + 12cosA + B – C – 12cosB + C – A + 12cosB + C – A – 12cosA – B + C= 0= RHS
(ii) Consider LHS:sin B – C cos A – D + sin C – A cos B – D + sin A – B cos C – D = 122sin B – C cos A -D + 122sin C – A cos B – D+122sin A – B cosC- D= 12sin B – C + A – D + sin B – C – A – D + 12sin C – A + B – D + sin C – A – B – D + 12sin A – B + C – D+ sin A – B – C – D= 12sin B – C + A – D + sin B – C – A + D + 12sin C – A + B – D + sin C – A – B +D + 12sin A – B + C – D + sin A – B – C + D=12sin B – C + A – D + sin B – C – A + D + 12sin –C + A – B + D + sin –C + A+ B – D + 12sin–A + B – C + D + sin A – B- C + D=12sinB-C+A-D+12sinB-C-A+D-12sin-C+A-B+D-12sin-C+A+B-D-12sin-A+B-C+D+12sinA-B-C+D=0= RHS
Q7.
Answer :
LHS = tanθtan60°-θtan60°+θ=sinθsin60°-θsin60°+θcosθcos60°-θcos60°+θ =sinθsin260°-sin2θcosθcos260°-sin2θ=sinθ34-sin2θcosθ14-sin2θ=sinθ3-4sin2θcosθ1-4sin2θ =3sinθ-4sin3θ4cos3θ-3cosθ=sin3θcos3θ=tan3θ=RHS
Q8.
Answer :
Let x = cos α cos β⇒x = 122cos α cos β⇒x = 12cos α + β + cos α – β⇒x = 12cos α – β + cos 90°⇒x = 12cos α – βNow,-1 ≤ cos α – β ≤ 1⇒-12≤12cosα-β≤12⇒-12≤x≤12⇒-12 ≤ cos α cos β ≤ 12Hence, 12 is the maximum value of cos α cos β.
Page 8.19 Ex – 8.2
Q1.
Answer :
(i) sin 12θ + sin 4θ=2sin 12θ + 4θ2 cos12θ – 4θ2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2=2 sin 8θ cos 4θ
(ii) sin 5θ – sin θ=2sin 5θ – θ2 cos 5θ + θ2 ∵ sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2=2 sin 2θ cos 3θ
(iii) cos 12θ + cos 8θ= 2cos 12θ + 8θ2 cos 12θ – 8θ2 ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2=2 cos 10θ cos 2θ
(iv) cos 12θ – cos 4θ=-2sin 12θ + 4θ2 sin 12θ – 4θ2 ∵ cos A – cos B = -2sin A + B2 sin A – B2=-2 sin 8θ sin 4θ
(v) sin 2θ + cos 4θ= sin 2θ + sin π2- 4θ= 2sin 2θ + π2 – 4θ2 cos 2θ – π2 + 4θ2 ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2= 2sin π4 – θ cos 3θ – π4
Q2.
Answer :
(i) Consider LHS:sin 38° + sin 22°= 2sin 38° + 22°2 cos 38° – 22°2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 30° cos 8°= 2×12cos(90°-8°)= sin 82°= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(ii) Consider LHS:cos 100° + cos 20°= 2cos 100° + 20°2 cos 100° – 20°2 ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2= 2cos 60° cos 40°= 2×12cos 40°= cos 40°Hence, LHS=RHS.
(iii) Consider LHS:sin 50° + sin 10°= 2sin 50° + 10°2 cos 50° – 10°2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 30° cos 20°=2×12cos 20°= cos 20°Hence, LHS = RHS.
(iv) Consider LHS:sin 23° + sin 37°= 2sin 23° + 37°2 cos 23°- 37°2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 30° cos -7°= 2sin 30°cos 7°= 2×12cos 7°= cos 7°Hence, LHS=RHS.
(v) Consider LHS:sin 105° + cos 105°= sin 105° + cos 90° + 15°= sin 105° – sin 15°= 2sin 105° – 15°2 cos 105° + 15°2 ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2= 2sin 45°cos 60°= 2sin 90° – 45° cos 60°= 2×12cos45°=cos 45°Hence, LHS=RHS.
(vi) Consider LHS:sin 40° + sin 20°= 2sin 40° + 20°2 cos 40° – 20°2 ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2= 2sin 30° cos 10°= 2×12cos 10°= cos10°Hence, LHS = RHS.
Q3.
Answer :
(i) Consider LHS:cos 55° + cos 65° + cos 175°= 2cos 55° + 65°2 cos 55° – 65°2 + cos 175° ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2= 2cos 60° cos-5° + cos 175°= 2×12cos 5° + cos 175°=cos 5° + cos 175°= 2cos 5° + 175°2 cos 5° – 175°2= 2cos 90° cos 85°= 0Hence, LHS=RHS.
(ii) Consider LHS:sin 50° – sin 70° + sin 10°= 2sin 50° -70°2 cos 50° + 70°2 + sin 10° ∵ sin A – sin B = 2sin A – B2 cos A + B2= 2sin -10° cos 60° + sin 10°=2×12sin -10° + sin 10°= -sin 10°+sin 10°= 0Hence, LHS=RHS.
(iii) Consider LHS:cos 80° + cos 40° – cos 20°= 2cos 80° + 40°2 cos 80° – 40°2 – cos 20° ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2= 2cos 60° cos 20°- cos 20°= 2×12cos 20° – cos20°= cos 20° – cos 20°= 0Hence, LHS=RHS.
(iv) Consider LHS:cos 20° + cos 100° + cos 140°= 2cos 20° + 100°2 cos 20° – 100°2 + cos 140° ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2= 2cos 60° cos -40° + cos 140°= 2×12cos 40° + cos 140°= cos 40° + cos 140°= 2cos 40° + 140°2 cos 40° – 140°2= 2 cos 90° cos 50°= 0Hence, LHS=RHS.
(v) LHS=sin5π18-cos4π9=sin5π18- cosπ2-π18=sin5π18- sinπ18=2sin5π18-π182cos5π18+π182 ∵ sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2=2sinπ9cosπ6=2sinπ9cosπ6=2×32sinπ9=3sinπ9=RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(vi) LHS= cos π12 – sin π12= cos π2 – 5π12 – sin π12= sin 5π12 – sin π12= 2sin 5π12 – π122 cos 5π12 + π122 ∵ sin A – sin B = 2sin A – B2 cos A + B2= 2sin π6 cos π4= 2×12×12=12Hence, LHS=RHS.
(vii) Consider LHS:sin 80° – cos 70°= sin 80° – cos 90° – 20°= sin 80° – sin 20°= 2sin 80° – 20°2 cos 80° + 20°2 ∵ sin A – sin B = 2sin A – B2 cos A + B2= 2sin 30° cos 50°= 2×12cos 50°= cos 50°= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(viii) Consider LHS:sin 51° + cos 81°= sin 51° + cos 90° – 9°= sin 51° + sin 9°= 2sin 51° + 9°2 cos 51° – 9°2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 30° cos 21°= 2×12cos21°= cos21°= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
Q4.
Answer :
(i) Consider LHS:cos 3π4 + x – cos 3π4 – x=-2sin3π4 + x + 3π4 – x2 sin 3π4 + x – 3π4 – x2 ∵ cos A – cos B = -2sin A + B2 sinA – B2= -2sin3π4 sin x= -2sin π- π4 sin x= -2sin π4 sin x= -2sin x
(ii) Consider LHS:cos π4 + x + cosπ4 – x=2cos π4 + x + π4 – x2cos π4 + x – π4 + x2 ∵ cos A + cos B = 2cos A + B2 cos A – B2 = 2cos π4 + x + π4 – x2cos π4+ x – π4 + x2= 2cos π4 cos x= 2×12×cosx= 2cosx=RHSHence, LHS=RHS
Q5.
Answer :
(i) Consider LHS:sin 65° + cos 65°= sin 65° + cos 90° – 25°= sin 65° + sin 25°= 2sin 65° + 25°2 cos 65° – 25°2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 45° cos 20°= 2×12 cos 20°= 2cos 20°= RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(ii) Consider LHS:sin 47° + cos 77°= sin 47° + cos 90°-13°= sin 47° + sin 13°= 2sin 47° + 13°2 cos 47° – 13°2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 30° cos 17°= 2×12cos 17°= cos 17°= RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
Q6.
Answer :
(i) Consider LHS: cos 3A + cos 5A + cos 7A + cos 15A= 2cos 3A + 5A2 cos 3A – 5A2 + 2cos 7A + 15A2 cos 7A – 15A2 ∵ cos A + cos B = 2cos A + B2 cos A – B2= 2cos 4A cos-A + 2cos 11A cos-4A
= 2cos 4A cos A + 2cos 11A cos 4A= 2cos 4A cos A + cos 11A= 2cos 4A×2cos A + 11A2 cos A – 11A2= 4cos 4A cos 6A cos-5A= 4cos 4A cos 5A cos 6A= RHSHence, LHS=RHS
(ii) Consider LHS: cos A + cos 3A + cos 5A + cos 7A=2cos A + 3A2 cos A – 3A2 + 2cos 5A + 7A2 cos 5A – 7A2 ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2= 2cos 2A cos-A + 2cos 6A cos-A
= 2cos 2A cos A + 2cos 6A cos A= 2cos A(cos 2A + cos 6A)=2cos A×2cos 2A + 6A2 cos 2A – 6A2= 4cos A cos 4A cos-2A= 4cos A cos 2A cos 4A= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(iii) Consider LHS: sin A + sin 2A + sin 4A + sin 5A= 2sin A + 2A2 cos A – 2A2 + 2sin 4A + 5A2 cos 4A – 5A2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 32A cos -A2 + 2sin 92A cos -A2
= 2sin 32A cos A2 + 2sin 92A cos A2= 2cos A2sin 32A + sin 92A= 2cos A2×2sin 32A + 92A2 cos 32A – 92A2= 4cos A2 cos 3A cos -32A= 4cos A2 cos 32A cos 3A= RHSHence, LHS=RHS
(iv) Consider LHS:= sin 3A + sin 2A – sin A= 2sin 3A + 2A2 cos 3A – 2A2 – sinA ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2= 2sin 52A cos A2 – sin A
= 2sin 52A cos A2 – 2sin A2 cos A2= 2cos A2 sin 52A – sin A2= 2cos A2 × 2sin 52A – A22 cos 52A + A22= 4cos A2 sin A cos 32A= 4sin A cos A2 cos 32A= RHSHence, LHS=RHS
(v) Consider LHS: cos 20° cos 100° + cos 100° cos 140° – cos 140° cos 200°=12(2cos 20° cos 100° + 2cos 100° cos 140° – 2cos 140° cos 200°)=12cos100°+20°cos 100°-20° +cos 140°+100°cos 140°-100°-cos 200°+140°cos 200°-140°=12cos120°+cos80°+cos240°+cos40°-cos340°-cos60° =12cos120°+cos240°-cos60°+cos80°+cos40°-cos340°=12-12-12-12+cos80°+cos40°-cos340°=12-32+2cos80°+40°2cos80°-40°2-cos360°-20°=12-32+2cos60°cos20°-cos20°=12-32+cos20°-cos20°=12-32=-34=RHSHence, LHS=RHS
(vi) LHS =sinθ2sin7θ2+sin3θ2sin11θ2=122sinθ2sin7θ2+2sin3θ2sin11θ2=12cos7θ2-θ2-cos7θ2+θ2+cos11θ2-3θ2-cos11θ2+3θ2=12cos3θ-cos4θ+cos4θ-cos7θ=12cos3θ-cos7θ=12-2sin3θ+7θ2sin3θ-7θ2=12-2sin5θsin-2θ=sin5θsin2θ=RHS
Hence, LHS = RHS
Q7.
Answer :
(i) Consider LHS: sin A + sin Bsin A – sin B= 2sin A + B2 cos A – B22sin A + B2 cos A – B2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2, and sin A – sin B = 2sin A – B2 cosA + B2= sin A + B2 cos A – B2sin A – B2 cos A + B2= tan A + B2 cot A – B2=RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(ii) Consider LHS: sin A + sin 3Acos A – cos 3A= 2sin A + 3A2 cos A – 3A22sin A + 3A2 sin 3A – A2 ∵ sin A + sin B = 2sin A + B2 cos A – B2, and cos A – cos B = 2sin A + B2 cos B – A2=sin 2A cos -Asin 2A sin A= sin 2A cos Asin 2A sin A= cot A=RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(iii) Consider LHS:sin 9A – sin 7Acos 7A – cos 9A= 2sin 9A – 7A2 cos 9A + 7A22sin 7A + 9A2 sin 9A – 7A2 ∵ sin A – sin B = 2sin A – B2 cos A + B2 and cos A – cos B = 2sin A + B2 cos B – A2=sin A cos 8Asin 8A sin A=cot 8A=RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(iv) Consider LHS: cos A + cos Bcos B – cos A= 2cos A – B2 cos A + B22sin A + B2 sin A – B2 ∵ cos A + cos B = 2cos A – B2 cos A + B2 and cos A – cos B = 2sin A + B2 cos B – A2= cos A – B2 cos A + B2sin A + B2 sin A – B2= cot A + B2 cot A – B2=RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(v) Consider LHS: sin A – sin Bcos A + cos B= 2sin A – B2 cos A + B22cos A + B2 cos A – B2 ∵ sin A – sin B = 2sin A – B2 cos A + B2 and cos A + cos B = 2cos A + B2 cos A – B2= sin A – B2 cos A + B2cos A + B2 cos A – B2= tanA – B2=RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
Page 8.20 Ex – 8.2
Q8.
Answer :
(i)Consider LHS: sin A + sin 3A + sin 5Acos A + cos 3A + cos 5A= sin A + sin 5A + sin 3Acos A + cos 5A + cos 3A= 2sin A + 5A2 cos A – 5A2 + sin 3A2cos A + 5A2 cos A – 5A2 + cos 3A = 2 sin 3A cos -2A + sin 3A2cos 3A cos -2A + cos 3A=2sin 3A cos 2A + sin 3A2cos 3A cos 2A + cos 3A=sin 3A 2cos 2A + 1cos 3A 2cos 2A + 1= tan 3A= RHSHence, RHS=LHS.
(ii)Consider LHS: cos 3A + 2cos 5A + cos 7Acos A + 2cos 3A + cos 5A=cos 3A + cos 7A + 2cos 5Acos A + cos 5A + 2cos 3A= 2cos 3A + 7A2 cos 3A – 7A2 + 2cos 5A2cos A + 5A2 cos A – 5A2 + 2cos 3A =2cos 5A cos -2A + 2cos 5A2cos 3A cos -2A + 2cos 3A=2cos 5A cos 2A + 2cos 5A2cos 3A cos 2A + 2cos 3A= 2cos 5A cos 2A + 12cos 3A cos 2A + 1= cos 5Acos 3A=RHSHence, RHS=LHS.
(iii) Consider LHS: cos 4A + cos 3A + cos 2Asin 4A + sin 3A + sin 2A= cos 4A + cos 2A + cos 3Asin 4A + sin 2A + sin 3A= 2cos 4A + 2A2 cos 4A – 2A2 + cos 3A2sin 4A + 2A2 cos 4A – 2A2 + sin 3A = 2cos 3A cos A + cos 3A2sin 3A cos A + sin 3A=cos 3A2cos A + 1sin 3A2cos A + 1= cot 3A= RHSHence, RHS = LHS.
(iv)Consider LHS: sin 3A + sin 5A + sin 7A + sin 9Acos 3A + cos 5A + cos 7A + cos 9A= sin 3A + sin 9A + sin 5A + sin 7Acos 3A + cos 9A + cos 5A + sin 7A= 2sin 3A + 9A2 cos 3A – 9A2 + 2sin 5A + 7A2 cos 5A – 7A22cos 3A + 9A2 cos 3A – 9A2 + 2cos 5A + 7A2 cos 5A – 7A2= 2sin 6A cos -3A + 2sin 6A cos -A2cos 6A cos -3A + 2cos 6A cos -A= 2sin 6A cos 3A + 2sin 6A cos A2cos 6A cos 3A + 2cos 6A cos A= 2sin 6Acos 3A + cos A2cos 6Acos 3A + cos A= tan 6A= RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(v)Consider LHS: sin 5A – sin 7A + sin 8A – sin 4Acos 4A + cos 7A – cos 5A – cos 8A=sin 5A – sin 7A + sin 8A – sin 4Acos 4A – cos 8A + cos 7A – sin 5A= 2sin 5A – 7A2 cos 5A + 7A2 + 2sin 8A – 4A2 cos 8A + 4A2-2sin 4A + 8A2 sin 4A – 8A2 – 2sin 7A +5A2 sin 7A – 5A2 =2sin -A cos 6A + 2sin 2A cos 6A-2sin 6A sin -2A – 2sin 6A sin A=-2sin A cos 6A + 2sin 2A cos 6A2sin 6A sin 2A – 2sin 6A sin A=2cos 6Asin 2A – sin A2sin 6Asin 2A – sin A= cot 6A= RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(vi)Consider LHS: sin 5A cos 2A -sin 6A cos Asin A sin 2A – cos 2A cos 3AMultiplying numerator and denominator by 2, we get= 2sin 5A cos 2A – 2sin 6A cos A2sin A sin 2A – 2cos 2A cos 3A=sin 5A + 2A + sin 5A – 2A – sin 6A +A – sin 6A – Acos A – 2A + cos A + 2A – cos 2A +3A -cos 2A – 3A=sin 7A + sin 3A -sin 7A – sin 5Acos -A + cos 3A -cos 5A – cos -A=sin 7A + sin 3A – sin 7A – sin 5Acos A + cos 3A – cos 5A – cos A= sin 3A – sin 5Acos 3A – cos 5A= 2sin 3A – 5A2 cos 3A + 5A2-2cos 3A + 5A2 cos3A -5A2= sin -A cos 4A-cos 4A cos -A= -sin A cos 4A-cos 4Acos A=sin Acos A= tanA= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(vii)Consider LHS: sin 11A sin A + sin 7A sin 3Acos 2A sin A + cos 6A sin 3AMultiplying numerator and denominator by 2, we get= 2sin 11A sin A + 2sin 7A sin 3A2cos 11A sin A + 2cos 7A sin 3A= cos 11A – A – cos 11A + A + cos 7A – 3A – cos 7A + 3Asin 11A + A – sin 11A – A + sin 7A + 3A – sin 7A – 3A=cos 10A -cos 12A + cos 4A – cos 10Asin 12A – sin 10A + sin 10A – sin 4A= cos 4A – cos 12Asin 12A – sin 4A= -2sin 4A + 12A2 sin 4A – 12A22sin 12A – 4A2 cos 12A + 4A2=-sin 8A sin -4Asin 4A cos 8A=sin 8A sin 4Asin 4A cos 8A=tan8A= RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(viii)Consider LHS: sin 3A cos 4A – sin A cos 2Asin 4A sin A + cos 6A cosAMultiplying numerator and denominator by 2, we get= 2sin 3A cos 4A – 2sin A cos 2A2sin 4A sin A + 2cos 6A cos A= sin 3A + 4A + sin 3A – 4A – sin A + 2A – sin A – 2Acos 4A – A – cos 4A + A + cos 6A + A +cos 6A – A= sin 7A + sin -A – sin 3A – sin -Acos 3A – cos 5A + cos 7A + cos 5A= sin 7A – sin A – sin 3A + sin Acos 3A – cos 5A + cos 7A + cos 5A= sin 7A – sin 3Acos 3A + cos 7A= 2sin 7A – 3A2 cos 7A + 3A22cos 3A + 7A2 cos 3A – 7A2= sin 2A cos 5Acos 5A cos -2A= sin 2A cos 5Acos 5A cos 2A= tan 2A= RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(ix)Consider LHS: sin A sin 2A + sin 3A sin 6Asin A cos 2A + sin 3A cos 6AMultiplying numerator and denominator by 2, we get=2sin A sin 2A + 2sin 3A sin 6A2sin A cos 2A + 2sin 3A cos 6A= cos A – 2A -cos A +2A + cos 3A – 6A – cos 3A + 6Asin A+ 2A + sin A – 2A + sin 3A + 6A + sin 3A- 6A= cos-A – cos 3A + cos -3A – cos 9Asin 3A sin -A + sin 9A + sin -3A= cos A – cos 3A + cos 3A – cos 9Asin 3A – sin A + sin 9A – sin 3A= cos A – cos 9A sin 9A-sin A= -2sin A + 9A2 sin A – 9A22cos A + 9A2 sin 9A-A2= sin5Acos4Asin 5A cos -4A= tan 5A= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(x) Consider LHS: sinA + 2sin3A + sin5Asin3A + 2sin5A + sin7A=sinA + sin5A + 2sin3Asin3A + sin7A + 2sin5A=2sinA+5A2cosA-5A2 + 2sin3A2sin3A+7A2cos3A-7A2 + 2sin5A =2sin3A cos-2A + 2sin3A2sin5A cos-2A + 2sin5A=2sin3A cos2A + 2sin3A2sin5A cos2A + 2sin5A=2sin3Acos 2A + 12sin5Acos2A + 1=sin3Asin5A= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
(xi)Consider LHS: sinθ+ϕ – 2sinθ + sinθ-ϕcosθ+ϕ – 2cosθ + cosθ-ϕ=sinθ+ϕ+ sinθ-ϕ – 2sinθcosθ+ϕ + cosθ-ϕ – 2cosθ=2sinθ+ϕ+θ-ϕ2cosθ+ϕ-θ+ϕ2-2sinθ2cosθ+ϕ+θ-ϕ2cosθ+ϕ-θ+ϕ2-2cosθ =2sinθcosϕ-2sinθ2cosθcosϕ-2cosθ=2sinθcosϕ-12cosθcosϕ-1= tanθ= RHSHence, RHS=LHS.
Q9.
Answer :
(i)Consider LHS: sin α + sin β + sin γ – sin (α + β + γ)= 2sinα + β2 cos α – β2 + 2cos γ + α + β + γ2 sin γ – α – β – γ2=2sinα+β2cosα-β2 + 2cos2γ+α+β2sin-α-β2=2sinα+β2cosα-β2 + 2cos2γ+α+β2sin-α+β2=2sinα+β2cosα-β2 – cos2γ+α+β2=2sinα+β2-2sinα-β+2γ+α+β4 sinα-β-2γ-α-β4=2sinα+β2-2sinα+γ2 sin-β-γ2=2sinα+β22sinα+γ2 sinβ+γ2=4sinα+β2 sinα+γ2 sinβ+γ2= RHSHence, LHS=RHS. (ii)Consider LHS:cos (A+B+C) + cos (A-B+C) + cos (A+B-C) + cos (-A+B+C)=2cos A+B+C+A-B+C2 cos A+B+C-A+B-C2 + 2cos A+B-C-A+B+C2 cos A+B-C+A-B-C2=2cosA+C cos B+2cos B cosA-C=2cos Bcos A+C + cos A-C=2cos B2cos A+C+A-C2 cos A+C-A+C2=2cos B2cos A cos C=4cos A cos B cos C= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
Q10.
Answer :
Given:
sin A + sin B = 14 …..(i)
cos A + cos B =12 …..(ii)
Dividing (i) by (ii):
⇒ sinA+sinBcosA+cosB=1412⇒2sinA+B2cosA-B22cosA+B2cosA-B2 =12 ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2 and cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2⇒sinA+B2cosA-B2cosA+B2cosA-B2=12⇒tanA+B2=12Hence proved.
Q11.
Answer :
Given:
1sinA+1cosA=1sinB+1cosB⇒1sinA-1sinB=1cosB-1cosA⇒sinB-sinAsinAsinB=cosA-cosBcosAcosB⇒sinB-sinAcosA-cosB=sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒2sinB-A2cosA+B2-2sinA-B2sinA+B2=sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒-sinA-B2cosA+B2-sinA-B2sinA+B2=sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒cosA+B2sinA+B2=sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒cotA+B2=tanAtanBHence proved.
Q12.
Answer :
Given:
sin 2A = λ sin 2B
⇒sin2Asin2B=λ
⇒ sin2A+sin2Bsin2A-sin2B=λ+1λ-1⇒2sin2A+2B2cos2A-2B22sin2A-2B2cos2A+2B2= λ+1λ-1 ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2 and sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2⇒sinA+BcosA-BsinA-BcosA+B=λ+1λ-1⇒tanA+BcotA-B=λ+1λ-1
⇒tanA+BtanA-B=λ+1λ-1
Hence proved.
Q13.
Answer :
(i)Consider LHS: cos(A+B+C) + cos(-A+B+C) + cos(A-B+C) + cos(A+B-C)sin(A+B+C) + sin(-A+B+C) + sin(A-B+C) – sin(A+B-C)=2cosA+B+C-A+B+C2cosA+B+C+A-B-C2+2cosA-B+C+A+B-C2cosA-B+C-A-B+C22sinA+B+C-A+B+C2cosA+B+C+A-B-C2+2sinA-B+C-A-B+C2cosA-B+C+A+B-C2=2cos B+C cos A +2cos A cos -B+C2sin B+C cos A+ 2sin -B+C cos A=2cos Acos B+C + cos-B+C2cos AsinB+C + sin-B+C=cos B+C + cos -B+CsinB+C + sin -B+C=2cos B+C-B+C2 cos B+C+B-C22sinB+C-B+C2 cos B+C+B-C2= cos C cos Bsin C cos B= cotC= RHSHence, LHS = RHS.
(ii)Consider LHS:sin (B-C) cos (A-D) + sin (C-A) cos (B-D) + sin (A-B) cos (C-D)Multiplying by 2: 2sin (B-C) cos (A-D) + 2sin(C-A) cos (B-D) + 2sin (A-B) cos (C-D)= sin B-C+A-D + sin B-C-A+D + sin C-A+B-D + sin C-A-B+D + sin A-B+C-D + sin A-B-C+D= sin-C+D-A-B+sin-A+C-B-D+sin-A+D-B-C+sinC-A-B+D+sinA-B+C-D+sinA-B-C+D=-sinC+D-A-B-sinA+C-B-D-sinA+D-B-C+sinC-A-B+D+sinA-B+C-D+sinA-B-C+D=0= RHSHence, LHS=RHS.
Q14.
Answer :
We have,cos A-Bcos A+B + cos C+Dcos C-D=0⇒cos A-B cos C-D + cos C+D cos A+Bcos A+B cos C-D=0⇒cos A-B cos C-D + cos C+D cos A+B = 0⇒cos A-B cos C-D = -cos C+D cos A+B⇒cos A cos B + sin A sin Bcos C cos D + sin C sin D = -cos C cos D – sin C sin Dcos A cos B – sin A sin B
Dividing both sides by cos A cos B cos C cos D we get,cosA cosB+sinAsinBcosCcosD+sinCsinDcosAcosBcosCcosD=-cosC cosD-sinCsinDcosAcosB-sinA sinBcosAcosBcosCcosD⇒cosA cosB+sinAsinBcosAcosB×cosCcosD+sinCsinDcosCcosD=-cosC cosD-sinCsinDcosCcosD×sinCcosAcosB-sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒1+tanAtanB1+tanCtanD=tanCtanD-11-tanAtanB⇒1+tanCtanD+tanAtanB+tanAtanBtanCtanD=tanCtanD-tanAtanBtanCtanD+tanAtanBtanD-1+tanAtanB⇒2tanAtanBtanCtanD=-2⇒tanAtanBtanCtanD=-1 Hence proved.
Q15.
Answer :
cos α+β sin γ+δ = cos α-β sin γ-δ⇒cos αcos β – sin α sin βsin γ cos δ + cos γ sin δ = cos α cos β + sin α sin βsin γ cos δ- cos γ sin δ
Dividing both sides by sin α sin β sin γ sin δ:cosα cosβ – sinα sinβsinγ cosδ + cosγ sinδsin α sin β sin γ sin δ=cosα cosβ + sinα sinβsinγ cosδ – cosγ sinδsin α sin β sin γ sin δ⇒cosα cosβ – sinαsinβsin α sin β ×sinγ cosδ + cosγ sinδ sin γ sin δ=cosα cosβ + sinα sinβsin α sin β ×sinγ cosδ – cosγ sinδ sin γ sin δ⇒cotα cotβ – 1cotδ + cotγ = cotα cotβ + 1cotδ – cotγ⇒cotα cotβ cotδ + cotα cotβ cotγ – cotδ – cotγ = cotα cotβ cotδ – cotα cotβ cotγ + cotδ – cotγ ⇒-cotδ – cotδ = -cotα cotβ cotγ – cotα cotβ cotγ⇒-2cotδ =-2cotα cotβ cotγ⇒cotα cotβ cotγ = cotδ Hence proved.
Q16.
Answer :
Given:
y sin ϕ = x sin (2θ + ϕ) ⇒yx=sin2θ+ϕsinϕApplying componendo and dividendo:⇒y-xy+x=sin2θ+ϕ – sinϕsin2θ+ϕ + sinϕ⇒y-xy+x=2sin2θ+ϕ-ϕ2cos2θ+ϕ+ϕ22sin2θ+ϕ+ϕ2cos2θ+ϕ-ϕ2⇒y-xy+x=2sin θ cosθ+ϕ2sinθ+ϕ cos θ⇒y-xy+x=sin θ cosθ+ϕsinθ+ϕ cos θ⇒y-xy+x=cot θ+ϕcot θ⇒y-x cotθ = y+x cotθ+ϕ
Q17.
Answer :
cos (A + B) sin (C − D) = cos (A − B) sin (C + D) ⇒[cosA cosB − sinA sinB] [sinC cosD − cosC sinD] = [cosA cosB + sinA sinB] [sinC cosD + cosC sinD]
Dividing both sides by cos A cos B cos C cos D,cosA cosB – sinA sinBsinC cosD- cosC sinDcosA cosB cosC cosD=cosA cosB + sinA sinBsinC cosD + cosC sinDcosA cosB cosC cosD⇒cosA cosB- sinA sinBcosA cosB×sinCcosD – cosC sinDcosC cosD = cosA cosB + sinA sinBcosA cosB×sinC cosD + cosC sinDcosC cosD⇒1 – tanA tanBtanC-tanD = 1 + tanA tanBtanC + tanD⇒tanC – tanD -tanA tanB tanC + tanA tanB tanD = tanC + tanD + tanA tanB tanC + tanA tanB tanD⇒-tanD – tanD = tanA tanB tanC + tanA tanB tanC⇒-2tanD=2tanA tanB tanC⇒tanA tanB tanC = -tanD⇒tanA tanB tanC + tanD = 0 Hence proved.
Page 8.21 (Very Short Answers)
Q1.
Answer :
(cos α + cos β)2 + (sin α + sin β)2 = λ cos2α-β2
Consider LHS:
(cos α + cos β)2 + (sin α + sin β)2
= 2cos α+β2 cos α-β22 + 2sin α+β2 cos α-β22= 4cos2 α+β2 cos2 α-β2 + 4sin2 α+β2 cos2 α-β2= 4cos2 α-β2cos2 α+β2 + sin2 α+β2= 4cos2 α-β2= RHS
Q2.
Answer :
sin π12 sin 5π12
= 12× 2sinπ12 sin5π12 = 12cosπ12-5π12 – cosπ12+5π12 ∵2sinA sinB = cos(A-B) – cos(A+B)= 12cos-π3 – cosπ2= 1212 – 0= 14
Q3.
Answer :
Given:
sin A + sin B = α …..(i)
cos A + cos B = β …..(ii)
Dividing (i) by (ii):
⇒ sinA+sinBcosA+cosB=αβ⇒2sinA+B2cosA-B22cosA+B2cosA-B2 =αβ ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2 and cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2⇒sinA+B2cosA-B2cosA+B2cosA-B2=αβ⇒tanA+B2=αβ
Q4.
Answer :
Given:cosA=mcosB⇒cosAcosB=m1⇒ cosA+cosBcosA-cosB=m+1m-1⇒2cosA+B2cosA-B2-2sinA+B2sinA-B2 = m+1m-1 ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA-B2cosA+B2 and cosA-cosB=-2sinA+B2cosA-B2⇒cosA-B2cosA+B2-sinA+B2sinA-B2 = m+1m-1 ⇒-cotA+B2cotA-B2 = m+1m-1
⇒cotA+B2cotA-B2= 1+m1-m
Q5.
Answer :
1-4sin10° sin70°2sin10°=1-22sin10° sin70°2sin10°=1-2cos10°-70° – cos10°+70°2sin10°=1-2cos-60° – cos80°2sin10°=1-2cos60° – cos80°2sin10°=1-212-cos90°-10°2sin10°=1-2×12+2cos90°-10°2sin10°=2sin10°2sin10°=1
Q6.
Answer :
Given:
A + B = π3 and cos A + cos B = 1 ⇒2cosA+B2cosA-B2 =1 ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2⇒2cosπ6cosA-B2=1 ∵ A+B=π3⇒2×32×cosA-B2=1⇒cosA-B2=13
Q7.
Answer :
sin12° sin48° sin54°=122sin12° sin48° sin54°=12cos12°-48°-cos12°+48° sin54°=12cos-36°-cos60° sin54°=12sin54°cos36°-12=12sin90°-36° cos36°-14sin90°-36°=12cos236° -14cos36°=125+142-5+116 cos36°=5+14=125+1+2516-5+116=6+2532-5+116=6+25-25-232=432=18
Q8.
Answer :
Given:
sin 2A = λ sin 2B
⇒sin2Asin2B=λ
⇒ sin2A+sin2Bsin2A-sin2B=λ+1λ-1⇒2sin2A+2B2cos2A-2B22sin2A-2B2cos2A+2B2= λ+1λ-1 ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2 and sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2⇒sinA+BcosA-BsinA-BcosA+B=λ+1λ-1⇒tanA+BcotA-B=λ+1λ-1⇒tanA+BtanA-B=λ+1λ-1
Q9.
Answer :
sinA+sin3AcosA+cos3A=2sinA+3A2cosA-3A22cosA+3A2cosA-3A2 ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2, and cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2=sin2A cos-Acos2A cos-A=sin2A cosAcos2A cosA=tan 2A
Q10.
Answer :
cos (A + B) sin (C − D) = cos (A − B) sin (C + D)
⇒[cosA cosB − sinA sinB] [sinC cosD − cosC sinD] = [cosA cosB + sinA sinB] [sinC cosD + cosC sinD]
Dividing both sides by cos A cos B cos C cos D:cosA cosB-sinA sinBsinC cosD-cosC sinDcosA cosB cosC cosD=cosA cosB+sinA sinBsinC cosD+cosC sinDcosA cosB cosC cosD⇒cosA cosB-sinA sinBcosA cosB×sinC cosD-cosC sinDcosC cosD=cosA cosB+sinA sinBcosA cosB×sinC cosD+cosC sinDcosC cosD⇒1-tanA tanBtanC-tanD=1+tanA tanBtanC+tanD⇒tanC-tanD-tanA tanB tanC+tanA tanB tanD=tanC+tanD+tanA tanB tanC+tanA tanB tanD⇒-tanD-tanD=tanA tanB tanC+tanA tanB tanC⇒-2tanD=2tanAtanBtanC⇒tanAtanBtanC=-tanD
Page 8.21 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q1.
Answer :
(d) -12
cos40° + cos80° + cos160° + cos240°=2cos40°+80°2cos40°-80°2 + cos160° – cos180°+60° ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2=2cos60° cos-20° + cos160° – 12=2×12cos20° + cos160° – 12=-cos180-20° + cos160° – 12=-12
Q2.
Answer :
(b) 12
sin163°cos347°+sin73°sin167°=sin180°-17°cos360°-13°+sin90°-17°sin180°-13°=sin17°cos13°+cos17°sin13°=sin17°+13° sinA+B=sinAcosB+sinBcosA=sin30°=12
Q3.
Answer :
(b) 58
Given:
sin 2θ + sin 2ϕ = 12 …..(i)
and
cos 2θ + cos 2ϕ = 32 …..(ii)
Squaring and adding (i) and (ii), we get:
(sin 2θ + sin 2ϕ)2 + (cos 2θ + cos 2ϕ)2 = 14+94
⇒2sin2θ+2ϕ2cos2θ-2ϕ22 + 2cos2θ+2ϕ2cos2θ-2ϕ22=52⇒4sin2θ+ϕ cos2θ-ϕ + 4cos2θ+ϕ cos2θ-ϕ=52⇒4cos2θ-ϕsin2θ+ϕ+cos2θ+ϕ=52⇒4cos2θ-ϕ=52⇒cos2θ-ϕ=58
Q4.
Answer :
(a) 0
cos52° + cos68° + cos172°=2cos52°+68°2cos52°-68°2+cos172° ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2=2cos60°cos-8°+cos172°=2×12cos8°+cos172°=cos8°+cos172°=2cos8°+172°2cos8°-172°2=2cos90°cos82°=0
Page 8.22 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q5.
Answer :
(d) None of these
sin78° – sin66° – sin42° + sin60°=sin78° – sin42° – sin66° + sin60°=2sin78°-42°2cos78°+422 – sin66° + sin60° ∵ sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2=2sin18° cos60° – sin66° + sin60°=2×12sin18° – sin66° + 32=sin18°-sin66°+32=5-14-0.914+32=0.309-0.914+0.866=0.261
Q6.
Answer :
(b) -ba
Given:
sin α + sin β = a …..(i)
cos α − cos β = b …..(ii)
Dividing (i) by (ii):
⇒ sinα+sinBcosα-cosB=ab⇒2sinα+β2cosα-β2-2sinα+β2sinα-β2 =ab ∵ sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2 and cosA+cosB=-2sinA+B2sinA-B2⇒sinα+β2cosα-β2-sinα+β2sinα-β2=ab⇒cotα-β2=-ab⇒1cotα-β2=1-ab⇒tanα-β2=-ba
Q7.
Answer :
(a) 0
cos35° + cos85° + cos155°= 2cos35° + 85°2 cos35° – 85°2 + cos155° ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA+B2cosA-B2= 2cos60° cos-25° + cos155°= 2×12cos25° + cos155°= cos25° + cos155°= 2cos25°+155°2 cos25°-155°2= 2cos90° cos65°=0
Q8.
Answer :
(b) 0
sin50° – sin70° + sin10°= 2sin50°-70°2 cos50°+70°2 + sin10° ∵ sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2=2sin-10° cos60° + sin10°= 2×12sin-10° + sin10°= -sin10°+sin10°=0
Q9.
Answer :
(d) cos 7°
sin47°+sin61°-sin11°-sin25°= sin47°-sin25°+sin61°-sin11°= 2sin47°-25°2cos47°+25°2+2sin61°-11°2cos61°+11°2= 2sin11°cos36°+2sin25°cos36°=2cos36°sin11°+sin25°=2cos36°2sin11°+25°2cos11°-25°2=4cos36°sin18°cos7°=4×5-145+14cos7° cos36°=5+14 and sin18°=5-14=5-14cos7°=cos7°
Q10.
Answer :
(c)m+1m-1
Given:cosA=mcosB⇒cosAcosB=m1⇒ cosA+cosBcosA-cosB=m+1m-1⇒2cosA-B2cosA+B2-2sinB+A2sinB-A2 = m+1m-1 ∵ cosA+cosB=2cosA-B2cosA+B2 and cosA-cosB=2sinA+B2cosB-A2⇒cosB-A2cosA+B2sinA+B2sinB-A2= m+1m-1 ⇒cotA+B2cotB-A2= m+1m-1
Q11.
Answer :
(b) cot B
Since A,B and C are in A.P,
B-A=C-Bor, 2B=A+C
sinA-sinCcosC-cosA=2sinA-C2cosA+C2-2sinC+A2sinC-A2 ∵ sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2 and cosA-cosB=-2sinA+B2cosA-B2=sinA-C2cosA+C2-sinA+C2sinC-A2
=sinA-C2cosA+C2sinA+C2sinA-C2=cosA+C2sinA+C2=cosBsinB=cotB
Q12.
Answer :
(b) HP
Given:
sin (B + C − A), sin (C + A − B) and sin (A + B − C) are in A.P.
⇒sinC+A-B – sinB+C-A = sinA+B-C – sinC+A-B⇒2sinC+A-B-B-C+A2 cosC+A-B+B+C-A2 = 2sinA+B-C-C-A+B2 cosA+B-C+C+A-B2⇒sinA-B cosC = sinB-C cosA⇒sinA cosB cosC – cosA sinB cosC = sinB cosCcosA – cosB sinC cosA⇒2sinB cosA cosC = sinA cosB cosC + cosA cosB sinCDividing both sides by cos AcosBcosC:2tanB=tanA+tanC ⇒2cotB=1cotA+1cotC
Hence, cotA, cotB and cotC are in HP.
Q13.
Answer :
We have,
sin x + sin y = 3 (cos y − cos x)
⇒2sinx+y2 cosx-y2 = 23sinx+y2 sinx-y2⇒2sinx+y2cosx-y2-23sinx+y2sinx-y2=0⇒2sinx+y2cosx-y2-3sinx-y2=0⇒sinx+y2cosx-y2-3sinx-y2=0⇒sinx+y2=0 or, cosx-y2-3sinx-y2=0⇒x+y2=0 or, tanx-y2=13=tanπ6⇒x=-y or, x-y2=π6⇒x=-y or, x-y=π3
Case-I
When x=-y
In this case,
sin3x+sin3y=sin-3y+sin3y=-sin3y+sin3y=0
Case-II
when x-y=π3
or, 3x=π+3ySo, sin 3x+sin 3y= sinπ+3y+sin 3y =-sin 3y+sin 3y =0
6. TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS OF MULTIPLE AND SUBMULTIPLE ANGLES
Page 9.29 Ex – 9.1
Q1.
Answer :
LHS=1-cos2θ1+cos2θ =2sin2θ2cos2θ ∵1-cos2θ=2sin2θ and 1+cos2θ=2cos2θ =sinθcosθ =tanθ=RHSHence proved.
Q2.
Answer :
LHS=sin2θ1-cos2θ =2sinθ×cosθ2sin2θ ∵sin2θ=2sinθcosθ ,1-cos2θ=2sin2θ =2sinθ×cosθ2sinθ×sinθ =cosθsinθ =cotθ=RHSHence proved.
Q3.
Answer :
LHS=sin2θ1+cos2θ =2sinθ×cosθ1+2cos2θ-1 ∵sin2θ=2sinθ×cosθ and cos2θ=2cos2θ-1 =2sinθ×cosθ2cosθ×cosθ =sinθcosθ =tanθ=RHSHence proved.
Q4.
Answer :
LHS=2+2+2cos4θ =2+21+cos4θ =2+2×2cos22θ ∵2cos22θ=1+cos4θ =2+2cos2θ
=21+cos2θ =2.2cos2θ ∵2cos2θ=1+cos2θ =2cosθ=RHS Hence proved.
Q5.
Answer :
LHS=1-cos2θ+sin2θ1+cos2θ+sin2θ =2sin2θ+sin2θ2cos2θ+sin2θ ∵2sin2θ=1-cos2θ and 2cos2θ=1+cos2θ =2sin2θ+2sinθcosθ2cos2θ+2sinθcosθ ∵sin2θ=2sinθcosθ =2sinθsinθ+cosθ2cosθcosθ+sinθ =tanθ=RHSHence proved.
Q6.
Answer :
LHS=sinθ+sin2θ1+cosθ+cos2θ =sinθ+sin2θcosθ+1+cos2θ =sinθ+2sinθcosθcosθ+2cos2θ ∵sin2θ=2sinθcosθ and 2cos2θ=1+cos2θ =sinθ1+2cosθcosθ1+2cosθ =tanθ=RHS Hence proved.
Q7.
Answer :
LHS=cos2θ1+sin2θ =cos2θ-sin2θsin2θ+cos2θ+2sinθ×cosθ ∵cos2θ=cos2θ-sin2θ and sin2θ+cos2θ=1 =cosθ-sinθcosθ+sinθcosθ+sinθ2 ∵a2-b2=a+ba-b =cosθ-sinθcosθ+sinθ
On dividing the numerator and denominator by cosθ, we get
=1-tanθ1+tanθ =tanπ4-θ=RHSHence proved.
Q8.
Answer :
LHS=cosθ1-sinθ =cos2θ2-sin2θ2sin2θ2+cos2θ2-2sinθ2×cosθ2 ∵cosθ=cos2θ2-sin2θ2, sinθ=2sinθ2cosθ2 and sin2θ2+cos2θ2=1 =cosθ2-sinθ2cosθ2+sinθ2cosθ2-sinθ22 =cosθ2+sinθ2cosθ2-sinθ2
On dividing the numerator and denominator by cosθ2, we get
=1+tanθ21-tanθ2 =tanπ4+θ2=RHSHence proved.
Q9.
Answer :
LHS=cos2π8+cos23π8+cos25π8+cos27π8 =cos2π8+cos23π8+cos2π-3π8+cos2π-π8 =cos2π8+cos23π8+-cos3π82+-cosπ82
=cos2π8+cos23π8+cos23π8+cos2π8 =2cos2π8+cos23π8 =2cos2π8+cos2π2-π8 =2cos2π8+sin2π8 =2=RHSHence proved.
Q10.
Answer :
LHS=sin2π8+sin23π8+sin25π8+sin27π8 =sin2π2-3π8+sin2π2-π8+sin25π8+sin27π8 =cos23π8+sin2π8+sin2π-3π8+sin2π-π8
=cos23π8+sin2π8+sin23π8+cos2π8 =cos2π8+sin2π8+cos23π8+sin23π8 =1+1=2=RHSHence proved.
Q11.
Answer :
LHS=cosα+cosβ2+sinα+sinβ2 =cos2α+cos2β+2cosαcosβ +sin2α+sin2β+2sinαsinβ =(cos2α + sin2α)+(cos2β + sin2β)+2cosαcosβ+sinαsinβ =1 +1 + 2cos(α-β) =21 + cos(α-β) =22cos2α-β2 =4cos2α-β2=RHSHence proved.
Q12.
Answer :
LHS=sin2π8+A2-sin2π8-A2 =121-cos2π8+A2-121-cos2π8-A2 =12cosπ4-A-cosπ4+A
Using the identity cosC-cosD=-2sinC+D2sinC-D2, we get
=12-2sinπ4-A+π4+A2 sinπ4-A-π4+A2 =-sinπ4sin-A =sinπ4sinA ∵sin-A= -sinA =12sinA=RHS Hence proved.
Page 9.30 Ex – 9.1
Q13.
Answer :
LHS=1+cos22θ
Using the identity cos2θ=cos2θ-sin2θ, we get
LHS=1+cos2θ-sin2θ2 =1+cos4θ+sin4θ-2cos2θsin2θ
=cos2θ+sin2θ2+cos4θ+sin4θ-2cos2θsin2θ ∵cos2θ+sin2θ=1 =cos4θ+sin4θ+2cos2θsin2θ+cos4θ+sin4θ-2cos2θsin2θ = 2(cos4θ+sin4θ)=RHS Hence proved.
Q14.
Answer :
RHS=4cos6θ-sin6θ =4cos2θ3-sin2θ3
Using the identity a3-b3=a-ba2+ab+b2, we get
=4cos2θ-sin2θ cos4θ+sin4θ+sin2θcos2θ =4cos2θ-sin2θ cos4θ+sin4θ+sin2θcos2θ
=4cos2θcos2θ-sin2θ2+2sin2θcos2θ+sin2θcos2θ =4cos2θcos22θ+3sin2θcos2θ =4cos2θcos22θ+31-cos2θ21+cos2θ2
=4cos2θcos22θ+341-cos22θ =cos2θ4cos22θ+31-cos22θ =cos2θ4cos22θ+3-3cos22θ =cos2θcos22θ+3 =cos32θ+3cos2θ=LHS Hence proved.
Q15.
Answer :
LHS=cos7° cos14° cos28° cos56°
On dividing and multiplying by 2sin7∘, we get
=12sin7°×2sin7°×cos7°×cos14°×cos28°×cos56° =2sin14°2×2sin7°×cos14°×cos28°×cos56° =2sin28°2×4sin7°×cos28°×cos56°
=2sin56°2×8sin7°×cos56° =sin112°16sin7° =sin180°-68°16sin90°-83° =sin68°16cos83° ∵sin180°-θ=sinθ & sin90°-θ=cosθ =RHS Hence proved.
Q16.
Answer :
(i)
LHS=cos2π15 cos4π15 cos8π15 cos16π15
On dividing and multiplying by 2sin2π15, we get
=12sin2π15×2sin2π15×cos2π15 ×cos4π15 ×cos8π15 × cos16π15 =12×2sin2π15×2sin4π15×cos4π15 ×cos8π15 × cos16π15 =12×4sin2π152sin8π15×cos8π15 × cos16π15 =12×8sin2π152sin16π15 × cos16π15 =116sin2π15sin32π15
=-116sin2π15sin2π-32π15 ∵sin2π-θ=-sinθ =-116sin2π15sin-2π15 =116=RHS Hence proved.
(ii)
LHS=cosπ65 cos2π65cos4π65 cos8π65cos16π65 cos32π65
On dividing and multiplying by 2sinπ65, we get
=12sinπ65×2sinπ65×cosπ65 ×cos2π65×cos4π65× cos8π65×cos16π65× cos32π65 =2×sin2π652×2sinπ65×cos2π65×cos4π65× cos8π65×cos16π65× cos32π65 =2×sin4π652×4sinπ65×cos4π65× cos8π65×cos16π65× cos32π65 =2×sin8π652×8sinπ65× cos8π65×cos16π65× cos32π65
=2×sin16π652×16sinπ65×cos16π65× cos32π65 =2×sin32π652×32sinπ65× cos32π65 =sin64π6564sinπ65=sinπ-π6564sinπ65 =sinπ6564sinπ65 ∵sinπ-θ=sinθ =164=RHSHence proved.
Q17.
Answer :
LHS=sin3A+sinA sinA+cos3A-cosAcosA
Using the identities sinC+sinD=2sinC+D2cosC-D2 and cosC-cosD=-2sinC+D2sinC-D2, we get
LHS=2sin3A+A2×cos3A-A2×sinA+-2sin3A+A2×sin3A-A2cosA =2sin2A×cosA×sinA-2sin2A×sinAcosA =0=RHSHence proved.
Q18.
Answer :
LHS=cos2π4-θ-sin2π4-θ =cos2π4-θ ∵cos2α-sin2α=cos2α =cosπ2-2θ =sin2θ=RHS ∵cosπ2-2α=sin2α Hence proved.
Q19.
Answer :
LHS=cos4A =cos2×2A =2cos2×2A-1 ∵cos2θ=2cos2θ-1 =22cos2A-12-1 ∵cos22θ=2cos2θ-12
=24cos4A-4cos2A+1-1 =8cos4A-8cos2A+1 =1-8cos2A+8cos4A=RHS Hence proved.
Q20.
Answer :
LHS=sin 4A =2sin2A cos2A ∵sin2θ=2sinθcosθ
Now, using the identities sin2α=2sinαcosα and cos2α=cos2α-sin2α, we get
LHS=2(2sinA cosA).(cos2A-sin2A) =4sinA cos3A-4sin3A cosA=RHS Hence proved.
Q21.
Answer :
LHS=3sinx-cosx4+6sinx+cosx2+4sin6x+cos6x =3sinx-cosx22+6sin2x+cos2x+2sinxcosx+4sin2x3+cos2x3
=3(sin2x+cos2x-2sinxcosx)2+6(1+sin2x)+4(sin2x+cos2x)(sin4x-sin2xcos2x+cos4x) =3(1-sin2x)2+6+6sin2x+4(sin4x-sin2xcos2x+cos4x) =31-sin2x2+6+6sin2x+4(sin2x)2+(cos2x)2-12sin2xcos2x
=31-sin2x2+6+6sin2x+4sin2x+cos2x2-2sin2xcos2x-12sin2xcos2x =3(1-sin2x)2+6+6sin2x+41-2sin2xcos2x-12sin2xcos2x =31-2sin2x+sin22x+6+6sin2x+4-20sin2xcos2x =-6sin2x+3sin22x+13+6sin2x-52sinxcosx2 =3sin22x+13-5sin22x =13-2sin22x=RHSHence proved.
Q22.
Answer :
LHS=2sin6x+cos6x−3sin4x+cos4x+1 =2sin2x3+cos23-3sin4x+cos4x+1
=2sin2x+cos2xsin4x-sin2xcos2x+cos4x-3sin4x+cos4x+1 =2sin4x+cos4x-2sin2xcos2x-3sin4x+cos4x+1 =-sin4x+cos4x+2sin2xcos2x+1 =-1+1=0=RHSHence proved.
Q23.
Answer :
LHS=cos6A-sin6A =cos2A3-sin2A3 =cos2A-sin2Acos4A+sin2A.cos2A+sin4A
=cos2Acos4A+2sin2Acos2A+sin4A-sin2Acos2A =cos2Asin2A+cos2A2-14×4sin2Acos2A
=cos2Asin2A+cos2A2-142sinAcosA2 =cos2A1-14sin2A2 =cos2A1-14sin22A=RHSHence proved.
Q24.
Answer :
LHS=tanπ4+θ+tanπ4-θ =tanπ4+tanθ1-tanπ4tanθ+tanπ4-tanθ1+tanπ4tanθ ∵tanA+B=tanA+tanB1-tanAtanB and tanA-B=tanA-tanB1+tanAtanB
=1+tanθ1-tanθ+1-tanθ1+tanθ =1+tanθ2+1-tanθ21+tanθ1-tanθ =2(1+tan2θ)1-tan2θ=2sec2θ1-sin2θcos2θ
=2sec2θcos2θcos2θ ∵cos2θ-sin2θ=cos2θ =2×1cos2θ =2sec2θ=RHS Hence proved.
Q25.
Answer :
LHS=cot2A-tan2A =cos2Asin2A-sin2Acos2A =cos2A2-sin2A2sin2Acos2A
=cos2A+sin2Acos2A-sin2Asin2Acos2A =1×cos2Asin2Acos2A ∵cos2A-sin2A=cos2A =4cos2A4sin2Acos2A
=4cos2Asin2A2 =4cos2Asin2A×1sin2A =4cot2Acosec2A=RHS Hence proved.
Q26.
Answer :
RHS=8cosθ-cosα cosθ+cosα cosθ-sinα cosθ+sinα =8cos2θ-cos2α cos2θ-sin2α =8cos4θ-cos2θ×sin2α-cos2α×cos2θ+cos2α×sin2α =8cos4θ-cos2θsin2α+cos2α+cos2α×sin2α =8cos4θ-cos2θ+cos2α×1-cos2α =8cos4θ-cos2θ+cos2α-cos4α =8cos2θcos2θ-1+cos2α×1- os2α =812cos2θ2cos2θ-2+12cos2α×2-2cos2α =812cos2θ2cos2θ-1-1-12cos2α×2cos2α-1-1 =812cos2θcos2θ-1-12cos2α×cos2α-1 ∵cos2α=2cos2α-1 =8142cos2θcos2θ-1-2cos2α×cos2α-1 =8141+cos2θcos2θ-1-1+cos2αcos2α-1
=814cos22θ-1-cos22α+1 =8182cos22θ-2cos22α =1+cos4θ-1+cos4α = 1+cos4θ-1-cos4α =cos4θ-cos4α=LHS Hence proved.
Q27.
Answer :
Here,tan82.5°=tan90-7.5° =cot7.5° =1tan7.5°We know,tanx2=sinx1+cosxOn putting x=15°, we get tan152°=sin15°1+cos15° =sin45-30°1+cos45-30° =sin45°cos30°-sin30°cos45°1+cos45°cos30°+sin45°sin30° =12×32-12×121+12×32+12×12 =322-1221+322+122 =3-122+3+1Now, tan82.5°=1tan7.5° =22+3+13-1 =22+3+13-1×3+13+1 =3+122+3+132-12 =26+3+3+22+3+13-1 =26+23+22+42 =6+3+2+2 =2+3+4+6 …1 =6+3+2+2 =32+1+22+1 =3+22+1 …2From eqs. 1 and 2, we get tan82.5°=3+22+1=2+3+4+6
Q28.
Answer :
Let A=2212°Using the identity cot2A=cot2A-12cotA, we getcot45°=cot22212°-12cot2212° ⇒1=cot22212°-12cot2212° ∵cot45°=1⇒2cot2212°-cot22212°+1=0
⇒cot22212∘-2cot2212∘-1=0⇒cot22212∘-2cot2212∘+1-2=0⇒cot2212∘-12=2⇒cot2212∘-1=2⇒cot2212∘=2+1
Q29.
Answer :
(i) cos x=-35
Using the identity cos2θ=cos2θ-sin2θ, we get
cosx=cos2x2-sin2x2⇒-35=2cos2x2-1⇒1-35=2cos2x2⇒25=2cos2x2⇒15=cos2x2⇒cosx2=±15
It is given that x lies in the third quadrant. This means that x2 lies in the second quadrant.
∴cosx2=-15
Again,
cosx=cos2x2-sin2x2⇒-35=-152-sin2x2⇒-35=15-sin2x2⇒-15-35=-sin2x2⇒45=sin2x2⇒sinx2=±25
It is given that x lies in the third quadrant. This means that x2 lies in the second quadrant.
∴sinx2=25
Now,sinx = 1-cos2x⇒sinx=1–352sinx=1-925=±45
Since x lies in the third quadrant, sinx is negative.
∴sinx = -45⇒sin2x=2sinxcosx⇒sin2x=2×-45×-35⇒sin2x=2425
(ii) cos x=-35
sinx=1-cos2x=1–35⇒sinx=±45
Here, x lies in the second quadrant.
∴sinx=45
We know,
sin2x = 2sinx cosx
∴sin2x=2×45×-35=-2425
Now,
cosx=1-2sin2x2⇒2sin2x2=1–35=85⇒sin2x2=45⇒sinx2=±25
Since x lies in the second quadrant, x2 lies in the first quadrant.
∴sinx2=25
Q30.
Answer :
Given:
sinx=53
Using the identity cosx=1-sin2x, we get
cosx=1-sin2x=1-532=±23
Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant, cosx is negative.
∴cosx=-23
Now,
cosx=1-2sin2x2⇒-23=1-2sin2x2⇒sinx2=±56
Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant, x2 lies in the 1st quadrant.
∴sinx2=56
Again,
cosx=2cos2x2-1⇒-23=2cos2x2-1⇒cosx2=±16⇒cosx2=16 ∵x2<π2
Now, tanx2=sinx2cosx2=5616=5
Q31.
Answer :
Given:
sin x=14
∴sinx=1-cos2x⇒142=1-cos2x⇒116-1=-cos2x⇒1516=cos2x⇒cosx=±154
Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant, cosx is negative.
Thus,
cosx=-154
Now, using the identity cosx=2cos2x2-1, we get
-154=2cos2x2-1⇒-158=cos2x2-12⇒cos2x2=4-158⇒cosx2=±4-158
Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant and x2 lies in the 1st quadrant, cosx2 is positive.
∴cosx2=4-158
Again,
cosx=cos2x2-sin2x2⇒-154=4-1582-sin2x2⇒-154=4-158-sin2x2⇒sin2x2=4+158⇒sinx2=±4+158=4+158
Now,
tanx2=sinx2cosx2 =4+1584-158=4+154-15 =4+154+154-154+15 =4+1542-152=4+1516-15=4+15
Q32.
Answer :
(i) Given:
cos θ=45
Thus,
tanθ=sinθcosθ=1-cos2θcosθ=1-45245 =1-162545=34 Because θ lies in the 1st quadrant, tanθ will be positive.Now, tan2θ=2×341-342 ∵tan2θ=2tanθ1-tan2θ =321-916=247
(ii) Given:
sin θ=45 and 0 < θ < π2
Thus,
cosθ=1-sin2θ=1-452=35 ∵ 0<θ<π2We know, sin2θ=2sinθcosθ∴sin2θ=2×45×35=2425
Again,cos2θ=1-sin22θ=1-24252=±725Because θ lies in the 1st quadrant and 2θ lies in the 2nd quadrant, cos2θ will be negative.∴cos2θ=-725Now,We know, sin4θ=2sin2θcos2θ∴sin4θ=2×2425×-725=-336625
Q33.
Answer :
Given:
tan A=17 and tan B=13
Using the identity tan2B=2tanB1-tan2B, we get
tan2B=2×131-19=34
Now, using the identities cos2A=1-tan2A1+tan2A and sin4B=2tan2B1+tan22B, we get
cos2A=1-1721+172 and sin4B=2×341+342⇒cos2A=4850 and sin4B=2×34×1625⇒cos2A=2425 and sin4B=2425
∴ cos 2A = sin 4B
Page 9.31 Ex – 9.1
Q34.
Answer :
Given:
2 tan α=3 tan β
LHS=tanα-tanβ1+tanα×tanβ =32×tanβ-tanβ1+32tan2β ∵2tanα=3tanβ =12×tanβ1+32tan2β=tanβ2+3tan2β =sinβcosβ2+3sin2βcos2β=sinβcosβ×cos2β2cos2β+3sin2β
=sinβ×cosβ2cos2β+2sin2β+sin2β =122sinβ×cosβ2cos2β+sin2β+sin2β =12sin2β2+sin2β=sin2β4+2sin2β =sin2β4+21-cos2β=sin2β6-2cos2β =sin2β6-1+cos2β ∵1+cos2β=2cos2β =sin2β5-cos2β=RHS Hence proved.
Q35.
Answer :
The given equations are sin α + sin β=a and cos α+cos β=b.
(i)
∵sinC+sinD=2sinC+D2cosC-D2∴2sinα+β2cosα-β2=a …(1)
Now, using the identity sinC+sinD=2sinC+D2cosC-D2 for the LHS of cos α+cos β=b, we get
2cosα+β2cosα-β2=b …(2)
On dividing (1) by (2), we get
tanα+β2=ab
We know,
sinθ=2tanθ21+tan2θ2
∴sinα+β=2tanα+β21+tan2α+β2⇒sinα+β=2×ab1+a2b2=2aba2+b2
(ii)
On squaring sinα+sinβ=a and cosα+cosβ=b and adding them, we get sin2α+sin2β+2×sinαsinβ+ cos2α+cos2β+2×cosαcosβ=a2+b2⇒1+1+2sinαsinβ+cosαcosβ=a2+b2⇒2sinαsinβ+cosαcosβ=a2+b2-2⇒2cosα-β=a2+b2-2 ∵cosA-B=sinAsinB+cosAcosB⇒cosα-β=a2+b2-22
Q36.
Answer :
RHS=3+5cos β5+3cos β =3+51-tan2 β21+tan2 β25+31-tan2 β21+tan2 β2 =3+3tan2 β2+5-5tan2 β25+5tan2 β2+3-3tan β2 =8-2tan2 β28+2tan2 β2 =8-8tan2 α28+8tan2 α2 ∵2tan α2=tan β2 =81-tan2 α281+tan2 α2 =1-tan2 α21+tan2 α2 =cos α =LHSHence proved.
Q37.
Answer :
Given:
cos θ=cos α+cos β1+cos α cos β …(1)
⇒1-tan2θ21+tan2θ2 =cosα+cosβ1+cosα×cosβ ∵cosθ=1-tan2θ21+tan2θ2 By componendo and dividendo, we get1-tan2θ2+1+tan2θ21-tan2θ2-1+tan2θ2 =1+cosα×cosβ+cosα+cosβ-1+cosαcosβ-cosα-cosβ⇒22tan2θ2=1+cosα1+cosβ1-cosα1-cosβ
⇒tan2θ2=1-cosα1-cosβ1+cosα1+cosβ⇒tan2θ2=2sin2α2×2sin2β22cos2α2×2cos2β2⇒tan2θ2=tan2α2×tan2β2⇒tanθ2=±tanα2×tanβ2Hence proved.
Q38.
Answer :
Equation sec θ+α+sec θ-α=2 sec θ can be written as
1cosθ+α+1cosθ-α=2cosθ⇒1cosθ×cosα-sinθ×sinα+1cosθ×cosα+sinθ×sinα=2cosθ ∵cosA+B=cosA×cosB-sinA×sinB and cosA-B=cosA×cosB+sinA×sinB ⇒2cosθ×cosαcos2θ×cos2α-sin2θ×sin2α=2cosθ⇒cosθ×cosαcos2θ×cos2α-1-cos2θ×sin2α=1cosθ
⇒cos2θ×cosαcos2θ×cos2α-1-cos2θ×sin2α=1⇒cos2θ×cosαcos2θ×cos2α-sin2α+cos2θsin2α=1⇒cos2θ×cosα=cos2θ×cos2α-sin2α+cos2θsin2α⇒cos2θ×cosα=cos2θcos2α+sin2α-sin2α⇒cos2θ×cosα=cos2θ-sin2α
⇒cos2θ×cosα-cos2θ=-sin2α⇒cos2θcosα-1=-sin2α⇒cos2θ1-cosα=sin2α⇒cos2θ=sin2α2sin2α2 ∵2sin2θ2=1-cosθ
⇒cos2θ=4sin2α2×cos2α22sin2α2 ∵sin2θ=4sin2θ2×cos2θ2 ⇒cosθ=±2 cosα2Hence proved.
Q39.
Answer :
Squaring and adding equations cos α + cos β=13 and sinα+sin β=14, we get
cos2α+cos2β+2cosα×cosβ+sin2α+sin2β+2sinα×sinβ=19+116⇒1+1+2cosα×cosβ+sinα×sinβ=25144⇒2+2cosα-β=25144 ∵cosA-B=cosA×cosB+sinA×sinB⇒cosα-β=-263288 … (1)
Now,
cos2α-β2=1+cosα-β2 =1-2632882 [From (1)] =25576 =±524
Q40.
Answer :
Given:
sin α=45 cos β=513.
Now,
cosα=1-sin2α=1-452=35And,sinβ=1-cos2α=1-5132=1213
Now,
cosα-β=cosα×cosβ+sinα×sinβ⇒cosα-β=35×513×45×1213=6365Thus,cosα-β2=1+cosα-β2 =1+63652 =865
Q41.
Answer :
LHS= sin3x+sin2x-sinx =sin3x+2sin2x-x2cos2x+x2 ∵sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2 =sin3x+2sinx2cos3x2 =2sin3x2cos3x2+2sin3x2cosx2 ∵sin2A=2sinAcosA =2cos3x2sin3x2cosx2 =2cos3x22sin3x2+x22cos3x2-x22 ∵sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2 =2cos3x22sinxcosx2 =4sinxcosx2cos3x2=RHS Hence proved.
Page 9.36 Ex – 9.2
Q1.
Answer :
LHS=sin5θ =sin3θ+2θ =sin3θ×cos2θ+cos3θ×sin2θ =3sinθ-4sin3θ1-2sin2θ+4cos3θ-3cosθ×2sinθcosθ =3sinθ-6sin3θ-4sin3θ+8sin5θ+8cos4θ-6cos2θsinθ =3sinθ-10sin3θ+8sin5θ+8sinθ1-sin2θ2-6sinθ1-sin2θ =3sinθ-10sin3θ+8sin5θ+8sinθ1-2sin2θ+sin4θ-6sinθ+6sin3θ =3sinθ-10sin3θ+8sin5θ+8sinθ-16sin3θ+8sin5θ-6sinθ+6sin3θ =5sinθ-20sin3θ+16sin5θ =RHS Hence proved.
Q2.
Answer :
We know, sin60°=cos30° =32⇒sin3×20°=cos3×10°⇒3sin20°-4sin320°=4cos310°-3cos10° ∵sin3θ=3sinθ-4sin3θ and cos3θ=4cos3θ-3cosθ ⇒4cos310+sin320°=3cos10°+sin20°Hence proved.
Q3.
Answer :
We know,cos3θ=4cos3θ-3cosθ⇒cos3θ=cos3θ+3cosθ4 …iAlso,sin3θ=3sinθ-4sin3θ⇒sin3θ=3sinθ-sin3θ4 …ii
Now,LHS=cos3θsin3θ+sin3θcos3θ =cos3θ+3cosθ4sin3θ+3sinθ-sin3θ4cos3θ Using i and ii =143sin3θcosθ+sinθcos3θ+cos3θsin3θ-sin3θcos3θ =143sin3θ+θ+0 =34sin4θ =RHSHence proved.
Q4.
Answer :
LHS=sin5A =sin3A+2A =sin3A×cos2A+cos3A×sin2A =3sinA-4sin3A2cos2A-1+4cos3A-3cosA×2sinAcosA =-3sinA+4sin3A+6sinAcos2A-8sin3Acos2A+8sinAcos4A-6sinAcos2A =8sinAcos4A-8sin3Acos2A-3sinA+4sin3A =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-3sinA+3sinAcos4A+4sin3A+2sin3Acos2A =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-3sinA1-cos4A+2sin3A2+cos2A
=5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-3sinA1-cos2A1+cos2A+2sin3A2+cos2A =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-3sin3A1+cos2A+2sin3A2+cos2A =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-sin3A31+cos2A-22+cos2A =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-sin3A3+3cos2A-4-2cos2A =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-sin3Acos2A-1 =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A-sin3A×-sin2A =5sinAcos4A-10sin3Acos2A+sin5A =5cos4A sinA-10cos2A sin3A+sin5A =RHS Hence proved.
Q5.
Answer :
LHS=tanθ tanθ+60°+tanθ tanθ-60°+ tanθ+60°tanθ-60° =tanθtanθ+31-3tanθ+tanθtanθ-31+3tanθ+tanθ+31-3tanθtanθ-31+3tanθ tanA+B=tanA+tanB1-tanAtanB and tanA-B=tanA-tanB1+tanAtanB =1+3tanθtanθtanθ+3+1-3tanθtanθtanθ-3+tan2θ-31+3tanθ1-3tanθ =tanθ+3tan2θtanθ+3+tanθ-3tanθtanθ-3+tan2θ-31-3tan2θ
=tan2θ+3tan3θ+3tanθ+3tan2θ+tan2θ-3tan3θ-3tanθ+3tan2θ+tan2θ-31-3tan2θ=9tan2θ-31-3tan2θ=-31-3tan2θ1-3tan2θ=-3=RHSHence proved.
Q6.
Answer :
LHS = tanA+tan60°+A-tan60°-A =tanA+tan60°+tanA1-tan60° tanA-tan60°-tanA1+tan60° tanA tanx+y=tanx+tany1-tanxtany and tanx-y=tanx-tany1+tanxtany =tanA+3+tanA1-3 tanA-3-tanA1+3 tanA =tanA+3+3tanA+tanA+3 tan2A+3+3tanA+tanA-3tan2A1-3 tanA1+3 tanA =tanA+8tanA1-3tan2A
=tanA-3tan3A+8tanA1-3tan2A=9tanA-3tan3A1-3tan2A=33tanA-tan3A1-3tan2A ∵tan3θ=3tanθ-tan3θ1-3tan2θ =3tan3A=RHSHence proved.
Q7.
Answer :
LHS=cotA+cot60°+A-cot60°-A =1tanA+1tan60°+A-1tan60°-A
=1tanA+1-3tanA3+tanA-1+3tanA3-tanA tanx+y=tanx+tany1-tanxtany and tanx-y=tanx-tany1+tanxtany=1tanA-8tanA3-tan2A=3-tan2A-8tan2AtanA3-tan2A=3-9tan2A3tanA-tan3A=31-3tan2A3tanA-tan3A=3×1tan3A ∵tan3θ=1-3tan2θ3tanθ-tan3θ=3cot3A=RHSHence proved.
Q8.
Answer :
LHS=cotA+cot60°+A+cot120°+A =cotA+cot60°+A-cot180°-120°+A ∵-cotθ=cot180°-θ =cotA+cot60°+A-cot60°-A =1tanA+1tan60°+A-1tan60°-A
=1tanA+1-3tanA3+tanA-1+3tanA3-tanA tanx+y=tanx+tany1-tanxtany and tanx-y=tanx-tany1+tanxtany=1tanA-8tanA3-tan2A=3-tan2A-8tan2A3tanA-tan3A=3-9tan2A3tanA-tan3A=31-3tan2A3tanA-tan3A=3×1tan3A ∵ tan3θ=3tanθ-tan3θ1-3tan2θ=3cot3A=RHSHence proved.
Q9.
Answer :
LHS=sin3A+sin32π3+A+sin34π3+A =3sinA-sin3A4+3sin2π3+A-sin32π3+A4+3sin4π3+A-sin34π3+A4 sin3θ=3sinθ-sin3θ4 =3sinA-sin3A4+3sinπ-2π3+A-sin2π+3A4+3sinπ+π3+A-sin4π+3A4 =143sinA-sin3A+3sinπ3-A-sin3A-3sinπ3+A+sin3A =143sinA-sin3A+3sinπ3-A-3sinπ3+A-sin3A-sin3A
=143sinA-3sin3A+3sinπ3-A-sinπ3+A=143sinA-3sin3A+32cosπ3-A+π3+A2sinπ3-A-π3-A2 ∵sinC-sinD=2cosC+D2sinC-D2=143sinA-3sin3A+6cosπ3sin-A=143sinA-3sin3A-3sinA=-34sinA=RHSHence proved.
Q10.
Answer :
We have, sinθ sin60-θ sin60+θ =sinθsin260-sin2θ ∵sinA+B sinA-B=sin2A-sin2B =sinθ34-sin2θ =14sinθ3-4sin2θ =143sinθ-4sin3θ =14sin3θ ∵3sinθ-4sin3θ=sin3θ ≤14 ∵sinx≤1 for all x∴ sinθ sin60-θ sin60+θ≤14Hence proved.
Q11.
Answer :
We have,cosθ cos60°-θ cos60°+θ=cosθcos260°-sin2θ cos2A-sin2B=cosA-B cosA+B=cosθ14-sin2θ =cosθ141-4sin2θ=14cosθ1-41-cos2θ=14cosθ-3+4cos2θ
=144cos3θ-3cosθ=14cos3θ ∵cos3θ=4cos3θ-3cosθ ≤14 ∵cosx≤1 for all x∴cosθ cos60°-θ cos60°+θ≤14
Page 9.41 Ex – 9.3
Q1.
Answer :
LHS=sin272°-sin260° =sin290°-18°-34 =cos218°-34 ∵sin90°-θ=cosθ =10+2542-34 ∵cos18°=10+254 =10+2516-34
=10+25-1216=25-216=5-18=RHSHence proved.
Q2.
Answer :
LHS=sin224°-sin26° =sin24°+6° sin24°-6° sinA+B sinA-B=sin2A-sin2B =sin30° sin18° =12×5-14 ∵sin18°=5-14 =5-18 =RHSHence proved.
Q3.
Answer :
LHS=sin242°-cos278° =sin290°-48°-cos290°-12° =cos248°-sin212° =cos48°+12° cos48°-12° cosA+B cosA-B=cos2A-sin2 =cos60° cos36° =12×5+14 ∵cos36°=5+14 =5+18 =RHSHence proved.
Q4.
Answer :
LHS=cos78° cos42° cos36° =2cos78° cos42°2 cos36° =cos78°+42°+cos78°-42°2 ×cos36° 2cosAcosB=cosA+B+cosA-B =12cos120°+cos36° cos36°
=12-cos180°-120°+cos36° cos36°=12-cos60°+cos36° cos36°=12-12+5+145+14=12×5-14×5+14=18=RHSHence proved.
Q5.
Answer :
LHS=cosπ15cos2π15cos4π15cos7π15
=2sinπ15cosπ152sinπ15cos2π15cos4π15cos7π15 On dividing and multiplying by 2sinπ15
=2sin2π15×cos2π152×2sinπ15cos4π15cos7π15=2sin4π15×cos4π152×2×2sinπ15cos7π15=sin8π152×2×2sinπ15cos7π15
=2sin8π15cos7π152×2×2×2sinπ15=2sin8π15cos7π1516sinπ15=sin8π15+7π15+sin8π15-7π1516sinπ15 ∵2sinAcosB=sinA+B+sinA-B
=sinπ+sinπ1516sinπ15=0+sinπ1516sinπ15=sinπ1516sinπ15=116=RHS
Hence proved.
Q6.
Answer :
LHS=cosπ15 cos2π15 cos4π15 cos3π15 cos5π15 cos6π15 cos7π15 =cosπ15 cos2π15 cos4π15cos3π15 cos6π15 ×-cos8π15 =-12cosπ15 cos2π15 cos4π15 cos8π15× 12× cos3π15 cos6π15 =-12×2324sinπ152sinπ15cosπ15 cos2π15 cos4π15 cos8π15 ×222×sin3π15 2sin3π15cos3π15 cos6π15 =-23132sinπ15sin2π15 cos2π15 cos4π15 cos8π15 ×24sin3π15 sin6π15 cos6π15 =-2232sinπ152sin2π15 cos2π15 cos4π15 cos8π15 ×14sin3π15 2sin6π15 cos6π15
=-232sinπ15sin8π15 cos8π15 ×sin12π154sin3π15=-132sinπ15sin16π15 ×sin12π154sin3π15=-sinπ+π15128sinπ15×sinπ-3π15sin3π15=–sinπ15128sinπ15×sin3π15sin3π15=1128=RHSHence proved.
Q7.
Answer :
LHS=cos6° cos42° cos66° cos78°=142cos6° cos66°2cos42° cos78° =14cos72°+cos60°cos120°+cos36° ∵2cosAcosB=cosA+B+cosA-B =14cos90°-72°+12-12+5+14
=14sin18°+12-12+5+14=145-14+125+14-12=145-1+245+1-24=1645+15-1=1645-1=116=RHSHence proved.
Q8.
Answer :
LHS=142 sin6° sin66°2sin42° sin78° =14cos60°-cos72° cos36°-cos120° 2sinAsinB=cosA-B-cosA+B =1412-sin18° 5+14+12
=1412-5-145+14+12=142-5+14 5+1+24=1643-5 3+5=1649-5=116=RHSHence proved.
Q9.
Answer :
LHS=cos36° cos42° cos60° cos78° =12cos36° cos60° 2cos42° cos78° 2cosAcosB=cosA+B+cosA-B =125+14 ×12cos120°+cos36° =5+116-12+5+14 =5+1 5-164 =5-164 =116 =RHS Hence proved.
Q10.
Answer :
LHS=sin36∘sin72∘sin108∘sin144∘ =sin36∘sin72∘sin72∘sin36∘ ∵sin144∘=sin180∘-36∘=sin36∘ and sin108∘=sin180∘-72∘=sin72∘ =sin36∘sin72∘2 =10-254×10+2542 =100-2042 =45162 =516 =RHS
Hence proved.
Page 9.41 (Very Short Answers)
Q1.
Answer :
We have, cos4x=1+k sin2x cos2x ⇒cos2×2x=1+k sin2x cos2x ⇒1-2sin22x=1+k sin2x cos2x ⇒ 1-22sinxcosx2=1+k sin2x cos2x ⇒1-8sin2xcos2x=1+k sin2x cos2x ⇒sin2xcos2xk+8=0⇒k+8=0∴ k=-8
Q2.
Answer :
Given:
tanx2=mn
⇒sinx2cosx2=mnLet sinx2 be mk and cosx2 be nk. Now, msinx+ncosx=2m sinx2cosx2+ncos2x2-sin2x2 =2m×mk×nk+nn2k2-m2k2
=2m2k2n+nk2n2-m2 =nk22m2+n2-m2 =nk2m2+n2 =nm2k2+n2k2 =nsin2x2+ cos2x2 =n1∴msinx+ncosx=n
Q3.
Answer :
∵π2<θ<3π2∴1+cos2θ2=2cos2θ2=cosθIn second quadrant cosθ is negative.∴1+cos2θ2=-cosθ
Q4.
Answer :
We have,
2+2+2cos2θ= 2+21+cos2θ =2+2.2cos2θ =2+2cosθ =2-2cosθ ∵π2<θ<π =21-cosθ =2.2sin2θ2 =2sinθ2 =2sinθ2 ∵π4<θ2<π2
Q5.
Answer :
We have,1-cos2θ1+cos2θ=2sin2θ2cos2θ =sinθcosθ =sinθ-cosθ ∵π2<θ<π =-tanθ
Q6.
Answer :
We have,1-cos2θ1+cos2θ=2sin2θ2cos2θ =sinθcosθ =sinθcosθ =-sinθ-cosθ ∵π<θ<3π2 ∴ 1-cos2θ1+cos2θ=tanθ
Q7.
Answer :
Let, ∠B=90°∴A+C=90°=π2⇒C=π2-A⇒sin C=sin π2-A⇒sin C=cos A …iNow,sin2 A+sin2 B+sin2 C= sin2 A+1+sin2 C ∵sin B=sin 90°=1 =sin2 A+cos2 A+1 Using i =1+1 =2
Q8.
Answer :
We have,cos276°+cos216°-cos76°cos16°=121+cos276°+1+cos216°-cos76+16°-cos76-16° ∵2cos2θ=1+cos2θ and 2cosA cos B=cosA+B +cosA-B=122+cos152°+cos32°-cos92°-12=1232-cos180-152°+cos32°-cos92°
=1232-cos28°+2sin92°+32°2 sin92°-32°2 cosC-cosD=2sinC+D2sinD-C2=1232-cos28°+2sin124°2 sin60°2=1232-cos28°+2sin62° sin30°=1232-cos28°+2sin62°×12=1232-cos28°+sin62°=1232-cos28°+sin90-28°=1232-cos28°+cos28°=34
Q9.
Answer :
We have,1-sin2θ=sin2θ+cos2θ-2sinθcosθ=sinθ-cosθ2 =sinθ-cosθ=sinθ-cosθ ∵sinθ>cosθ for π4<θ<π2∴1-sin2θ=sinθ-cosθ
Q10.
Answer :
We have, cosπ7 cos2π7 cos4π7=2sinπ7 cosπ7 cos2π7 cos4π72sinπ7 On dividing and multiplying by 2sinπ7 =2×sin2π7 cos2π7 cos4π72×2sinπ7
Proceeding in the same way, we get
cosπ7 cos2π7 cos4π7=sin8π78sinπ7 =sinπ+π78sinπ7 =-sinπ78sinπ7∴cosπ7 cos2π7 cos4π7=-18
Page 9.41 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q1.
Answer :
(d) sin x
We have, 8sinx8 cosx2 cosx4 cosx8 =4×2sinx8 cosx8 cosx2 cosx4 =4×sinx4cosx2 cosx4 =2×2sinx4 cosx4 cosx2 =2×sinx2cosx2 =sinx
Q2.
Answer :
(b) tan 8Atan 2A
We have,sec8A-1sec4A-1=1cos8A-11cos4A-1 =cos4Acos8A×1-cos8A1-cos4A
=cos4Acos8A×2sin24A2sin22A 2sin2θ=1-cos2θ=2cos4A sin4A sin4A2×cos8A sin22A=sin8A sin4Acos8A×2sin2A×sin2A=tan8A×2sin2A×cos2A2sin2A×sin2A=tan8A×cot2A=tan8Atan2A
Page 9.42 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q3.
Answer :
(d) none of these
We have,cosπ65 cos2π65 cos4π65 cos8π65 cos16π65 cos32π65= 2sinπ652sinπ65 cosπ65 cos2π65 cos4π65 cos8π65 cos16π65 cos32π65 dividing and multiplying by 2sinπ65= 2sin2π652×2sinπ65 cos2π65 cos4π65 cos8π65 cos16π65 cos32π65= 2sin4π652×4sinπ65 cos4π65 cos8π65 cos16π65 cos32π65
= 2sin8π652×8sinπ65 cos8π65 cos16π65 cos32π65= 2sin16π652×16sinπ65 cos16π65 cos32π65= 2sin32π652×32sinπ65 cos32π65= sin64π6564sinπ65= sinπ-π6564sinπ65=sinπ6564sinπ65=164
Q4.
Answer :
(a) 1
We have,cos2x+2cosx=1⇒2cos2x-1+2cosx=1⇒cos2x+cosx-1=0⇒cosx=-1±12+42⇒cosx=-1±52⇒cosx=-1+52
Now,2-cos2xsin2x=2–1+522 1-cos2x =2-141-25+5 1-141-25+5 =141+55-1=44=1
Q5.
Answer :
(b) tan x
We have,cotx-2cot 2x=cotx-2cot2x-12cotx =cot2x-cot2x+1cotx =1cotx =tanx
Q6.
Answer :
(a) 0
We have,2tanπ10+3secπ10-4cosπ10=2tan18°+3sec18°-4cos18°=2sin18°cos18°+3×1cos18°-4cos18°=2×5-1410+254+3×110+254-4×10+254=2×5-110+25+3×410+25-10+25=25-2+12-10+25210+25=25+10-10-2510+25=0
Q7.
Answer :
(d) none of these
ABC is a triangle.
∴A+B+C=π⇒A+B=π-C⇒tanA+B=tanπ-C⇒tanA+tanB1-tanA tanB=-tanC⇒tanA+tanB=-tanC+tanA tanB tanC⇒tanA+tanB+tanC =tanA tanB tanC⇒0=tanA tanB tanC [Given: tanA tanB tanC=0]⇒tanA tanB tanC=0⇒1tanA tanB tanC=10⇒cotA cotB cotC →∞
Q8.
Answer :
(b) 12
Given:cosθ=12a+1a cos3θ=λa3+1a3Now,cos3θ=18a3+1a3+3a1aa+1a⇒cos3θ=18a3+1a3+3×2cosθ ∵ cosθ=12a+1a⇒cos3θ=18cos3θλ+6cosθ⇒cos3θ=184cos3θ-3cosθλ+6cosθ⇒cos3θ=4cos3θ8λ-3cosθ8λ+6cosθ8On comparing the powers of cos3θ on both sides, we get1=48λ⇒λ=12
Q9.
Answer :
(a) sin 2 β5-cos 2 β
Given: 2tanα=3tanβNow,tanα-β=tanα-tanβ1+tanαtanβ =32tanβ-tanβ1+32tanβtanβ =3tanβ-2tanβ2+3tan2β =tanβ2+3tan2β =sinβcosβ2+3sin2βcos2β =sinβcosβ2cos2β+3sin2β =sinβcosβ2+sin2β =2sinβcosβ4+2sin2β =sin2β4+1-cos2β∴ tanα-β=sin2β5-cos2β
Q10.
Answer :
(b) tan 2 α = tan β
tanα=1-cosβsinβ =2sin2β22sinβ2cosβ2 =sinβ2cosβ2⇒tanα=tanβ2⇒α=β2⇒2α=β∴tan2α=tanβ
Q11.
Answer :
(b) -ba
Given: sinα+sinβ=a⇒2sinα+β2cosα-β2=a …(1)Also,cosα+cosβ=b⇒-2sinα+β2sinα-β2=b …(2)On dividing (1) by (2), we get-cosα-β2sinα-β2=ab⇒-sinα-β2cosα-β2=ba⇒tanα-β2=-ba
Q12.
Answer :
(d) 4
We have,cotx2-tanx22 1-2tanx cot2xcot2x2-2cotx2tanx2+tan2x2 1-2tanx cot2x-12cotxcot2x2-2+tan2x21-tanx cot2x-1cotxcot2x2+tan2x2-21-cotx-tanxcotxcot2x2+tan2x2-2tan2xcot2x2+tan2x2-22tanx21-tan2x22
=11-tan2x224+4tan4x2-8tan2x2=11-tan2x22 4-8tan2x2+4tan4x2=41-tan2x22 tan2x22-2tan2x2+1=4tan2x2-121-tan
Q13.
Answer :
(d) none of these
We have,tanθ sinπ2+θ cosπ2-θ=sinθcosθcosθ sinθ=sin2θ
Q14.
Answer :
(b) 2
We have,sin2π18+sin2π9+sin27π18+sin24π9=121-cosπ9+1-cos2π9+1-cos7π9+1-cos8π9 ∵sin2θ=1-cos2θ2=124-cosπ9-cos2π9–cosπ-7π9–cosπ-8π9=124-cosπ9-cos2π9+cos2π9+cosπ9=42=2
Q15.
Answer :
(c) 4 tan β
We have,5 sin α=3 sin α+2 β⇒53=sin α+2 βsin α⇒5-35+3=sin α+2 β-sin αsin α+2 β+sin α Using componendo and dividendo⇒28=sin α+2 β-sin αsin α+2 β+sin α⇒14=2cosα+2 β+α2sinα+2 β-α22sinα+2 β+α2cosα+2 β-α2⇒14=cosα+ β sin βsinα+ β cos β⇒14=cot α+ β tan β⇒14=1 tan α+ βtan β∴ tan α+ β=4 tan β
Q16.
Answer :
(c) 0
We have,2cosθ-cos3θ-cos5θ-16cos3θ sin2θ=2cosθ-cos3θ-cos5θ-16cos3θ+3cosθ4×1-cos2θ2=2cosθ-cos3θ-cos5θ-2cos3θ+3cosθ1-cos2θ=2cosθ-cos3θ-cos5θ-2cos3θ-cos3θcos2θ+3cosθ-3cosθcos2θ=2cosθ-cos3θ-cos5θ-2cos3θ+3cosθ+2cos3θcos2θ+32cosθcos2θ=2cosθ-cos3θ-cos5θ-2cos3θ+3cosθ+cos5θ+cosθ+3cos3θ+3cosθ 2cosAcosB=cosA+B+cosA-B=2cosθ-cos3θ-cos5θ-2cos3θ-6cosθ+cos5θ+cosθ+3cos3θ+3cosθ=0
Q17.
Answer :
(a) -1, 3
A=2sin2θ-cos2θ =2sin2θ-1-2sin2θ =4sin2θ-1∵0≤sin2θ≤1⇒4×0≤4×sin2θ≤4×1⇒0≤4sin2θ≤4⇒0-1≤4sin2θ-1≤4-1⇒-1≤4sin2θ-1≤3⇒-1≤A≤3⇒A∈-1,3
Page 9.43 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q18.
Answer :
(a) cos θ
We have,∴cos3θ2cos2θ-1=4cos3θ-3cosθ22cos2θ-1-1 ∵cos3θ=4cos3θ-3cosθ =4cos3θ-3cosθ4cos2θ-2-1 =4cos3θ-3cosθ4cos2θ-3 =cosθ4cos2θ-34cos2θ-3 =cosθ
Q19.
Answer :
(d) 2
Given: tanπ4+θ+tanπ4-θ=λ sec 2θ⇒tanπ4+tanθ1-tanπ4×tanθ+tanπ4-tanθ1+tanπ4×tanθ=λ sec 2θ⇒1+tanθ1-tanθ+1-tanθ1+tanθ=λ sec 2θ⇒1+tanθ2+1-tanθ21-tanθ1+tanθ=λ sec 2θ⇒21+tan2θ1-tan2θ=λ sec 2θ
⇒2sec2θ1-tan2θ=λ sec 2θ⇒2cos2θ1-tan2θ=λ sec 2θ⇒2cos2θ1-sin2θcos2θ=λ sec 2θ⇒2cos2θ-sin2θ=λ sec 2θ⇒2cos2θ=λ sec 2θ⇒2sec2θ=λ sec 2θ⇒2=λ∴ λ=2
Q20.
Answer :
(a) 12 cos 2 θ
We have,cos2π6+θ-sin2π6-θ=cos2π6+θ-cos2π2-π6-θ=cos2π6+θ-cos2π3+θ=cosπ6+θ+cosπ3+θcosπ6+θ-cosπ3+θ=2cosπ6+θ+π3+θ2 cosπ6+θ-π3-θ2 2sinπ6+θ+π3+θ2 sinπ3+θ-π6-θ2=4cosπ4+θcos-π12 sinπ4+θ sinπ12=4cosπ4+θcosπ12 sinπ4+θ sinπ12=2sinπ4+θcosπ4+θ2 sinπ12cosπ12=sinπ2+2θsinπ6=cos2θ×12=12cos2θ
Q21.
Answer :
(b) sin θ
We have,sin 3θ1+2cos 2θ=3sin θ-4sin3 θ1+21-2sin2 θ =3sin θ-4sin3 θ1+2-4sin2 θ =sin θ3-4sin2 θ3-4sin2 θ =sin θ
Q22.
Answer :
(c) cos 2A
We have,2sin2B+4cosA+B sinA sinB+cos2A+B=1-cos2B+cos2A+B+4cosA+B sinA sinB=1+cos2A+B-cos2B+4cosA+B sinA sinB=1-2sinAsinA+2B+4cosA+B sinA sinB ∵ cosC-cosD=-2sinC+D2sinC-D2=1-2sinAsinA+2B-2sinBcosA+B=1-2sinAsinA+2B-sinB+A+B+sinB-A+B ∵ 2sinCcosD=sinC+D+sinC-D=1-2sinAsinA+2B-sinA+2B+sin-A=1-2sinAsinA=1-2sin2A=cos2A
Q23.
Answer :
(c) cosec θ
We have,2sin2θ+2cos2θ-1cosθ-sinθ-cos3θ+sin3θ=2sin2θ+cos2θcosθ-sinθ-4cos3θ+3cosθ+3sinθ-4sin3θ=2sin2θ+cos2θ4cosθ-4cos3θ+2sinθ-4sin3θ=2sin2θ+cos2θ4cosθ1-cos2θ+2sinθ1-2sin2θ=2sin2θ+cos2θ4cosθsin2θ+2sinθcos2θ=2sin2θ+cos2θ2×2sinθ cosθ sinθ+2sinθ cos2θ=2sin2θ+cos2θ2sin2θ sinθ+2sinθ cos2θ=2sin2θ+cos2θ2sinθsin2θ+cos2θ=1sinθ=cosecθ
Q24.
Answer :
(a) sin 17 θ-sin 11 θ
We have, 21-2sin2 7θ sin 3θ=2cos 14θ sin3θ ∵cos2θ=1-2sin2 θ =2 sin3θ cos 14θ = sin 17θ-sin 11θ ∵2 sinA cosB=sinA+B-sinA-B ∴ 21-2sin2 7θ sin 3θ= sin 17θ-sin 11θ
Q25.
Answer :
(a) 2 tan β
Given: cos2α=3cos 2β-13-cos2β⇒cos2α-1cos2α+1=3cos 2β-1-3-cos2β3cos 2β-1+3-cos2β Using componendo and dividendo⇒cos2α-1cos2α+1=4cos 2β-42cos 2β+2⇒-1-cos2α1+cos2α=-41-cos 2β21+cos 2β⇒1-cos2α1+cos2α=21-cos 2β1+cos 2β⇒2sin2α2cos2α=22sin2β2cos2β⇒tan2α=2tan2β∴tan α=2 tan β
Q26.
Answer :
(d) cos θ-e1-e cos θ
Given: tanθ2=1-e1+etanα2⇒tanθ2tanα2=1-e1+eSquaring both sides, we get,tan2θ2tan2α2=1-e1+e⇒tan2α21-e=tan2θ21+e
⇒sin2α2cos2α21-e=sin2θ2cos2θ21+e⇒121-cosα121+cosα1-e=121-cosθ121+cosθ1+e⇒1-cosα1+cosθ1-e=1+cosα1-cosθ1+e⇒1+cosθ1-e-cosα1+cosθ1-e=1-cosθ1+e+cosα1-cosθ1+e⇒cosα1+cosθ1-e+1-cosθ1+e=1+cosθ1-e-1-cosθ1+e⇒cosα=2cosθ-2e2-2ecosθ=cosθ-e1-ecosθ
Q27.
Answer :
(b) 1
2n+1θ=π Given⇒2nθ+θ=π⇒2nθ=π-θ⇒sin 2nθ =sinπ-θ⇒sin 2nθ =sin θ …(1)
2n cos θ cos 2 θ cos 22 θ … cos 2n-1 θ=2n ×sin 2nθ2nsin θ =sin 2nθsin θ =sin θ sin θ From (1) =1
Q28.
Answer :
(a) 1+t1-t
tan 2θ + sec 2θ=2 tan θ1-tan2 θ+1+tan2 θ1-tan2 θ =2tan θ+1+tan2 θ1-tan2 θ =1+tan θ21-tan2 θ =1+tan θ1+tan θ1+tan θ1-tan θ =1+tan θ1-tan θ =1+t1-t tan θ=t given
Q29.
Answer :
(c) cos 4 θ
cos4 θ+sin4θ-6cos2θ sin2θ= cos4 θ+sin4θ-2cos2θ sin2θ-4cos2θ sin2θ =cos2θ-sin2θ2-2sin θ cos θ2 =cos22θ-sin22θ =cos4θ
Q30.
Answer :
(a) cos 2A
cos36°-Acos36°+A+cos 54°-Acos54°+A =cos90°-54°+Acos90°-54°-A+cos 54°-Acos54°+A =sin54°+Asin54°-A+cos54°-Acos54°+A cos90°-θ=sinθ =cos54°+A-54°+A cosA-B=cosAcosB+sinAsinB =cos 2A
Q31.
Answer :
(c) tan 3 θ
tanθ tan60°-θ tan60°+θ=tan θ×tan60°-tanθ1+tan60°tanθ×tan60°+tanθ1-tan60°tanθ =tan θ×3-tanθ1+3tanθ×3+tanθ1-3tanθ =tanθ3-tan2θ1-3tan2θ =3tanθ-tan3θ1-3tan2θ =tan 3θ
Q32.
Answer :
(a) 3 tan 3 θ
tan θ+ tan60°+θ+tan120°+θ=tan θ+tan60°+tanθ1-tan60°tanθ+tan 120°+tan θ1-tan 120° tanθ =tan θ +3+tan θ1-3tanθ+-3+tanθ1+3tanθ =tan θ1-3tan2θ+3+tanθ1+3tanθ+-3+tanθ1-3tanθ1-3tan2θ =tan θ-3tan3θ+3+3tanθ+tanθ+3tan2θ+tanθ-3tan2θ-3+3tanθ1-3tan2θ =9tanθ-3tan3θ1-3tan2θ =33tanθ-tan3θ1-3tan2θ =3tan3θ
Q33.
Answer :
(c) tan α/2
sin5α-sin3αcos5α+2cos4α+cos3α= sin5α-sin3αcos5α+cos3α+2cos4α =2sinαcos4α2cos4αcosα+2cos4α =2sinαcos4α2cos4αcosα+1 =sinαcosα+1 =2sinα2cosα2cos2α2-sin2α2+sin2α2+cos2α2 =2sinα2cosα22cos2α2 =sinα2cosα2 =tanα2
Page 9.44 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q34.
Answer :
(a)
16 cos4 θ-12 cos2θ+1 To find:sin 5θsinθNow,sin5θ= sin3θ+2θ = sin3θcos2θ+cos3θsin2θ =3sinθ-4sin3θ1-2sin2θ+4cos3θ-3cosθ2sinθcosθ =3sin θ-6sin3θ-4sin3θ+8sin5θ +2sinθcos2θ4cos2θ-3 =3sin θ-10sin3θ+8sin5θ+2sinθ1- sin2θ41-sin2θ-3 =3sin θ-10sin3θ+8sin5θ+2sinθ-2sin3θ4-4sin2θ-3 =3sin θ-10sin3θ+8sin5θ+2sinθ-8sin3θ-2sin3θ+8sin5θ =5sinθ-20sin3θ+16sin5θ∴sin 5θsinθ=5sinθ-20sin3θ+16sin5θsinθ =5-20sin2θ+16sin4θ =5-201-cos2θ+161-cos2θ2 =5-20+20cos2θ+161+cos4θ-2cos2θ =5-20+20cos2θ+16+16cos4θ-32cos2θ =16cos4θ-12cos2θ+1
Q35.
Answer :
(d) sin 2n α2n sin α
∵cos α cos 2 α cos 4α … cos 2n-1 α=sin2nα2nsin α
7. SINE & COSINE FORMULAE & THEIR APPLICATIONS
Page 10.12 Ex – 10.1
Q1.
Answer :
Let asinA=b sinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation a2-c2b2=sin A-Csin A+C.
LHS=ksinA2-ksinC2ksinB2 =k2sin2A-sin2Ck2sin2B =sinA+CsinA-Csin2B ∵sin2A-sin2C=sinA+CsinA-C =sinA+CsinA-CSin2π-A+C ∵A+B+C=π =sinA+CsinA-Csin2A+C =sinA-CsinA+C=RHS Hence proved.
Q2.
Answer :
Let asinA=b sinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of he equation b sin B-c sin C=a sin B-C.
LHS=ksinBsinB-ksinCsinC
=ksin2B-sin2C=ksinB+CsinB-C ∵ sin2B-sin2C=sinB+CsinB-C=ksinπ-AsinB-C ∵ A+B+C=π=ksinAsinB-C ∵a=ksinA=asinB-C=RHSHence proved.
Q3.
Answer :
Let asinA=b sinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the RHS of the equation a2 sin B-C=b2-c2 sin A.
RHS=k2sinAsin2B-sin2C =k2sinAsinB+CsinB-C ∵sin2B-sin2C=sinB+CsinB-C =k2sinAsinπ-AsinB-C ∵A+B+C=π =k2sinAsinAsinB-C =k2sin2AsinB-C =a2sinB-C =LHS ∵a=ksinAHence proved.
Q4.
Answer :
Consider the LHS of the equation sin A-sin Bsin A+sin B=a+b-2aba-b.
LHS=sinA-sinBsinA+sinB =sinA-sinBsinA+sinB×sinA-sinBsinA-sinB =sinA+sinB-2×sinAsinBsinA-sinB
Let asinA=b sinB=csinC=k
Then,
LHS=ak+bk-2×akbkak-bk =1ka+b-2×ab1ka-b =a+b-2aba-b=RHSHence proved.
Q5.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation b cos B + c cos C = a cos B-C.
LHS=bcosB+ccosC =ksinBcosB+sinCcosC =k22sinBcosB+2sinCcosC =k2sin2B+sin2C …1 RHS= acosB-C =ksinAcosB-C =k22sinAcosB-C =k2sinA+B-C+sinA-B+C ∵2sinAcosB=sinA+B+sinA-B =k2sinπ-C-C+sinπ-B-B ∵sinπ-A=sinA, A+B+C=π =k2sin2C+sin2B =k2sin2B+sin2C=LHS from1Hence proved.
Q6.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation cos 2Aa2-cos 2Bb2-1a2-1b2.
LHS=cos2Aa2-cos2Bb2 =1-2sin2Aa2-1-2sin2Bb2 =1-2a2k2a2-1-2b2k2b2 =k2-2a2k2a2-k2-2b2k2b2 =k2b2-2a2b2-k2a2+2a2b2a2b2 =k2b2-a2k2a2b2 =1a2-1b2=RHSHence proved.
Q7.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation cos2 B-cos2 Cb+c+cos2 C-cos2 Ac+a+cos2 A-cos2 Ba+b=0.
LHS=cos2B-cos2Cb+c+cos2C-cos2Ac+a+cos2A-cos2Ba+bNow,cos2B-cos2Cb+c=cos2B-cos2CksinB+sinC =cosB+cosCcosB-cosCksinB+sinC ∵ cos2B-cos2C = cosB+cosCcosB-cosC =2cosB+C2cosB-C2-2sinB+C2sinB-C22ksinB+C2sinB-C2 =-2cosB+C2sinB-C2k=-sinB-sinCk=sinC-sinBk
Also,
cos2C-cos2Ac+a=cos2C-cos2AksinC+sinA =cosC+cosAcosC-cosAksinC+sinA =2cosC+A2cosC-A2-2sinC+A2sinC-A22ksinC+sinAk =-2cosC+A2cosC-A2k=-sinC-sinAk=sinA-sinCk
Similarly,
cos2A-cos2Ba+b=sinB-sinAk
Thus,
LHS=sinA-sinCk+sinB-sinAk+sinC-sinBk =0 = RHS
Hence, in any triangle ABC, cos2 B-cos2 Cb+c+cos2 C-cos2 Ac+a+cos2 A-cos2 Ba+b=0.
Q8.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation a sin B-sin C + sin C-sin A+c sin A-sin B=0.
LHS =asinB-sinC+bsinC-sinA+csinA-sinB =ksinAsinB-sinC+ksinBsinC-sinA+ksinCsinA-sinB =ksinAsinB-ksinAsinC+ksinBsinC-ksinBsinA+ksinCsinA-ksinCsinB =0=RHSHence proved.
Q9.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation a2 sin B-Csin A+b2 sin C-Asin B+c2 sin A-Bsin C=0.
LHS=a2sinB-CsinA+b2sinC-AsinB+c2sinA-BsinC =k2sin2AsinB-CsinA+k2sin2BsinC-AsinB+k2sin2CsinA-BsinC =k2sinAsinB-C+k2sinBsinC-A+k2sinCsinA-B =k2sinAsinBcosC-sinCcosB+sinBsinCcosA-sinAcosC+sinCsinAcosB-sinBcosA =k2sinAsinBcosC-sinAsinCcosB+sinBsinCcosA-sinAsinBcosC+sinAsinCcosB-sinCsinBcosA =0=RHSHence proved.
Q10.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation a2 cos2 B-cos2 C +b2 cos2 C-cos2 A+c2 cos2 A-cos2 B=0.
LHS=a2cos2B-cos2C+b2cos2C-cos2A+c2cos2A-cos2B =k2sin2A1-sin2B-1+sin2C+k2sin2B1-sin2C-1+sin2A+k2sin2C1-sin2A-1+sin2B =k2sin2Asin2C-sin2B+k2sin2Bsin2A-sin2C+k2sin2Csin2B-sin2A =k2sin2Asin2C-sin2Asin2B+sin2Asin2B-sin2Bsin2C+sin2Csin2B-sin2Csin2A =k2×0=0=RHSHence proved.
Q11.
Answer :
LetasinA=bsinB=csinC=k …1Consider the LHS of the equation a cos A+bcos B+c cos C.acosA+bcosB+ccosC=ksinAcosA+sinBcosB+sinCcosC =k22sinAcosA+2sinAcosA+2sinCcosC =k2sin2A+sin2B+sin2C =k22sinA+BcosA-B+2sinCcosC =k22sinπ-CcosA-B+2sinCcosC =k22sinCcosA-B+2sinCcosC =2ksinC2cosA-B+cosC
=ksinCcosA-B+cosπ-A+B=ksinCcosA-B-cosA+B=ksinC2sinAsinB=2ksinAsinBsinC …(1)
Now,on putting ksinC=C in equation (1), we get:2csinAsinBand on putting ksinB=b in equation (1), we get:2bsinAsinC
So, from (1), we have
a cos A+bcos B+c cos C=2b sin A sin C=2 c sin A sin B .
Hence proved.
Q12.
Answer :
AssumeasinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Consider the LHS of the equation a-ba+b=tan A-B2tan A+B2.
LHS = a-ba+b =ksinA-sinBksinA+sinB
∵ sinA-sinB=2sinA-B2cosA+B2, sinA+sinB=2sinA+B2cosA-B2.
∴ LHS=2sinA-B2cosA+B22sinA+B2cosA-B2 =tanA-B2tanA+B2=RHS Hence proved.
Q13.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k …(1)
Consider the LHS of the equation a-b cos C2=c sin A-B2
LHS=a-bcosC2 =ksinA-sinBcosC2 using 1 =k×2sinA-B2cosA+B2cosC2 =2ksinA-B2cosA+B2cosπ-A+B2 ∵A+B+C=π =2ksinA-B2cosA+B2sinA+B2 =ksinA-B2sinA+B ∵ 2cosA+B2sinA+B2=sinA+B =ksinA-B2sinπ-C ∵ A+B+C=π =ksinCsinA-B2 =CsinA-B2=RHS
Hence proved.
Q14.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k …(1)
We need to prove:
ca-b=tanA2+tan B2tan A2-tan B2
Consider
LHS=ca-b =ksinCksinA-sinB using 1 =2sinC2cosC22sinA-B2cosA+B2 =sinπ-A+B2cosC2sinA-B2cosA+B2 ∵A+B+C=π =cosC2cosA+B2sinA-B2cosA+B2 =cosC2sinA-B2 …2
RHS=tanA2+tanB2tanA2-tanB2=sinA2cosA2+sinB2cosB2sinA2cosA2-sinB2cosB2=sinA2cosB2+sinB2cosA2sinA2cosB2-sinB2cosA2=sinA+B2sinA-B2=sinπ-C2sinA-B2=cosC2sinA-B2 =LHS from 2Hence proved.
Q15.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k …(1)
We need to prove:
ca+b=1-tan A2 tan B21+tan A2 tan B2
Consider
LHS=ca+b =ksinCksinA+sinB using1 =2sinC2cosC22sinA+B2cosA-B2 =sinC2cosπ-A+B2sinA+B2cosA-B2 ∵ A+B+C = π =sinC2sinA+B2sinA+B2cosA-B2 =sinC2cosA-B2 … 2RHS=1-tanA2tanB21+tanA2tanB2 =1-sinA2cosA2sinB2cosB21+sinA2cosA2sinB2cosB2 =cosA2cosB2-sinA2sinB2cosA2cosB2+sinA2sinB2 =cosA+B2cosA-B2 =cosπ-C2cosA-B2 ∵ A+B+C = π =sinC2cosA-B2=LHS from2Hence proved.
Q16.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k …(1)
Then,
Consider the LHS of the equation a+bc=cos A-B2sin C2.
LHS=a+bc =ksinA+ksinBksinC using 1 =2sinA+B2cosA-B22sinC2cosC2 =sinA+B2cosA-B2sinC2cosπ-A+B2 ∵A+B+C=π =sinA+B2cosA-B2sinC2sinA+B2 =cosA-B2sinC2=RHS Hence proved.
Q17.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
Consider the RHS of the equation sin B-C2=b-ca cosA2
RHS=b-cacosA2 =ksinB-sinCksinAcosπ-B+C2 ∵A+B+C=π =2sinB-C2cosB+C2sinA =sinB-C22cosB+C2sinAsinB+C2 =sinB-C2sinB+CsinA =sinB-C2sinπ-AsinA =sinAsinB-C2sinA =sinB-C2=LHSHence proved.
Q18.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Then,
asin45°=bsin60°=csin75°=k⇒a12=b32=c1221+3 ∵sin75°=sin30°+45°=sin30°cos45°+sin45°cos30°
On multiplying by 22 , we get:
a : b : c=2 : 6 : 1+3
Hence, the ratio of the sides is 2 : 6 : 1+3.
Q19.
Answer :
We know, A+B+C=π ∴ A=π-B+C⇒A=180°-45°+105°=30°Now,According to sine rule, asinA=bsinB .⇒2sin30°=bsin45° ∵ a=2, ∠B=45°⇒212=b12⇒4×12=b⇒b=22
Page 10.13 Ex – 10.1
Q20.
Answer :
Given,∠C = 90°, a = 18, b = 24 and c = 30
According to sine rule, asinA =bsinB=csinC.
⇒csinC=asinA⇒sinA=asinCc =18×sin90°30 =1830 =35Also, bsinB=csinC⇒sinB=bsinCc =24sin90°30 =2430 =45and sinC=sin90°=1
Q21.
Answer :
sin2A2, sin2B2 and sin2C2 is a H.P.⇔1sin2A2, 1sin2B2 and 1sin2C2 is an A.P.⇔1sin2B2-1sin2A2=1sin2C2-1sin2B2⇔sin2A2-sin2B2sin2A2sin2B2=sin2B2-sin2C2sin2B2sin2C2⇔sinA+B2sinA-B2sin2A2=sinB+C2sinB-C2sin2C2⇔cosC2sinA-B2sin2A2=cosA2sinB-C2sin2C2 As, A+B+C=π⇔sin2C2cosC2sinA-B2=sin2A2cosA2sinB-C2⇔2sinC2sinC2cosC2sinA-B2=2sinA2sinA2cosA2sinB-C2⇔sinC2sinC sinA-B2=sinA2sinAsinB-C2 ∵sin2θ=2sinθcosθ⇔sinC cosA+B2sinA-B2=sinA cosB+C2 sinB-C2 As, A+B+C=π⇔sinCsinA-sinB2=sinAsinB-sinC2 sinC-sinD=2cosC+D2sinC-D2⇔sinCsinA-sinB=sinAsinB-sinC⇔ckak-bk=akbk-ck sinAa=sinBb=sinCc=k say⇔ca-cb=ab-ac⇔2ac=ab+bc⇔2b=1c+1a multiplying both the sides by abc⇔a, b, c are in H.P.
Q22.
Answer :
Suppose asinA=bsinB=csinC=k. …(1)
Consider the RHS of the equation b cosθ = c cos (A − θ) + a cos (C + θ).
RHS=ccosA-θ+acosC+θ =ksinCcosA-θ+ksinAcosC+θ from 1 =k22sinCcosA-θ+2sinAcosC+θ =k2sinA+C-θ+sinC+θ-A+sinA+C+θ+sinA-C-θ =k2sinπ-B-θ+sinC+θ-A+sinπ-B+θ-sinC+θ-A ∵A+B+C=π =k2sinB+θ+sinB-θ =k2sinBcosθ+sinθcosB+sinBcosθ-sinθcosB =k22sinBcosθ =ksinBcosθ =bcosθ=LHSHence proved.
Q23.
Answer :
In ∆ ABC,
Given, sin2A+sin2B=sin2C ……1
Suppose asinA=bsinB=csinC=k .
⇒ sinA=ak, sinB=bk, sinC=ck
On putting these values in equation (1), we get:
a2k2+b2k2=c2k2⇒a2+b2=c2
Thus, ∆ ABC is right-angled.
Q24.
Answer :
Suppose asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Consider:
acosBcosC+cosA=ksinAcosBcosC+cosA =ksinAcosBcosC+cosAsinA=k12cosCsinA+B+sinA-B+sinAcosA=k12sinA+BcosC+sinA-BcosC+sinAcosA=k1212sinA+B+C+sinA+B-C+sinA-B+C+sinA-B-C+sinAcosA=k14sinπ+sinπ-2C+sinπ-2B-sinπ-2A+sin2A2 ∵ A+B+C=π=k4sin2C+sin2B+sin2A ….1and bcosAcosC+cosB=ksinBcosAcosC+sinBcosB=k12cosAsinB+C+sinB-C+sin2B2=k12sinB+CcosA+sinB-CcosA+sin2B2=k14sinB+C+A+sinB+C-A+sinB-C+A+sinB-C-A+sin2B2=k4sinπ+sinπ-2A+sinπ-2C-sinπ-2B+sin2B2 ∵ A+B+C=π=k4sin2A+sin2C+sin2B …2Similarly,ccosAcosB+cosC=k4sin2A+sin2B+sin2C …3
From (1), (2) and (3), we get:
a cos B cos C+cos A=b cos C cos A+cos B=c cos A cos B+cos C
Hence proved.
Q25.
Answer :
Let ABC be any triangle.
Suppose asinA=bsinB=csinC=k
Now,
bsecB+csecCtanB+tanC=bcosB+ccosCsinBcosB+sinCcosC =bcosC+ccosBsinBcosC+sinCcosB =ksinBcosC+ksinCcosBsinBcosC+sinCcosB = ksinBcosC+sinCcosBsinBcosC+sinCcosB=k …1
Also,
csecC+asecAtanC+tanA=ccosC+acosAsinCcosC+sinAcosA =ccosA+acosCsinCcosA+sinAcosC =ksinCcosA+ksinAcosCsinCcosA+sinAcosC =ksinCcosA+sinAcosCsinCcosA+sinAcosC =k …2andasecA+bsecBtanA+tanB=acosA+bcosBsinAcosA+sinBcosB =acosB+bcosAsinAcosB+sinBcosA =ksinAcosB+sinBcosAsinAcosB+sinBcosA =k …3
From (1), (2) and (3), we get:
b sec B+c sec Ctan B+tan C=c sec C+a sec Atan C+tan A=a sec A+b sec Btan A+tan B
Hence proved.
Q26.
Answer :
Consider
asinA2sinB-C2+bsinB2sinC-A2+csinC2sinA-B2
=ksinAsinA2sinB-C2+sinBsinB2sinC-A2+sinCsinC2sinA-B2=ksinπ-B+CsinA2sinB-C2+sinπ-C+A sinB2sinC-A2+sinπ-A+BsinC2sinA-B2 ∵A+B+C=π=ksinB+CsinA2sinB-C2+sinA+CsinB2sinC-A2+sinA+BsinC2sinA-B2=k2sinB+C2cosB-C2sinA2sinB-C2+2sinA+C2cosC-A2sinB2sinC-A2+2sinA+B2cosA-B2sinC2sinA-B2=2ksinB+C2sinA2sinA2sinB-C2+sinA+C2sinB2sinB2sinC-A2+sinA+B2sinC2sinC2sinA-B2=2ksinB+C2sinB-C2sin2A2+sinA+C2sinC-A2sin2B2+sinA+B2sinA-B2sin2C2=2ksin2A2sin2B2-sin2C2+2ksin2B2sin2C2-sin2A2+2ksin2C2sin2A2-sin2B2=2ksin2A2sin2B2-sin2A2sin2C2+sin2B2sin2C2-sin2A2sin2B2+sin2A2sin2C2-sin2C2sin2B2=k0=0
Hence proved.
Q27.
Answer :
Suppose asinA=bsinB=csinC=k .
We need to prove that a cos C-cos B=2 b-c cos2A2.
Consider
LHS=acosC-cosB=ksinAcosC-sinAcosB =k22sinAcosC-2sinAcosB=k2sinA+C+sinA-C-sinA+B-sinA-B=k2sinπ-B+sinA-C-sinπ-C-sinA-B ∵A+B+C=π=k2sinB-sinC+sinA-C-sinA-B=k2[2sinB-C2cosB+C2+2sinA-C-A+B2cosA-C+A-B2]=ksinB-C2cosπ-A2+cos2A-π-A2=ksinB-C2cosπ-A2+cosπ-3A2=ksinB-C2sinA2+sin3A2=2ksinB-C2sinA2+3A22cos3A2-A22=2ksinB-C2sinAcosA2=4ksinB-C2sinA2cos2A2 …1RHS=2b-ccos2A2 =2ksinB-sinCcos2A2 =4ksinB-C2cosB+C2cos2A2=4ksinB-C2cosπ2-A2cos2A2=4ksinB-C2sinA2cos2A2=LHS from equation 1
Hence, a cos C-cos B=2 b-c cos2A2
Q28.
Answer :
Let sinAa=sinBb=sinCc=k
Then,
sinA=ka, sinB=kb, sinC=kc
a2, b2 and c2 are in A.P.
⇒2b2=a2+c2 ⇒2a2+c2-b2=22b2-b2=2b2=b2+b2+c2-a2-c2+a2⇒2a2+c2-b2=b2+c2-a2+a2+b2-c2⇒2a2+c2-b22abc=b2+c2-a22abc+a2+b2-c22abc⇒2cosBkb=cosAka+cosCkc⇒2cosBsinB=cosAsinA+cosCsinC⇒2cotB=cotA+cotC⇒cotA,cotB and cotC are in AP.
Q29.
Answer :
ConsideracosC-cosB=ksinAcosC-sinAcosB ∵asinA=bsinB=csinC=k=k22sinAcosC-2sinAcosB=k2sinA+C+sinA-C-sinA+B-sinA-B=k2sinπ-B+sinA-C-sinπ-C-sinA-B ∵ A+B+C=π=k2sinB-sinC+sinA-C-sinA-B=k22sinB-C2cosB+C2+2sinA-C-A+B2cosA-C+A-B2=ksinB-C2cosπ2-A2+cos2A-π-A2=ksinB-C2sinA2+sin3A2=ksinB-C22sinA2+3A22cos3A2-A22=2ksinB-C2sinAcosA2=4ksinB-C2sinA2cos2A2 …1Now,Consider2b-ccos2A2=2ksinB-sinCcos2A2=2k2sinB-C2cosB+C2cos2A2=4ksinB-C2cosπ2-A2cos2A2=4ksinB-C2sinA2cos2A2 …2 From 1 & 2, we geta cos C-cos B=2 b-c cos2A2Hence proved.
Q30.
Answer :
Suppose BD be the tree and the upper part of the tree is broken over by the wind at point A.
The total height of the tree is x+y.In △ABC,∠C=30° and ∠B=90°.∴∠A=60°.So, on using sine rule, we get:ABsin30°=BCsin60°=ACsin90°⇒xsin30°=15sin60°=ysin90° So, xsin30°=15sin60°⇒x12=1532⇒x=153=53Also,15sin60°=ysin90°⇒1532=y⇒y=303=103So, the height of the tree is x+y=53+103 m =153m
Q31.
Answer :
Suppose, AB is a mountain of height t + x.
In △DFC,sin30°=x1000 ⇒x=1000×12=500 mand tan30°=xy⇒y=xtan30°=5003In ∆ABC,tan45°=t+xy+z⇒t+x=y+z …1In ∆ADE,tan60°=tz⇒t=3z …2From 1 and 2, we have 3z+x=y+z⇒z3-1=5003-1⇒z=500 m∴ t=3z=5003
Hence, height of the mountain = t+x=5003+500=5003+1 m .
Q32.
Answer :
Suppose, AB is a peak whose height above the ground is t+x.
In △DFC,sinβ=xc ⇒x=csinβand tanβ=xy⇒y=xtanβ=csinβsinβ×cosβ=ccosβ …1In ∆ADE,tanγ=tz⇒z=t cotγ …2In ∆ABC,tanα=t+xy+z⇒t+x=ccosβtanα+tcotγtanα from 1 and 2⇒t-tcotγtanα=ccosβtanα-csinβ ∵x=csinβ⇒t1-sinαcosγcosαsinγ=ccosβsinα-cosαsinβcosα⇒tsinγcosα-sinαcosγcosαsinγ=csinα-βcosα⇒tsinγ-βcosαsinγ=csinα-βcosα⇒t=csinγsinα-βsinγ-β …3Now, AB=t+x=csinγsinα-βsinγ-β+csinβ using 3 =csinγsinα-βsinγ-β+sinβ =csinγsinα-β+sinβsinγ-βsinγ-β =csinγsinαcosβ-sinβsinγcosα+sinβsinγcosα-sinβcosγsinαsinγ-β =csinγsinαcosβ-sinβcosγsinαsinγ-β =csinαsinγ-βsinγ-β =csinαsinγ-βsinγ-βHence proved.
Page 10.23 Ex – 10.2
Q1.
Answer :
Let ABC be any triangle.
Consider bccosA-acosC=bccosA-abcosC =bcb2+c2-a22bc-aba2+b2-c22ab =b2+c2-a2-a2-b2+c22 =2c2-a22 =c2-a2
Hence proved.
Q2.
Answer :
Consider c-bcosAb-ccosA
On using the projection formula, c=acosB+bcosA, b=ccosA+acosC, we get:
c-bcosAb-ccosA=acosB+bcosA-bcosAccosA+acosC-ccosA =acosBacosC =cosBcosC
Hence proved.
Q3.
Answer :
Consider
cacosB-bcosA=cacosB-cbcosA =caa2+c2-b22ac-cbb2+c2-a22bc =a2+c2-b2-b2-c2+a22 =2a2-b22 =a2-b2
Hence proved.
Q4.
Answer :
LHS = 2 bc cos A+ca cos B+ab cos C
On using the cosine law, we get:
LHS=2bcb2+c2-a22bc+caa2+c2-b22ac+aba2+b2-c22ab
=b2+c2-a2+a2+c2-b2+a2+b2-c2=a2+b2+c2=RHS
Hence proved.
Page 10.24 Ex – 10.2
Q5.
Answer :
We know that cosA=b2+c2-a22bc,sinAa=sinBb=sinCc=k
So,c2-a2+b2tanA=c2-a2+b2sinAcosA =c2-a2+b2sinA2bcb2+c2-a2 =2bcsinA =2kabc …1a2-b2+c2tanB=a2-b2+c2sinBcosB =a2-b2+c2sinB2aca2+c2-b2 =2acsinB =2kabc …2b2-a2+c2tanC=b2-a2+c2sinCcosC =b2-c2+a2sinC2aba2+b2-c2 =2absinC =2kabc ….3
From (1), (2) and (3), we get:
c2-a2+b2 tan A=a2-b2+c2 tan B=b2-c2+a2 tan C
Q6.
Answer :
LHS=4bc cos2A2+ca cos2B2+ab cos2 C2=4bc1+cosA2+ca1+cosB2+ab1+cosC2=2bc+2bccosA+2ca+2cacosB+2ab+2abcosC=2ab+bc+ca+2bcb2+c2-a22bc+2cac2+a2-b22ca+2aba2+b2-c22ab
=2ab+bc+ac+b2+c2-a2+c2+a2-b2+a2+b2-c2=a2+b2+c2+2ab+2bc+2ac=a+b+c2=RHS
Hence proved.
Q7.
Answer :
Let asinA=bsinB=csinC=k …1LHS=sin3AcosB-C+sin3BcosC-A+sin3CcosA-B =sin2AsinAcosB-C+sin2BsinBcosC-A+sin2AsinAcosA-B =a2k2sinAcosB-C+b2k2sinBcosC-A+c2k2sinAcosA-B from 1 =12k2a22sinAcosB-C+b22sinBcosC-A+c22sinAcosA-B =12k2a22sinπ-B+CcosB-C+b22sinπ-A+CcosC-A+c22sinπ-B+CcosA-B =12k2a22sinB+CcosB-C+b22sinC+AcosC-A+c22sinA+BcosA-B =12k2a2sin2B+sin2C+b2sin2C+sin2A+c2sin2A+sin2B =12k22a2sinBcosB+sinCcosC+2b2sinCcosC+sinAcosA+2c2sinAcosA+sinBcosB =12k32a2ksinBcosB+ksinCcosC+2b2ksinCcosC+ksinAcosA+2c2ksinAcosA+ksinBcosB =1k3a2bcosB+ccosC+2b2ccosC+acosA+2c2acosA+acosB =1k3abacosB+bcosA+bcbcosC+ccosB+acacosC+ccosA =1k3abc+bca+acb =3abc×1k3 =3sinAsinBsinC×1k3×k3 =3sinAsinBsinC =RHS Hence proved.
Q8.
Answer :
RHS=b+c2-4bccos2A2 =b2+c2+2bc-4bc1+cosA2 =b2+c2+2bc-2bc1+cosA =b2+c2+2bc1-1-cosA =b2+c2-2bccosA =b2+c2-2bcb2+c2-a22bc ∵cosA=b2+c2-a22bc =b2+c2-b2-c2+a2 =a2=LHS
Hence proved.
Q9.
Answer :
Let ABC be any triangle.
LHS=c-bcosAb-ccosA =acosB+bcosA-bcosAacosC+ccosA-ccosA Using projection formula:c=acosB+bcosA, b=acosC+ccosA =acosBacosC =cosBcosC=RHS
Hence proved.
Q10.
Answer :
Consider:
c2+b2-a2tanA=c2+b2-a2sinA2bcc2+b2-a2=2bcsinA=2kabc ∵sinAa=sinBb=sinCc=k ….(1)
Similarly,
a2+c2-b2tanB=a2+c2-b2sinB2aca2+c2-b2=2acsinB=2kabc …(2)
and
a2+b2-c2tanC=a2+b2-c2sinC2aba2+b2-c2=2absinC=2kabc …(3)
From (1), (2) and (3), we get:
c2+b2-a2 tan A=a2+c2-b2 tan B=a2+b2-c2 tan C
Hence proved.
Q11.
Answer :
Let ABC be any triangle.
i Consider the LHS of the given equation.LHS=acosB+cosC-1+bcosC+cosA-1+ccosA+cosB-1 =acosB+bcosC+acosC+bcosA+ccosA+ccosB-a+b+c =acosB+bcosA+bcosC+ccosB+acosC+ccosA-a+b+c =c+a+b-a+b+c ..Using projection formula : a=bcosC+ccosB, b=acosC+ccosA, c=acosB+bcosA =0=RHS ii Consider the LHS of the given equation. LHS=cosAbcosC+ccosB+cosBccosA+acosC+cosCacosB+bcosA =cosAa+cosBb+cosCc =b2+c2-a22abc+c2+a2-b22abc+a2+b2-c22abc =b2+c2-a2+c2+a2-b2+a2+b2-c22abc =a2+b2+c22abc=RHSHence proved.
Q12.
Answer :
GIven: a=18, b=24 and c=30 .cosA=b2+c2-a22bc=576+900-3242×24×30=11521140=45cosB=a2+c2-b22ac=324+900-5762×18×30=6481080=35cosC=a2+b2-c22ab=576+324-9002×24×18=0
Hence, cosA=45, cosB=35, cosC=0
Q13.
Answer :
Let b+c12=c+a13=a+b15=k⇒b+c=12k, c+a=13k, a+b=15k⇒b+c+c+a+a+b=12k+13k+15k⇒2a+b+c=40k⇒a+c+b=20k⇒a+12k=20k ∵b+c=12k⇒a=8kAlso, c+a=13k⇒c=13k-a=13k-8k=5kand a+b=15k⇒b=15k-a=15k-8k=7kNow,cosA=b2+c2-a22bc=k249+25-64k22×35=17cosB=a2+c2-b22ac=k264+25-492×40k2=12cosC=a2+b2-c22ab=k264+49-252×56k2=1114∴ cosA:cosB:cosC=17:12:1114=2:7:11⇒ cosA2=cosB7=cosC11
Hence proved.
Q14.
Answer :
Given, ∠B=60°We know that, cosB=a2+c2-b22ac⇒cos60°=a2+c2-b22ac⇒12 =a2+c2-b22ac ∵ cos60°=12⇒ac=a2+c2-b2⇒3ac-2ac=a2+c2-b2⇒3ac=a2+c2-b2+2ac⇒3ac=a2+c2+2ac-b2⇒3ac=a+c2-b2⇒3ac=a+c+ba+c-b⇒3ac=a+b+ca-b+c
Hence proved.
Q15.
Answer :
Let ABC be any triangle.
In ∆ABC,
cos2 A+cos2 B+cos2 C=1⇒cos2 A+cos2 B+cos2 π-B+A=1 ∵ A+B+C=π⇒cos2 A+cos2 B+cos2 B+A=1⇒cos2 A+cos2 B=1-cos2 B+A⇒cos2 A+cos2 B=sin2 B+A⇒cos2 A+cos2 B=sinAcosB+cosAsinB2⇒cos2 A+cos2 B=sin2Acos2B+cos2Asin2B+2sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒cos2 A1-sin2B+cos2 B1-sin2A=2sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒2cos2 Acos2B=2sinAsinBcosAcosB⇒cos AcosB=sinAsinB⇒cos AcosB-sinAsinB=0⇒cos A+B=0⇒cos A+B=cos90°⇒ A+B=90° ⇒ C=90° ∵ A+B+C=180°
Hence, ∆ABC is right angled.
Q16.
Answer :
Given: a=4, b=6 and c=8.
Then,
cosB=a2+c2-b22ac=16+64-362×4×8=1116cosA=b2+c2-a22bc=36+64-162×6×8=78cosC=b2+a2-c22ab=16+36-642×4×6=-14Now, 8cosA+16cosB+4cosC=8×78+16×1116-4×14⇒8cosA+16cosB+4cosC=7+11-1=17
Hence proved.
Q17.
Answer :
Given: a=5, b=6, c=60°Area of a triangle=12absinC =12×5×6×sin60°=15×32sq. units Hence proved.
Q18.
Answer :
Given: a=2, b=3, c=5∵ cosC=a2+b2-c22ab⇒cosC=2+3-52×6=0⇒cosC=0⇒cosC=cos90°⇒C=90°Thus, sinC=sin90°=1Hence, Area of ∆ABC=12absinC=126×1=62sq.units .
Q19.
Answer :
Let ABC be any triangle.
Given, cosA=sinB-cosC⇒cosA+cosC=sinB⇒2cosA+C2cosA-C2=2sinB2cosB2⇒cosπ2-B2cosA-C2=sinB2cosB2 ∵A+B+C=π⇒sinB2cosA-C2=sinB2cosB2⇒cosA-C2=cosB2⇒A-C2=B2⇒A-C=B …1Now,∵ A+B+C=180°∴ A+A-C+C=180°⇒2A=180°⇒A=90°So, ∆ABC is a triangle which is right angled at A.Hence, ∆ABC is a right angled triangle.
Q20.
Answer :
Let ∆ABC be any triangle.
Suppose sinAa=sinBb=sinCc=k
If cosC=sinA2sinB, then
b2+a2-c22ab=ka2kb ∵cosC=b2+a2-c22ab
⇒b2+a2-c2=a2⇒b2-c2=0⇒b-cb+c=0⇒b-c=0⇒b=c ∵ b, c > 0
Thus, the lengths of two sides of the ∆ABC are equal.
Hence, ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Q21.
Answer :
Suppose asinA=bsinB=csinC=k …(1)
Consider the LHS of the given equation.
LHS=acosA+bcosB+ccosC
=ksinAcosA+sinBcosB+sinCcosC …from1 =k22sinAcosA+2sinBcosB+2sinCcosC Multiplying and dividing by 2=k2sin2A+sin2B+sin2C =k2{2sinA+BcosA-B+sin2C} =k2{2sinπ-CcosA-B+2sinCcosC} ∵A+B+C=π=k{sinCcosA-B+sinCcosC}=ksinC{cosA-B+cosC}=2ksinCcosA-B+C2cosA-B-C2=2ksinCcosπ2-2B2cosπ2-2A2=2ksinCsinBsinA =2asinBsinC ∵asinA=k=RHS
Hence proved.
Q22.
Answer :
After three hours, let the ships be at P and Q respectively.Then,OP=24×3=72 km and OQ=32×3=96 kmFrom figure, we have∠POQ=180°-∠NOP-∠SOQ =180°-38°-52° =90°Now,Since OPQ is a right angled triangle∴PQ2=OP2+OQ2⇒PQ2=722+962⇒PQ2=5184+9216⇒PQ2=14400⇒PQ=14400=120 kmHence, the distance between the ships after 3 hours is 120 km.
8. TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
Page 11.19 Ex – 11.1
Q1.
Answer :
We have:
(i) sinθ = 12
The value of θ satisfying sinθ = 12 is π6.
∴ sinθ = 12
⇒ sinθ = sinπ6
⇒ θ = nπ + (-1)n π6, n ∈ Z
(ii) cosθ =-32
The value of θ satisfying cosθ =-32 is 7π6.
∴ cosθ =-32
⇒ cosθ = cos7π6
⇒ θ= 2nπ ± 7π6, n ∈ Z
(iii) cosecθ =-2(or) sinθ =-12
The value of θ satisfying sinθ =-12 is -π4.
∴ sinθ =-12
⇒ sinθ = sin (-π4)
⇒ θ = nπ + -1n -π4, n ∈ Z
⇒ θ = nπ + (-1)n + 1 π4, n ∈ Z
(iv) secθ = 2(or) cosθ = 12
The value of θ satisfying cosθ = 12 is π4.
∴ cosθ = 12
⇒ cosθ = cos π4
⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π4, n ∈ Z
(v) tan θ =-13
The value of θ satisfying tan θ =-13 is -π6.
∴ tan θ =-13
⇒ tan θ = tan (-π6)
⇒ θ = nπ – π6, n ∈ Z
(vi) 3 secθ = 2
⇒ secθ = 23 (or) cosθ = 32
The value of θ satisfying cosθ = 32 is π6.
∴ cosθ = 32
⇒ cosθ = cosπ6
⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π6, n ∈ Z
Q2.
Answer :
We have:
(i) sin2θ = 32
⇒ sin2θ = sin π3
⇒ 2θ = nπ + (-1)n π3 n ∈Z
⇒ θ = nπ2 + (-1)n π6, n ∈Z
(ii) cos3θ = 12
⇒ cos3θ = cos π3
⇒ 3θ = 2nπ ± π3 n ∈Z
⇒ θ = 2nπ3 ± π9, n ∈ Z
(iii) sin9θ = sinθ
⇒ sin9θ – sinθ = 0
⇒ 2 sin 9θ – θ2 cos 9θ + θ2= 0
⇒ sin 8θ2 = 0 or cos 10θ2 = 0
⇒ sin 4θ = 0 or cos 5θ = 0
⇒ 4θ = nπ, n ∈Z or 5θ = (2n + 1)π2, n ∈Z
⇒ θ = nπ4, n ∈Z or θ = (2n + 1)π10, n ∈Z
(iv) sin2θ = cos3θ
cos3θ =sin2θ
⇒ cos3θ = cos π2-2θ
⇒ 3θ = 2nπ ± π2-2θ, n∈Z
On taking positive sign, we have:
3θ = 2nπ + π2-2θ
⇒ 5θ = 2nπ + π2
⇒ θ = 2nπ5 + π10
⇒ θ = (4n + 1)π10, n ∈ Z
Now, on taking negative sign, we have:
3θ = 2nπ – π2 + 2θ, n∈Z
⇒ θ = 2nπ – π2
⇒ θ = (4n – 1)π2, n∈ Z
(v) tanθ + cot2θ = 0
⇒ tan θ =-cot2θ⇒ tanθ = tan π2 + 2θ⇒ θ = nπ + π2 + 2θ, n∈Z⇒ -θ = nπ + π2, n∈Z⇒ θ = -nπ – π2, n∈Z⇒ θ = mπ – π2, m =-n∈Z
(vi) tan3θ = cotθ
⇒ tan3θ = tan π2 – θ⇒ 3θ = nπ + π2 – θ, n∈Z⇒ 4θ = nπ + π2, n∈Z⇒ θ = nπ4 + π8, n∈Z
(vii) tan2θ tanθ = 1
⇒tan2θ =1tan θ⇒ tan2θ = cot θ⇒ tan2θ =tan π2 – θ⇒ 2θ = nπ + π2 – θ, n∈Z⇒ 3θ = nπ + π2, n∈Z⇒ θ = nπ3 + π6, n∈Z
(viii) tanmθ + cotnθ = 0
⇒ tanmθ =-cotnθ⇒ tanmθ = tan π2 + nθ⇒ mθ = rπ + π2 + nθ, r ∈Z⇒ (m – n) θ = rπ + π2, r ∈Z⇒ θ = 2r + 1m – nπ2, r ∈Z
(ix) tanpθ =cotqθ
⇒tanpθ = tan π2 – qθ⇒ pθ = nπ + π2 – qθ , n∈ Z⇒ (p + q)θ = nπ + π2, n∈ Z⇒ θ = 2n + 1p + qπ2, n∈Z
(x) sin2θ + cosθ = 0
⇒cosθ = -sin 2θ⇒ cosθ = cos π2 + 2θ⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π2 + 2θ, n∈Z
On taking positive sign, we have:
θ= 2nπ + π2 + 2θ⇒ -θ = 2nπ + π2⇒ θ = 2mπ – π2, m =-n ∈Z⇒θ = (4m -1)π2, m∈Z
On taking negative sign, we have:
θ = 2nπ – π2 – 2θ⇒ 3θ = 2nπ – π2⇒ θ =(4n – 1)π6, n∈ Z
(xi) sinθ = tanθ
⇒ sinθ – tanθ = 0⇒ sinθ – sinθcosθ = 0⇒ sinθ 1 – 1cosθ = 0⇒sinθ (cosθ -1) = 0
⇒ sinθ = 0 or cosθ – 1 = 0
Now,
sinθ= 0 ⇒θ = nπ, n∈Z
cosθ – 1 = 0 ⇒ cosθ = 1 ⇒ cosθ= cos0 ⇒ θ = 2mπ, m ∈Z
(xii) sin3θ + cos2θ = 0
⇒cos2θ =- sin3θ⇒ cos2θ = cosπ2 + 3θ⇒ 2θ = 2nπ ± π2 + 3θ, n ∈Z
On taking positive sign, we have:
2θ = 2nπ + π2 + 3θ⇒ -θ = 2nπ + π2⇒ θ = 2mπ – π2, m=-n ∈ Z⇒ θ = (4m -1)π2, m∈ Z
On taking negative sign, we have:
2θ = 2nπ – π2 – 3θ⇒ 5θ = 2nπ – π2⇒ θ = (4n -1)π10, n∈Z
Q3.
Answer :
(i) sin2θ – cos θ = 14
⇒ 1 – cos2θ – cosθ = 14⇒4 – 4 cos2θ – 4 cosθ = 1⇒ 4 cos2θ + 4 cosθ – 3= 0⇒ 4 cos2θ + 6 cosθ – 2 cosθ – 3 = 0⇒2 cosθ (2 cosθ + 3) – 1(2 cosθ + 3) = 0⇒ (2 cosθ + 3) (2 cosθ -1) = 0
⇒(2 cosθ – 1) = 0 or 2 cosθ + 3 = 0
⇒ cosθ =12 or cosθ = -32
cosθ=-32 is not possible.
∴cosθ= 12 ⇒ cosθ = cosπ3 ⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π3, n∈Z
(ii)
2 cos2θ – 5 cosθ + 2 = 0⇒ 2 cos2θ – 4 cosθ – cosθ + 2 = 0⇒2 cosθ ( cosθ – 2) -1 ( cosθ – 2) = 0⇒( cosθ – 2) ( 2 cosθ – 1) = 0
⇒ ( cos θ – 2 ) = 0 or, ( 2 cos θ – 1) = 0
cosθ = 2 is not possible.
∴2 cosθ – 1 = 0 ⇒ cosθ = 12 ⇒ cosθ= cos π3 ⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π3, n∈Z
(iii)
2 sin2x + 3 cosx + 1 = 0⇒ 2 – 2 cos2x + 3 cosx + 1 = 0⇒ 2 cos2x -3 cosx – 3 = 0⇒ 2 cos2x – 23 cosx + 3 cosx – 3 = 0⇒ 2 cosx (cosx – 3) + 3 (cosx – 3) = 0⇒ (2 cosx + 3) (cosx – 3) = 0
⇒ (2 cosx + 3) = 0 or (cosx – 3) =0
cos x = 3 is not possible.
∴2 cosx + 3 =0 ⇒ cosx =-32 ⇒ cosx = cos 5π6 ⇒ x = 2nπ ± 5π6, n∈
(iv)
4sin2θ-8cosθ+1=0
⇒ 4 – 4 cos2θ – 8 cosθ + 1 = 0⇒ 4 cos2θ + 8 cosθ – 5 = 0⇒ 4 cos2θ + 10 cosθ – 2 cosθ – 5 = 0⇒ 2 cosθ (2 cosθ + 5 ) -1 (2 cosθ + 5) = 0⇒ (2 cosθ – 1) (2 cosθ + 5) = 0
⇒ (2 cosθ – 1) = 0 or (2 cosθ + 5) = 0
Now,
2 cos θ + 5 = 0 ⇒ cos θ =-52 (It is not possible.)
∴2 cosθ – 1 = 0 ⇒ cosθ = 12 ⇒ cosθ = cos π3 ⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π3, n∈Z
(v)
tan2x + (1 – 3) tanx – 3 = 0
⇒tan2x + tanx – 3 tanx – 3 = 0⇒tanx (tanx + 1) -3 (tanx + 1) = 0⇒ (tanx – 3) (tanx +1) = 0
⇒ (tan x – 3) = 0 or (tan x + 1) = 0
Now,
tanx – 3 = 0 ⇒ tanx = 3 ⇒ tanx = tan π3 ⇒ x = nπ + π3, n∈Z
And,
tanx =-1 ⇒ tanx = tan-π4 ⇒ x = mπ – π4, m∈Z
(vi)
3 cos2θ – 23 sinθ cosθ – 3 sin2θ = 0
Now,
3 (cos2θ – sin2θ) – 3 sin2θ = 0⇒ 3 cos2θ – 3 sin2θ = 0⇒3 (3 cos2θ – sin2θ) = 0⇒ (3 cos2θ – sin2θ) = 0⇒ sin2θcos2θ = 3 ⇒ tan2θ = tan π3⇒ 2θ = nπ + π3, n∈Z⇒ θ = nπ2 + π6, n∈Z
(vii)
cos4θ = cos2θ⇒ 4θ = 2nπ ± 2θ , n∈Z
On taking positive sign, we have:
4θ = 2nπ + 2θ⇒2θ = 2nπ⇒θ = nπ, n∈ Z
On taking negative sign, we have:
4θ = 2nπ – 2θ⇒ 6θ = 2nπ⇒ θ = nπ3, n∈Z
Q4.
Answer :
(i) cos θ + cos 2θ + cos 3θ = 0
Now,
(cosθ + cos3θ) + cos2θ = 0⇒ 2 cos 4θ2 cos 2θ2 + cos2θ = 0⇒ 2 cos2θ cosθ + cos2θ = 0⇒ cos2θ ( 2 cosθ + 1) = 0
⇒cos 2θ = 0 or, 2 cos θ + 1 = 0
⇒ cos 2θ = cos π2 or cos θ =-12= cos 2π3
⇒ 2θ = (2n + 1) π2, n ∈ Z or θ = 2mπ ± 2π3, m ∈ Z
⇒θ = (2n + 1)π4, n ∈ Z or θ= 2mπ ± 2π3, m∈ Z
(ii)
(cosθ + cos3θ) – cos2θ = 0⇒ 2 cos 4θ2 cos 2θ2 – cos2θ = 0⇒ 2 cos2θ cosθ – cos2θ = 0⇒ cos2θ ( 2 cosθ – 1) = 0
⇒ cos2θ = 0 or 2 cosθ – 1 = 0
⇒ cos2θ = cos π2 or cosθ = 12⇒ cosθ = cosπ3
⇒ 2θ = (2n + 1)π2, n∈ Z or θ = 2mπ ± π3, m∈ Z
⇒ θ = (2n + 1)π4, n∈ Z or θ = 2mπ ± π3, m∈ Z
(iii) sinθ + sin5θ = sin3θ
⇒2 sin6θ2 cos 4θ2 = sin3θ⇒2 sin3θ cos2θ = sin3θ⇒2 sin3θ cos2θ – sin3θ = 0⇒ sin3θ (2 cos2θ – 1) = 0
⇒sin3θ = 0 or (2 cos2θ – 1) = 0
⇒ sin3θ = sin 0 or cos2θ = 12 = cos π3
⇒ 3θ = nπ or 2θ = 2mπ ± π3
⇒ θ = nπ3, n∈ Z or θ = mπ ± π6, m∈ Z
(iv) cosθ cos2θ cos3θ = 14⇒cosθ+2θ+cos2θ-θ2cos3θ=14⇒2cos3θ+cosθcos3θ=1⇒2cos23θ+2cosθcos3θ-1=0⇒2cos23θ-1+2cosθcos3θ=0⇒cos6θ+cos4θ+cos2θ=0⇒cos6θ+cos2θ+cos4θ=0⇒2cos4θcos2θ+cos4θ=0⇒cos4θ2cos2θ+1=0⇒cos4θ=0 or 2cos2θ+1=0⇒cos4θ=0 or cos2θ=-12⇒cos4θ=cosπ2 or cos2θ=cos2π3⇒4θ=2n+1π2, n∈Z or 2θ=2mπ±2π3, m∈Z⇒θ=2n+1π8, n∈Z or θ=mπ±π3, m∈Z
(v) cosθ+ sinθ = cos2θ + sin2θ
⇒cosθ – cos2θ = sin2θ – sinθ⇒- 2 sin 3θ2 sin -θ2 = 2 sin θ2 cos 3θ2⇒ 2 sin 3θ2 sin θ2 = 2 sin θ2 cos 3θ2⇒ 2 sin θ2 sin 3θ2 – cos 3θ2 = 0
⇒ sin θ2 = 0 or sin 3θ2 – cos 3θ2 = 0
⇒ sin θ2 = sin 0 or sin 3θ2 = cos 3θ2
⇒ θ2 = nπ, n ∈ Z or cos 3θ2 = cos π2 – 3θ2
⇒θ = 2nπ, n ∈ Z or 3θ2 = 2mπ ± π2 – 3θ2, m ∈ Z
⇒θ = 2nπ, n∈ Z or 3θ2 = 2mπ + π2 – 3θ2, m ∈ Z (Taking negative sign will give absurd result.)
θ = 2nπ, n∈ Z or θ = 2mπ3 + π6, m ∈ Z
(vi) sinθ + sin2θ + sin3θ = 0
⇒ sinθ + sin3θ + sin2θ = 0⇒ 2 sin 4θ2 cos 2θ2 + sin2θ = 0⇒ 2 sin2θ cosθ + sin2θ = 0⇒ sin2θ (2 cosθ + 1) = 0
⇒ sin2θ = 0 or 2 cosθ + 1 = 0
⇒ sin2θ = sin 0 or cosθ =-12 ⇒cosθ= cos 2π3
⇒θ= nπ2, n ∈ Z or θ = 2mπ ± 2π3, m ∈ Z
(vii) sinθ + sin2θ + sin3θ + sin4θ = 0
⇒ sin3θ + sinθ + sin4θ + sin2θ = 0⇒ 2 sin 4θ2 cos 2θ2 + 2 sin 6θ2 cos 2θ2 = 0⇒ 2 sin2θ cosθ + 2 sin3θ cos θ = 0⇒ 2 cosθ ( sin2θ + sin3θ ) = 0⇒ 2 cosθ 2 sin 5θ2 cos θ2 = 0⇒ 4 cosθ sin 5θ2 cos θ2 = 0
⇒ cos θ = 0 , sin 5θ2 = 0 or cos θ2 = 0
⇒ cos θ = cos π2 , sin 5θ2 = sin 0 or cos θ2 = cos π2
⇒ θ = (2n + 1) π2, n∈Z or 5θ2= nπ , n ∈ Z or, θ2 = (2n+ 1) π2 , n ∈ Z
⇒ θ = (2n + 1) π2 , n∈ Z or θ= 2nπ5 , n ∈ Z or θ = (2n + 1)π, n ∈ Z
(viii) sin3θ – sinθ = 4 cos2θ – 2
⇒ sin3θ – sinθ = 2 ( 2 cos2θ – 1)⇒ 2 sin 2θ2 cos 4θ2 = 2 cos 2θ⇒ 2 sinθ cos2θ = 2 cos2θ⇒ sinθ cos2θ = cos2θ⇒ cos2θ ( sinθ – 1) = 0
⇒ cos 2θ = 0 or sinθ – 1 = 0
⇒cos 2θ = cos π2 or sinθ = 1⇒sinθ = sin π2
⇒ 2θ = (2n + 1)π2, n ∈Z or θ = nπ + (-1)n π2 , n∈ Z
⇒ θ = (2n + 1)π4 , n∈Z or θ = nπ + (-1)n π2 , n∈Z
(ix) sin 2θ – sin 4θ + sin 6θ = 0.
⇒ 2 sin 8θ2 cos 4θ2 – sin4θ = 0⇒ 2 sin4θ cos2θ – sin4θ = 0⇒ sin4θ ( 2 cos2θ – 1) = 0
⇒ sin 4θ = 0 or 2 cos2θ – 1 = 0
⇒ 4θ = nπ , n ∈Z or cos2θ = 12⇒ cos2θ= cos π3
⇒ θ = nπ4, n∈ Z or θ = nπ ± π6, n∈ Z
Page 11.20 Ex.11.1
Q5.
Answer :
(i)
We have:
tan θ + tan 2θ + tan 3θ = 0
Now,
tanθ+ tan2θ + tan (θ + 2θ) = 0⇒tanθ + tan2θ + tan θ + tan 2θ1 – tan θ tan 2θ = 0⇒ (tanθ + tan2θ) (1 – tanθ tan2θ) + tanθ + tan2θ= 0⇒(tanθ + tan2θ) (2 – tanθ tan2θ) = 0
⇒ tan θ + tan 2θ = 0 or 2 – tanθ tan2θ = 0
Now,
tanθ + tan2θ = 0 ⇒ tanθ = – tan2θ ⇒ tanθ = tan -2θ ⇒ θ = nπ – 2θ ⇒ 3θ = nπ ⇒ θ = nπ3, n∈Z
And,
2 – tanθ tan2θ = 0 ⇒ tanθ tan2θ = 2 ⇒ sinθcosθsin2θcos2θ = 2⇒ 2 sin2θ cosθcosθ = 2 cos2θ – 2 sin2θ ⇒ 4 sin2θ = 2 cos2θ ⇒ tan2θ =12⇒ tan2θ = tan2α ⇒ θ = mπ + α, m∈Z, α = tan-1 12
∴ θ = nπ3, n∈Z or θ = mπ + α, m∈Z
Here,
α= tan-112
(ii)
Given:
tanθ+ tan2θ = tan3θ
Now,
tanθ + tan2θ = tan (θ + 2θ)⇒tanθ + tan 2θ = tanθ + tan2θ1 – tanθ tan2θ⇒ tanθ + tan2θ – tanθ + tan2θ1 – tanθ tan2θ = 0⇒ (tanθ + tan2θ) (1 – tanθ tan2θ) – (tanθ + tan2θ) = 0⇒ (tanθ + tan 2θ) (1 – tanθ tan2θ – 1) = 0⇒ (tanθ + tan2θ) (- tanθ tan2θ) = 0
⇒ tan θ + tan 2θ = 0 or tanθ tan2θ = 0
Now,
tan θ + tan 2θ = 0 ⇒ tan θ = – tan 2θ ⇒ tan θ = tan -2θ⇒ θ = nπ – 2θ, n∈Z⇒ 3θ = nπ ⇒θ = nπ3, n∈Z
And,
tanθ tan2θ = 0 ⇒ sinθcosθ sin2θcos2θ = 0 ⇒ 2 sin2θcos2θ – sin2θ = 0 ⇒ sin2θ =0⇒ sin2θ = sin20 ⇒ θ = mπ, m∈Z
∴ θ = nπ3, n∈Z or θ = mπ, m∈Z
(iii)
Given:
tan3θ + tanθ = 2 tan2θ
Now,
tan3θ – tan2θ = tan2θ – tanθ⇒ tanθ (1 + tan3θ tan2θ) = tanθ (1 + tan2θ tanθ) tan A – B =tan A – tan B1 + tan A tan B ⇒tanθ (1 + tan3θ tan2θ – 1 – tan2θ tanθ)= 0⇒tanθ tan2θ (tan3θ – tanθ)= 0
⇒ tan 2θ = 0 or, tan θ = 0 or, tan3θ – tanθ = 0
And,
tan 2θ = 0 ⇒ 2θ = nπ ⇒ θ = nπ2, n∈Z
Or,
tan 3θ – tan θ = 0 ⇒ tan 3θ = tan θ ⇒ 3θ = nπ + θ ⇒ 2θ =nπ ⇒ θ = nπ2, n∈Z
And,
tan θ = 0 ⇒ θ = mπ, m∈Z
∴ θ = nπ2, n∈Z or θ = mπ, m∈Z
Q6.
Answer :
(i)
Given:
sinθ + cosθ = 2 …(i)
The equation is of the form a sinθ + b cosθ = c, where a = 1, b = 1 and c = 2.
Let:
a = r sin α and b = r cos α
Now,
r = a2 + b2 = 12+12 = 2 and tan α = 1 ⇒ α = π4
On putting a = 1 = r sin α and b = 1 = r cos α in equation (i), we get:
r sin α sin θ + r cos α cos θ = 2
⇒r cos (θ – α) = 2⇒ 2 cos θ – π4 = 2⇒ cos θ – π4 = 1⇒ cos θ -π4 = cos 0⇒ θ – π4 = nπ ± 0, n∈ Z⇒θ =nπ + π4, n∈ Z⇒ θ = (8n + 1)π4, n ∈ Z
(ii)
Given:
3 cos θ + sin θ = 1 …(ii)
The equation is of the form of a cos θ + b sin θ = c, where a = 3, b = 1 and c =1.
Let:
a = r cos α and b = r sin α
Now,
r = a2 + b2 =(3)2 + 12 = 2 and tan α = ba = 13 ⇒ α = π6
On putting a = 3 = r cos α and b = 1 = r sin α in equation (ii), we get:
r cos α cos θ + r sin α sin θ = 1
⇒ r cos (θ – α) = 1⇒ 2 cos (θ – α) = 1⇒ cos θ – π6 = 12⇒ cos θ – π6 = cos π3⇒ θ – π6 = 2nπ ± π3, n∈Z
On taking positive sign, we get:
θ – π6 =2nπ + π3 ⇒ θ = 2nπ + π3 + π6⇒ θ = 2nπ + π2, n ∈ Z⇒θ =(4n + 1)π2, n ∈ Z
Now, on taking negative sign of the equation, we get:
θ – π6 = 2mπ – π3, m∈ Z⇒θ = 2mπ – π3 + π6, m ∈Z⇒θ = 2mπ- π6 = (12m -1) π6, m ∈ Z
(iii)
Given:
sin θ + cos θ = 1 …(iii)
The equation is of the form a sin θ + b cos θ = c, where a = 1, b = 1 and c = 1.
Let:
a = r sin α and b = r cos α
Now,
r = a2 + b2 = 12 + 12 = 2 and tanα = ba = 1 ⇒ α = π4
On putting a = 1 = r sin α and b = 1 = r cos α in equation (iii), we get:
r sin α sin θ + r cos α cos θ = 1
⇒ r cos ( θ – α) =1⇒ 2 cos θ – π4 = 1⇒ cos θ – π4 =12⇒ cos θ – π4 = cos π4⇒ θ – π4 = 2nπ ± π4, n∈Z
On taking positive sign, we get:
θ – π4 = 2nπ + π4⇒ θ = 2nπ + π4 + π4⇒ θ = 2nπ + π2, n ∈ Z
On taking negative sign, we get:
θ- π4 = 2mπ – π4⇒ θ = 2mπ, m ∈ Z
(iv)
Given:
cosec θ = 1 + cot θ
⇒1 sin θ = 1 + cos θsin θ⇒ sin θ + cos θ = 1 …(iv)
The equation is of the form a sin θ + b cos θ = c, where a = 1, b =1 and c = 1.
Let:
a = r sin α and b = r cos α
Now,
r = a2+ b2 = 12+ 12 = 2 and tan α = 1 ⇒ α = π4
On putting a = 1 = r sin α and b = 1 = r cos α in equation (iv), we get:
r sinα sinθ + r cosα cosθ = 1⇒r cos (θ – α) = 1⇒ 2 cosθ – π4 = 1⇒ cos θ – π4 = 12⇒ cos θ – π4 = cos π4⇒ θ – π4 = 2nπ ± π4, n∈ Z
On taking positive sign, we get:
θ= 2nπ + π2, n∈ Z
On taking negative sign, we get:
θ = 2mπ, m∈ Z
Page 11.21 (Very Short Answers)
Q1.
Answer :
Given:
tanx + secx = 2 cosx
⇒ sinxcosx + 1cosx = 2 cosx⇒ sinx + 1cosx = 2 cosx⇒ sinx + 1 = 2 cos2x⇒ sinx = 2 cos2x – 1
⇒21- sin2x – 1 = sinx⇒ 2-2 sin2x -1=sinx⇒1-2sin2x = sinx⇒ 2sin2x+sinx-1=0⇒2sin2x+2sinx-sinx-1=0⇒2sinxsinx+1-1sinx+1=0⇒sinx+12sinx-1=0⇒sinx+1=0 or 2sinx-1=0⇒sinx=-1 or sinx=12
Now,
sinx = -1⇒ sinx =sin3π2⇒ x = nπ +-1n 3π2, n∈ ZBecause it contains an odd multiple of π2 and we know that tanx and secx are undefined on the odd multiple, this value will not satisfy the given equation.
And,
sinx = 12⇒ sinx =sinπ6⇒ x = nπ +-1n π6, n∈ ZNow, For n=0, x=π6For n=1, x=11π6 For other values of n, the condition is not true.
Hence, the given equation has two solutions in 0, 2π.
Page 11.22 (Very Short Answers)
Q2.
Answer :
We have:
4 sinx – 3 cosx = 7 …(i)
The equation is of the form a sinx + b cosx = c, where a = 4, b = -3 and c = 7.
Now,
Let:
a = r sin α and b = r cos α
Thus, we have:
r = a2 + b2 = 42+32 = 5 and tan α = -43 ⇒ α = tan-1-43
By putting a = 4 = r sin α and b = -3 = r cos α in equation (i), we get:
r sinα sinx + r cosα cosx = 7
⇒r cos (x – α) = 7⇒ 5 cos x – tan-1-43 = 7⇒ cos x – tan-1-43 = 75
The solution is not possible.
Hence, the given equation has no solution.
Q3.
Answer :
Given:
tan2 2x = 1⇒tan 2x =tan π4⇒2x = nπ + π4⇒x = nπ2 + π8, n ∈ Z
Hence, the general solution of the equation is nπ2 + π8, n ∈ Z.
Q4.
Answer :
Given:
3 sin x – cos x = a⇒3 sinx – cosx2 = a2⇒32 sinx – 12 cosx = a2⇒ cos 30° sinx – sin 30° cosx = a2⇒sin ( x – 30°) = a2⇒ x – 30° = sin-1a2⇒ x = sin-1a2 + 30°
If a = 2 or a =-2 , then the equation will possess a solution.
For no solution, a∈(-∞, -2) ∪ (2, ∞).
Q5.
Answer :
Given: cosx = k
If k = 0, then
cosx = 0⇒cosx = cos π2⇒ x = (2n + 1) π2, n ∈ Z
Now, x = 3π2 , 5π2, 7π2, … for n = 1, 2, 3,…
If k = 1, then
cos x = 1⇒cos x = cos 0⇒x = 2mπ, m ∈ Z
Now, x = 2π, 4π, 6π, 8π,… for m = 1, 2, 3, 4,…
If k =-1, then
cos x =-1⇒cos x = cos π⇒ x = 2pπ ± π, p ∈ Z
Now,
x = 2pπ + π, i.e., x = 3π, 5π, 7π,… when p = 1, 2, 3,…
And,
x = 2pπ – π, i.e., x = π, 3π, 5π, 7π,… when p = 1, 2, 3, 4,…
Clearly, we can see that for x = π, cosx = k has exactly one solution.
∴ k = -1
Q6.
Answer :
Given curves: 2y =1 and y = cosx
Now,
2y = 1 ⇒ y = 12
Also,
cos x = y⇒ cos x = 12⇒ cos x = cos π3 and cos x = cos 4π3
⇒ x = 2nπ±π3 or x = 2nπ±4π3By putting n=0, we get: x=π3 and x=2π3
For the other value of n, the value of x will not satisfy the given condition.
Hence, the number of points of intersection of the curves is two, i.e., π3 and 4π3.
Q7.
Answer :
(i)
sin2x, 12 and cos2x are in AP.∴sin2x+cos2x=2×12⇒sin2x+cos2x=1 …(1)
This equation is of the form a sinθ + b cosθ = c, where a = 1, b = 1 and c = 1.
Now,
Let:
a = r sin α and b = r cos α
Thus, we have:
r = a2 + b2 = 12+12 = 2 and tan α = 1 ⇒ α = π4
On putting a = 1 = r sin α and b = 1 = r cos α in equation (1), we get:
r sin α sin2x + r cosα cos2x = 1
⇒r cos (2x – α) = 1⇒ 2 cos 2x – π4 = 1⇒ cos 2x- π4 = 12⇒ cos 2x-π4 = cos π4⇒ 2x – π4 = 2nπ ± π4 , n∈ ZTaking positive value, we get: ⇒2x – π4 = 2nπ + π4⇒x = nπ+π4Taking negative value, we get: ⇒2x – π4 = 2nπ – π4⇒2x – π4 = 2nπ – π4⇒ x =nπ, n∈ Z
For n = 0, the values of x are π4 and 0 and for n = 1, the values of x are 5π4 and π.
5π4 does not satisfy the condition.
For the other value of n, the given condition is not true, i.e., [0, π].
Q8.
Answer :
Given:
2y =-1 and y = cosecx
Now,
2y =-1 ⇒ y =-12
Also,
cosecx = y⇒cosecx =-12⇒1sinx =-12⇒ sinx = -2
The value of sine function lies between -1 and 1. Therefore, the two curves will not intersect at any point.
Hence, the number of points of intersection of the curves is 0.
Q9.
Answer :
Given: (2 cos θ + 1) ( 4 cos θ + 5) = 0
Now,
2 cos θ + 1 = 0 or 4 cos θ + 5 = 0
⇒ cos θ =-12 or cos θ =-54
cos θ=-54 is not possible.
Thus, we have:
cosθ =-12 ⇒cosθ=cos2π3⇒θ=2nπ±2π3
By putting n = 0 and n = 1 in the above equation, we get:
θ = 2π3 or θ= 4π3 in the interval 0, 2π
For the other value of n, θ will not satisfy the given condition.
∴ θ = 2π3 and 4π3
Q10.
Answer :
Given equation:
sin2θ – cos θ = 14
Now,
(1 – cos2θ) – cosθ = 14⇒ 4 – 4 cos2θ – 4 cosθ = 1⇒ 4 cos2θ + 4 cosθ – 3 = 0⇒ 4 cos2θ + 6 cosθ – 2 cosθ – 3 = 0⇒2 cosθ (2 cosθ + 3) -1 (2 cosθ + 3) = 0⇒(2 cosθ + 3) ( 2 cosθ – 1) = 0
Here,
2 cos θ + 3 = 0 ⇒ cos θ = -32
is not possible.
Or,
2 cos θ – 1 = 0⇒ cos θ = 12⇒ cos θ = cos π3⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π3
Taking positive sign,
θ = 7π3, 13π3, 19π3,…
Taking negative sign,
θ= 5π3, 11π3, 17π3,… θ = 5π3
and
7π3
will satisfy the given condition, i.e.,
θ
in [0, 2π].
Hence, two values will satisfy the given equation.
Page 11.22 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q1.
Answer :
(c) π/6
Given:
3(cotθ + tanθ) = 4⇒ 3 cosθsinθ+ sinθcosθ= 4⇒ 3 (cos2θ + sin2θ ) = 4 sinθ cosθ⇒ 3 = 2 sin2θ [ sin2θ =2 sinθ cosθ]⇒ sin2θ = 32⇒sin2θ = sin π3⇒ 2θ = nπ + (-1)nπ3, n ∈ Z⇒ θ = nπ2 + (-1)nπ6, n ∈ Z
To obtain the smallest value of θ, we will put n = 0 in the above equation.
Thus, we have:
θ = π6
Hence, the smallest value of θ is π6.
Q2.
Answer :
(a) π/3
Given: cosθ + 3sinθ = 2 …(i)
This equation is of the form a cosθ + b sinθ = c, where a = 1, b = 3 and c = 2.
Let:
a = r cos α and b = sin α
Now,
1 = r cos α , 3 = r sin α
⇒ r = a2 + b2 = 1 + 3 = 4 = 2
And,
tanα = ba ⇒tanα = 31 ⇒tanα= 3
⇒α = π3
On putting a = 1 = r cos α and b = 3 = r sin α in equation (i), we get:
r cos θ cos α + r sin θ sin α = 2⇒r cos ( θ – α) = 2⇒ 2 cos θ – π3= 2⇒ cos θ – π3 =1⇒ cos θ – π3 = cos 0⇒ θ – π3 = 2nπ ± 0⇒ θ = 2nπ ± π3
For n = 0, θ= π3.
∴ θ = π3
Q3.
Answer :
(a) AP
Given:
tanpθ – tanqθ = 0
⇒tanpθ = tanqθ⇒ sinpθcospθ = sinqθcosqθ⇒ sinpθ cosqθ = sinqθ cospθ⇒12sinp + q2θ + sinp – q2θ = 12sinq + p2θ + sinq – p2θ
Now,
sin A cos B = 12sinA + B2 + sinA – B2
⇒sin p – q2θ = sin q – p2θ⇒ sin p – q2θ = – sin p – q2θ⇒ 2 sin p – q2θ = 0⇒ sin p – q2θ = 0
⇒ p – q2θ = nπ, n ∈ Z⇒ θ = 2nπ(p – q), n∈ Z
Now, on putting the value of n, we get:
n = 1, θ = 2π(p- q)= a1
n = 2, θ = 4π(p – q) = a2
n = 3, θ = 6π(p – q) = a3
n = 4, θ = 8π(p – q) = a4
And so on.
Also,
d =a2 – a1 = 4π(p – q) – 2π(p – q) = 2π(p – q)d = a3 – a2 = 6π(p – q) – 4π(p – q) = 2π(p – q)d = a4 – a3 = 8π(p – q) – 6π( p – q) = 2π(p – q)
And so on.
Thus, θ forms a series in AP.
Q4.
Answer :
(c) 1
Given:
cotx – tanx = a⇒ 1tanx – tanx = a⇒ 1 – tan2x = a tanx⇒ tan2x + a tanx – 1 = 0
It is a quadratic equation.
If tan x = z, then the equation becomes
z2 + az – 1 = 0
⇒ z = – a ± a2 + 42⇒ tan x = -a ± a2 + 42⇒ x = tan-1-a ± a2 + 42
There are two roots of the given equation, but we need to find the number of roots in the first quadrant.
There is exactly one root of the equation, that is, x = tan-1-a + a2 + 42.
Q5.
Answer :
(c) θ=nπ±π3, n ∈ Z
Given:
7 cos2 θ + 3 sin2θ = 4⇒ 7 cos2θ + 3 (1 – cos2θ) = 4⇒ 7 cos2θ + 3 – 3 cos2θ = 4⇒ 4 cos2θ + 3 = 4⇒ 4 (1 – cos2θ) = 3⇒4 sin2θ = 3⇒ sin2θ = 34⇒ sin θ = 32⇒ sin θ = sin π3⇒ θ = nπ ±π3, n ∈ Z
Q6.
Answer :
(d) 5π/4, 7π/4
Given:
cos2θ + sinθ + 1 = 0⇒ (1 – sin2θ) + sinθ + 1 = 0⇒ 1 – sin2θ + sinθ + 1 = 0⇒ sin2θ – sinθ – 2 = 0⇒ sin2θ – 2 sinθ + sinθ – 2 = 0⇒ sinθ (sinθ – 2) + 1 (sinθ – 2) = 0⇒ (sinθ – 2) (sinθ + 1) = 0
⇒ sinθ – 2 = 0 or sinθ + 1 = 0
⇒ sinθ = 2 or sin θ = -1
sin θ = 2 is not possible.
⇒sin θ = -1
∴ sinθ = sin 3π2
⇒ θ = nπ +(-1)n 3π2, n ∈ Z
The values of θ lies in the third and fourth quadrants.
Hence, θ lies in 5π4, 7π4.
Q7.
Answer :
(c) 6
Given:
cos3x tan5x = sin7x⇒cos (5x – 2x) tan5x = sin (5x + 2x)⇒ tan5x = sin (5x + 2x)cos (5x – 2x)⇒ tan5x = sin5x cos2x + cos5x sin2xcos5x cos2x + sin5x sin2x⇒sin5xcos5x = sin5x cos2x + cos5x sin2xcos5x cos2x + sin5x sin2x⇒ sin5x cos5x cos2x + sin2 5x sin2x = sin5x cos5x cos2x + cos2 5x sin2x⇒ sin2 5x sin2x = cos2 5x sin2x⇒(sin2 5x -cos2 5x) sin2x = 0⇒(sin5x – cos5x) (sin5x + cos5x) sin2x = 0
⇒ sin 5 x – cos 5x = 0 , sin 5x + cos 5x = 0 or sin 2x = 0
⇒sin 5xcos 5x = 1, sin 5xcos 5x =-1 or sin 2x = 0
Now,
tan5x = 1 ⇒ tan5x = tanπ4⇒ 5x = nπ+ π4, n∈Z⇒ x = nπ5+π20, n∈Z
For n = 0, 1 and 2, the values of x are π20, π4 and 9π20, respectively.
Or,
tan5x = 1 ⇒ tan5x = tan 3π4⇒ 5x = nπ+3π4, n∈Z⇒ x = nπ5+3π20, n∈Z
For n = 0 and 1, the values of x are 3π20 and 7π20, respectively.
And,
sin2x = 0 ⇒sin2x = sin 0 ⇒2x= nπ , n∈Z⇒ x= nπ2, n∈Z
For n = 0, the value of x is 0.Also, for the odd multiple ofπ2, tanx is not defined.
Hence, there are six solutions.
Page 11.23 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q8.
Answer :
(b) x=nπ+-1nπ3-π6, n ∈ Z
Given:
3 sinx + cosx = 3 …(i)
This equation is of the form a sinθ + b cosθ = c, where a = 3, b = 1 and c = 3.
Let:
a = r cos α and b = r sin α
Now,
r = a2 + b2 = (3)2 + 12 = 2 and tanα = ba ⇒tanα = 13 ⇒ α = π6
On putting a = 3 = r cosα and b = 1= r sinα in equation (i), we get:
r cosα sinx + r sinα cosx = 3⇒r sin (x + α) = 3⇒ 2 sin ( x + α) = 3⇒ sin (x + α) = 32⇒ sin (x+ α) = sin π3⇒ sin x + π6 = sin π3⇒ x = nπ + (-1)nπ3 – π6 , n ∈ Z
Q9.
Answer :
(a) 5π6
Given:
2 sin2θ + 3cosθ + 1 = 0
⇒2 (1 – cos2θ) + 3 cosθ + 1 = 0⇒ 2 – 2 cos2θ + 3 cosθ + 1 = 0⇒ 2 cos2θ – 3 cosθ – 3 = 0⇒ 2 cos2θ -23 cosθ + 3 cosθ – 3 = 0⇒2 cosθ (cosθ – 3) + 3 (cosθ – 3) = 0⇒ (2 cosθ + 3) (cosθ – 3) = 0
⇒2 cos θ + 3 = 0 or, cos θ – 3 = 0
∴ cosθ = -32 or, cosθ = 3 is not possible.
⇒cosθ=cos5π6⇒θ=2nπ±5π6 , n∈Z
For n = 0, the value of θ is ±5π6.
Hence, the smallest positive angle is 5π6.
Q10.
Answer :
(c) nπ±π6, n ∈ Z
Given:
4 sin2θ = 1⇒ sin2θ = 14⇒ sinθ = 12 or sinθ =- 12⇒sinθ = sin π6 or sinθ = sin -π6⇒ θ = nπ +(-1)n π6, n ∈ Z or θ = nπ +(-1)n -π6, n ∈ Z⇒ θ = nπ ± π6, n ∈ Z
Q11.
Answer :
(b) nπ+ -1nπ6, n ∈ Z
Given equation:
cotθ – tanθ = secθ⇒cosθsinθ- sinθcosθ = 1cosθ⇒ cos2θ – sin2θsinθ cosθ = 1cosθ⇒ cos2θ – sin2θ =sinθ⇒ (1 – sin2θ) – sin2θ = sinθ⇒ 1 – 2 sin2θ = sinθ⇒2 sin2θ + sinθ – 1 = 0⇒2 sin2θ + 2 sinθ – sinθ – 1 = 0⇒2 sinθ ( sinθ + 1) -1 (sinθ + 1) = 0⇒ (sinθ + 1) (2 sinθ -1) = 0
⇒ sin θ + 1 = 0 or 2 sin θ – 1 = 0
⇒ sin θ = -1 or sin θ = 12
Now,
sin θ = -1 ⇒ sin θ = sin 3π2 ⇒ θ = mπ + (-1)m3π2 , m ∈ Z
And,
sin θ = 12 ⇒ sin θ = sin π6 ⇒ θ = nπ + (-1)nπ6 , n ∈ Z
∴ θ= nπ + (-1)nπ6 , n ∈ Z
Q12.
Answer :
(d) π3
Given equation:
cosθ + 3 sinθ = 2 …(i)
Thus, the equation is of the form a cos θ + b sin θ = c, where a = 1, b = 3 and c = 3.
Let:
a = r cos α and b = r sin α
1 = r cos α and 3= r sin α
⇒ r = a2 + b2=(3)2 + 12 = 2 and tan α = ba ⇒tan α = 31 ⇒tan α= tan π3 ⇒ α = π3
On putting a = 1 = r cos α and b = 3 = r sin α in equation (i), we get:
r cos α cos θ + r sin α sin θ = 2⇒ r cosθ – α = 2⇒ r cosθ – π3 = 2⇒2 cos θ – π3 = 2⇒ cos θ- π3 = 1⇒cos θ – π3 = cos 0⇒ θ – π3 = 0⇒ θ = π3
Q13.
Answer :
(d) 2
Given equation:
tanθ + tan2θ + tan3θ = tanθ tan2θ tan3θ⇒ tanθ + tan2θ = – tan3θ + tanθ tan2θ tan3θ⇒tanθ + tan2θ = – tan3θ (1 – tanθ tan2θ)⇒ tanθ + tan2θ1 – tanθ tan 2θ = – tan3θ⇒ tan ( θ + 2θ) = – tan3θ⇒tan3θ = – tan3θ⇒2 tan3θ = 0⇒ tan3θ =0⇒ 3θ = nπ⇒ θ= nπ3
Now,
θ = π3 , n = 1
θ = 2π3 , n = 2
θ= 3π3 = 180°, which is not possible, as it is not in the interval (0, 2π).
Hence, the number of solutions of the given equation is 2.
Q14.
Answer :
(b) 2
sin2θ – cosθ = 14⇒ (1 – cos2θ) – cosθ = 14⇒ 4 – 4 cos2θ – 4 cosθ = 1⇒ 4 cos2θ + 4 cosθ – 3 = 0⇒ 4 cos2θ + 6 cosθ – 2 cosθ -3 = 0⇒ 2 cosθ ( 2 cosθ + 3) -1 ( 2 cosθ + 3) =0⇒ (2 cosθ + 3 ) (2 cosθ – 1) = 0
⇒ 2 cosθ + 3 = 0 or, 2 cosθ – 1 = 0
⇒cosθ = -32 or cosθ = 12
Here, cosθ = -32 is not possible.
∴ cos θ = 12
⇒ cos θ = cos π3⇒θ=2nπ±π3
Now for n = 0 and 1, the values of θ are π3,5π3 and 7π3, but 7π3 is not in 0, 2π.
Hence, there are two solutions in 0, 2π.
Q15.
Answer :
(d) none of these
Given equation: esin x – e-sin x – 4 = 0
Let :
esin x = y
Now,
y – y-1 – 4 = 0⇒ y2 – 4y – 1 = 0
∴ y = 4 ±16 + 42
⇒ y = 4 ± 202⇒ y = 4 ± 252 = 2 ± 5
And,
y = esin x ⇒esinx = 2 ± 5
Taking log on both sides, we get:
sin x = loge (2 ± 5)
⇒ sin x = loge ( 2 + 5) or sin x = loge ( 2 – 5)⇒ sin x = loge ( 4.24) or sin x = loge ( -0.24)loge ( 4.24) >1 and sinx cannot be greater than 1.In the other case, the log of negative term occurs, which is not defined.
Q16.
Answer :
(d) no
Given equation:
3 cosx + 4 sinx = 6 …(i)
Thus, the equation is of the form a cos x + b sin x = c, where a = 3, b = 4 and c = 6.
Let:
a = 3 = r cos α and b = 4 = r sin α
Now,
tan α = ba = 43⇒ α = tan-143
Aso,
r = a2 + b2 = 9 + 16 = 25 = 5
On putting a = 3 = r cos α and b = 4 = r sin α in equation (i), we get:
r cosα cosθ + sinα sinθ = 6⇒ r cos (θ – α ) = 6⇒ 5 cos (θ – α) = 6⇒ cos (θ – α) = 65
From here, we cannot find the value of θ.
Q17.
Answer :
(d) n π+-1nπ4-π3, n ∈ Z
Given equation:
3cosθ + sinθ = 2 …(i)
This is of the form a cos θ + b sin θ = c, where a = 3 , b = 1 and c = 2.
Let:
a = r sin α and b = r cos α.
Now,
r = a2 + b2 = (3)2 + 12 = 2
And,
tan α = ab ⇒tan α= 31 ⇒tan α= tan π3 ⇒ α = π3
Putting a = 3 = r sin α and b = 1 = r cos α in equation (i), we get:
r cosθ sinα + r sinθ cosα = 2⇒ r sin (θ + α) = 2⇒ 2 sin (θ + α) = 2⇒ sin θ + π3 = 12⇒ sin θ + π3 = cos π4⇒ θ + π3 = nπ + (-1)n π4, n∈ Z⇒ θ = nπ + (-1)n π4 – π3, n ∈Z
Q18.
Answer :
(c) θ=n π7+π14, n ∈ Z
Given:
tan5θ = cot2θ⇒tan5θ = tan π2 – 2θ⇒ 5θ = nπ + π2 – 2θ⇒ 7θ = nπ + π2⇒ θ = nπ7 + π14 , n ∈ Z
Page 11.24 (Multiple Choice Questions)
Q19.
Answer :
(d) 5π/4, 7π/4
Given equation:
cos2θ + sinθ + 1 = 0⇒(1 – sin2θ) + sinθ + 1 = 0⇒2 – sin2θ + sinθ = 0⇒ sin2θ – sinθ – 2 = 0⇒ sin2θ -2 sinθ + sinθ – 2 = 0⇒ sinθ ( sinθ – 2 ) + 1 ( sinθ – 2 ) = 0⇒ (sinθ – 2) ( sinθ + 1) = 0
⇒ sinθ – 2 = 0 or sinθ + 1 =0
⇒ sinθ = 2 or sin θ =-1
Now, sinθ = 2 is not possible.
And,
sin θ = -1 ⇒ sin θ = sin 3π2 ⇒ θ = nπ+-1n3π2
For n = 0, θ = 3π2, for n = 1, θ = 7π2 and so on.
Hence, 3π2 lies in the interval 5π4, 7π4.
Q20.
Answer :
(b) θ=120°, 240°
Given equation:
cos θ =-12⇒cos θ = cos 120°⇒θ=120°
Or,
cos θ = cos 240°⇒θ=240°
So, both 120° and 240° lie in 0 < θ < 360°.
Q21.
Answer :
(c) 6
Given:
3 sin2x – 7 sinx + 2 = 0
⇒ 3 sin2x -6 sinx – sinx + 2 = 0⇒ 3 sinx (sinx – 2) -1 (sinx – 2) = 0⇒(3 sinx -1) (sinx – 2) = 0
⇒ 3 sin x – 1 = 0 or sin x – 2 = 0
Now, sin x = 2 is not possible, as the value of sin x lies between -1 and 1.
⇒ sin x = 13
Also, sin x is positive only in first two quadrants. Therefore, sin x is positive twice in the interval 0,π.
Hence, it is positive six times in the interval 0,5π, viz 0,π, 2π,3π and 4π,5π.
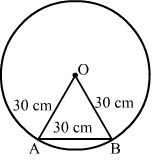
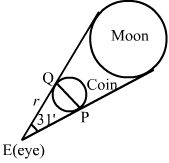
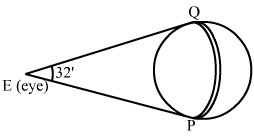
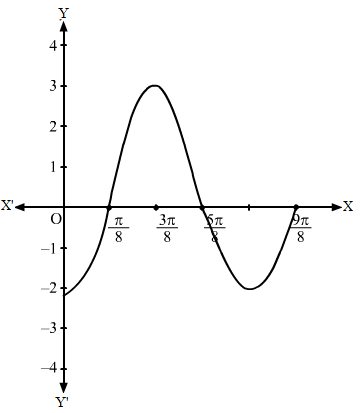
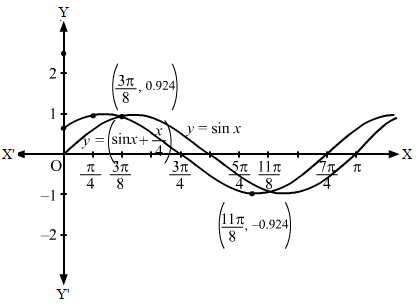
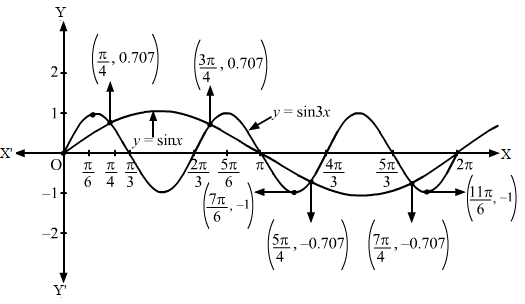
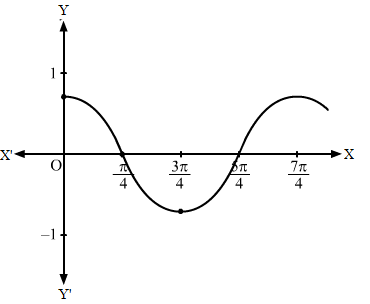
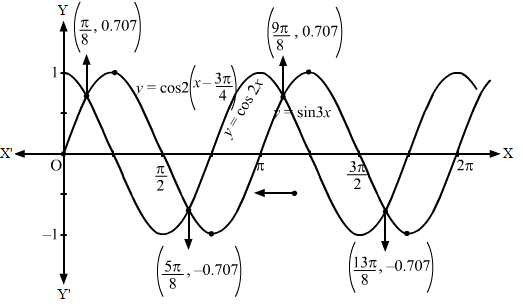
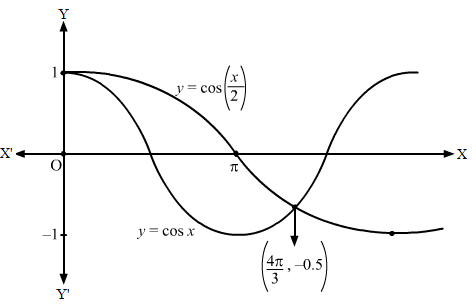
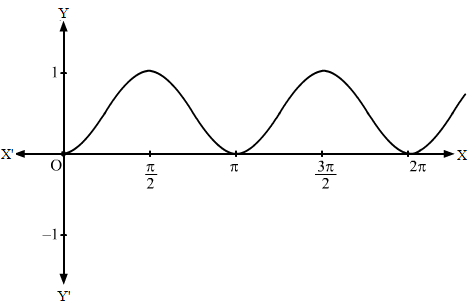
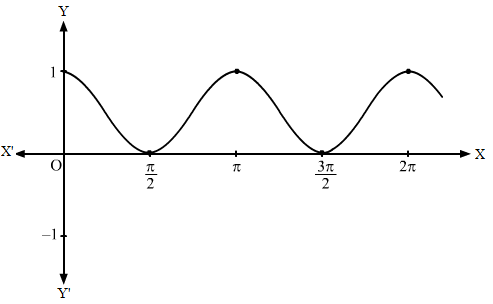
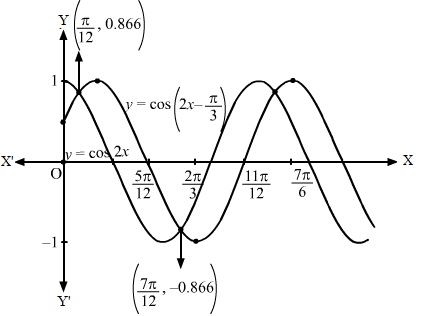
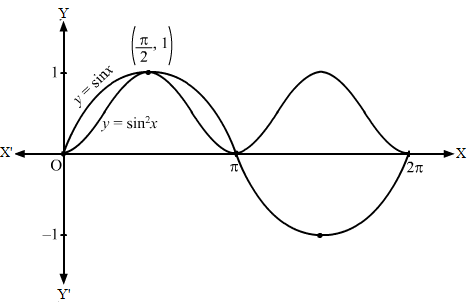
Leave a Reply