Notes For All Chapters Science Class 9 CBSE
Facts that Matter
Introduction
- Everything in this universe is made of materials which scientist has names ‘matter’.
- The matter is made up of very small tiny particles. It is not continuous but is particulate.
- The matter is anything that occupies space and has mass.
- Particles of matter have space between them and are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
States of Matter :
The physical states of a matter are :
( i ) Solid,
( ii ) Liquid,
( iii ) Gas.
We can classify our body into three states of matter i.e.:-
Bones and teeth are solids.
Blood and water present in our body are liquids.
Air in our lungs is gaseous.
( i ) Solid State :
Characteristics of solid states are :
Have definite shape. Fixed mass, volume and shape.
Have distinct boundaries.
Inter-particle distances are least.
Have rigidity and incompressibility.
Have definite volume.
High density and do not diffuse.
Inter particle forces of attraction are strongest.
Constituent particles are very closely packed.
Macroscopic Explanation for Properties of solids :
Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume because the particles are locked into place.
Solids do not flow easily because the particles cannot move/slide past one another.
Solids are not easily compressible because there is little free space between particles.
( ii ) Liquid State :
The characteristics of liquid state are :
Have fluidity i.e., they are not rigid.
Low compressibility.
No definite shape and boundaries. They take the shape of the vessels.
Have definite volume.
Microscopic Explanation for Properties of Liquids :
Liquids are substances having fixed (definite) volume and no fixed shape. They take the shape of the container in which they are stored.
Force of attraction between the particles of liquid keeps its volume same.
Diffusion is much more in liquids than in solids due to free movement of particles of liquids.
( iii ) Gaseous State :
The characteristics of gaseous state are :
Have fluidity.
Have high compressibility.
Have no definite boundaries.
Have no definite shape.
Have no definite volume.
Microscopic Explanation for Properties of Gases :
Gases are substance that do not have fixed volume and occupy all the volume available to them.
The gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) from the atmosphere diffuse and dissolve in water. Due to these gases aquatic plants and animals are able to survive.
The particles in a gas are free to move in any direction hence gases can flow.
Pressure of gas is the force applied on the walls of vessel by the irregular moving gas particles.
Matter can change its state from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas and vice-versa.
Effect of temperature: On increasing the heat, the particles gain energy and start vibrating with greater energy. Due to increased kinetic energy the particles overcome the force of attraction and a new state is obtained.
Melting point: The temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
Boiling point: The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon.
Latent heat of fusion: The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at its melting point is called the latent heat of fusion of the solid.
Latent heat of vaporization: The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a liquid to vapour at atmospheric pressure, at its boiling point is called the latent heat of vaporization of the liquid.
Effect of change of pressure on the matter: On applying pressure, the particles of matter can be brought close together and the state of matter can be changed. For example, CO2 gas can be solidified by applying pressure and lowering temperature.
Evaporation: The phenomenon of changing of a liquid into its vapour state at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon.
Factors affecting evaporation.
An increase in surface area increases evaporation.
An increase in temperature increases the rate of evaporation.
A decrease in humidity increases the rate of evaporation.
An increase in wind speed increases the rate of evaporation.
Evaporation causes a cooling effect.
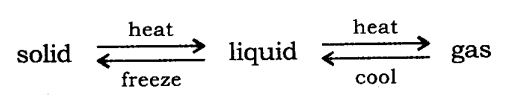
Easy way to introduce and learn the thing
We again want the same pdf form of notes!!
They were really very helpfully ♡