Notes For All Chapters Maths Class 9
1. Triangle: A closed figure formed by three intersecting lines is called a triangle (‘Tri’ means ‘three’). A triangle has three sides, three angles and three vertices.
e.g., In triangle ABC, denoted as ∆ABC. AB, BC, CA are the three sides, ∠A, ∠B, ∠C are the three angles and A, B, C are three vertices.
2. Congruence of Triangles: Two triangles are congruent if the sides and angles of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and angles of the other triangle.
If ∆PQR is congruent to ∆ABC, we write ∆PQR = ∆ABC.
Note: Congruent triangles corresponding parts are equal and we write in short ‘CPCT’ for Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles.
3. Criteria for Congruence of Triangles.
- SAS congruence rule: Two triangles are congruent if two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the sides and the included angle of the other triangle.
- ASA congruence rule: Two triangles are congruent if two angles and the included sides of one triangle are equal to two angles and the included side of another triangle.
- AAS congruence rule: Two triangles are congruent if any two pairs of angles and one pair of corresponding sides are equal.
- SSS congruence rule: Two triangles are congruent if three sides of one triangle are equal to the sides of the other triangle.
- RHS congruence rule: If in two right triangles, hypotenuse and one side of a triangle are equal to the hypotenuse and one side of other triangles, then the two triangles are congruent.
4. Properties of a Triangle
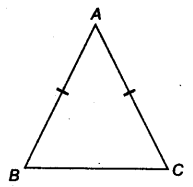
- Isosceles triangle: A triangle in which two sides are equal is called an isosceles triangle. So, ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC.
- Theorem 1: Angles opposite to equal sides of an isosceles triangle are equal.
i.e., ∠B = ∠C - Theorem 2: The sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal. i.e., AB = AC
5. Inequalities in a Triangle
- If two sides of a triangle are unequal, the angle opposite to the longer side is larger (or greater).
- In any triangle, the side opposite to the larger (or greater) angle is longer (converse of (i)).
- The sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side, i.e., AB + BC > CA.
good