Solutions For All Chapters Beehive Class 9
Download PDF Beehive class 9 Solutions chapter 10
Thinking about The Text (Page 102)
Activity
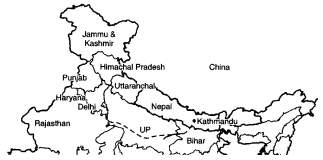
Question 1. On the following map mark out the route, which the author thought of but did not take, to Delhi.
Answer:
Route ¡s shown by dotted line
1. Kathmandu to Patna by bus & train
2. Patna to Allaha bad by boat/Ganges
3. Allahabad to Delhi by boat/Yamuna
Question 2. Find out the possible routes (by rail, road or air) from Kathmandu to New Delhi/ Mumbai/Kolkata/Chennai.
Answer: For self-attempt. Students may take the Atlas of the country and see or find themselves the air, road routes from Kathmandu to New Delhi/Mumbai/ Kolkata/ Chennai.
Some possible routes are:
By Road
1. Kathmandu—Viratnagar—Patna
2. Kathmandu—Nepalganj—Gorakhpur
By Rail
Patna—Delhi
Gorakhpur—Delhi
Patna—Kolkata
Gorakhpur—Varanasi—Kolkata
Patna—Mumbai
Gorakhpur—Allahabad—Mumbai
Patna—Khadarpur—Chennai
Gorakhpur—Allahabad—Nagpur—Chennai
I. Answer these questions in one or two words or in short phrases.
Question 1. Name the two temples the author visited in Kathmandu.
Answer: Pashupatinath and Baudhnath Stupa.
Question 2. The writer says, “All this I wash down with Coca Cola.” What does ‘all this’ refer to?
Answer: Com-on-the-cob and marzipan.
Question 3. What does Vikram Seth compare to the quills of a porcupine?
Answer: The flutes tied on the top of the flute seller’s pole.
Question 4. Name five kinds of flutes.
Answer: The reed neh, the recorder, the Japanese shakuhachi, the deep bansuri, the breathy flutes of South America, the high pitched Chinese flutes.
II. Answer each question in a short paragraph.
Question 1. What difference does the author note between the flute seller and the other hawkers?
Answer: The author finds a difference in selling the articles. The flute seller does not shout out his wares. He makes a sale in a curiously offhanded way as if this was incidental to his enterprise.
Question 2. What is the belief at Pashupatinath about the end of Kaliyug?
Answer: People believe that when a small shrine emerges fully on Bagwati river, the goddess inside will escape, and the evil period of the Kalyug will end on earth.
Question 3. The author has drawn powerful images and pictures. Pick out three examples each of
(i) the atmosphere of ‘febrile confusion’ outside the temple of Pashupatinath (for example: some people trying to get the priest’s attention are elbowed aside…)
(ii) the things he sees
(iii) the sounds he hears
Answer:
- The author describes the monkey’s fight vividly and graphically. A fight breaks out between two monkeys. One chases the other, who jumps onto a shivalinga, then runs screaming around the temples and down to the river.
- The author observes a princess of the Nepalese royal house. Everyone bows to her. He sees monkeys. He sees felt bags, Tibetan prints and silver jewellery. He looks at flute sellers, hawkers of postcards, shops selling western cosmetics, etc.
- He hears film songs from the radios, car horns, bicycle bells, stray cows low and vendors shout out their wares. He also listens to the various flutes played by the flute seller.
III. Answer the following questions in not more than 100-150 words each.
Question 1. Compare and contrast the atmosphere in and around the Baudhnath shrine with the Pashupatinath temple.
Answer: At Pashupatinath there is an atmosphere of ‘febrile confusion’. Priests, hawkers, devotees, tourists, cows, monkeys, pigeons and dogs roam through the grounds. There are so many worshippers that some people trying to get the priest’s attention are elbowed aside by others pushing their way to the front. At the Baudhnath stupa, the Buddhist shrine of Kathmandu, there is a sense of stillness. Its immense white dome is ringed by a road. Small shops stand on its outer edge. Most of the shops are owned by Tibetan immigrants. There are no crowds and this is a haven of quietness in the busy streets around.
Question 2. How does the author describe Kathmandu’s busiest streets?
Answer: The author says that Kathmandu is vivid, mercenary, religious, with small shrines to flower-adorned deities along the narrowest and busiest streets. There are fruit sellers, flute sellers, hawkers of postcards, shops selling western cosmetics, film rolls and chocolate or copper utensils and Nepalese antiques. Film songs blare out from the radios, car horns sound, bicycle bells ring, stray cows low, vendors shout out their wares. The author buys a com-on- the-cob roasted in a charcoal brazier on the pavement. He also buys coca cola and orange drink.
Question 3. “To hear any flute is to be drawn into the commonality of all mankind.” Why does the author say this?
Answer: The author says this because he is aware of the fact that music appeals to senses. It gives pleasure to every listener. The flute seller does not sell only one kind of flute. He has various types of flutes that represent different customs and culture. The flute seller is a wise sales person. He does not shout out his wares. He plays melodious tunes which fascinate others. Mankind does not have multiple appearances and shapes. It is universal and cosmopolitan. Music soothes everyone’s heart irrespective of their caste, colour and creed. So the author says that to hear any flute is to be drawn into the commonality of all mankind.
Thinking about language (Page 103)
Question 1. Read the following sentences carefully to understand the meaning of the italicised phrases. Then match the phrasal verbs in column A with their meanings in column B.
- A communal war broke out when the princess was abducted by the neighboring prince.
- The cockpit broke off from the plane during the plane crash.
- The car broke down on the way and we were left stranded in the jungle.
- The dacoit broke away from the police as they took him to court.
- The brothers broke up after the death of the father.
- The thief broke into our house when we were away.
| A | B |
| (i) break out | (a) to come apart due to force |
| (ii) break off | (b) end a relationship |
| (iii) break down | (c) break and enter illegally; unlawful trespassing |
| (iv) break away (from someone) | (d) to start suddenly, (usually a fight, a war or a disease) |
| (v) break up | (e) to escape from someone’s grip |
| (vi) break into | (f) stop working |
Answers:
| A | B |
| (i) break out | (d) to start suddenly, (usually a fight, a war or a disease) |
| (ii) break off | (a) to come apart due to force |
| (iii) break down | (f) stop working |
| (iv) break away (from someone) | (b) end a relationship |
| (v) break up | (e) to escape from someone’s grip |
| (vi) break into | (c) break and enter illegally; unlawful trespassing |
II.
1. Use the suffixes -ion or -tion to form nouns from the following verbs. Make the necessary changes in the spellings of the words.
Example: proclaim-proclamation
Answer:
2. Now fill in the blanks with suitable words from the ones that you have formed.
1. Mass literacy was possible only after the of the ……….. printing machine.
2. Ramesh is unable to tackle the situation as he lacks ………..
3. I could not resist the ……….. to open the letter.
4. Hardwork and ……….. are the main keys to success.
5. The children were almost fainting with ……….. after being made to stand in the sun.
Answer: 1. invention, 2. imagination, 3. temptation, 4. dedication, 5. exhaustion.
III. Punctuation
Question 1. Use capital letters, full stops, question marks, commas and inverted commas wherever necessary in the following para-graph.
an arrogant lion was wandering through the jungle one day he asked the tiger who is stronger than you you O lion replied the tiger who is more fierce than a leopard asked the lion you sir replied the leopard he marched upto an elephant and asked the same question the elephant picked him up in his trunk swung him in the air and threw him down look said the lion there is no need to get mad just because you don’t know the answer
Answer: An arrogant lion was wandering through the jungle one day. He asked the tiger, “Who is stronger than you ?” “You, O! lion,” replied the tiger. “Who is more fierce than a leopard?” asked the lion. “You, sir,” replied the leopard. He marched up to an elephant and asked the same question. The elephant picked him up in his trunk, swung him in the air and threw him down. “Look”, said the lion, “there is no need to get mad just because you don’t know the answer.”
IV. Simple Present Tense
Question 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in brackets.
(i) The heart is a pump that …………. (send) the blood circulating through our body. The pumping action …………. (take place) when the left ventricle of the heart …………. (contract). This …………. (force) the blood out into the arteries, which …………. (expand) to receive the on coming blood.
(ii) The African lungfish can live without water for up to four years. During a drought it ………… (dig) a pit and ………… (enclose) itself in a capsule of slime and earth, leaving a tiny opening for air. The capsule ………… (dry) and ………… (harden), but when rain ………… (come), the mud ………… (dissolve) and the lungfish (swim) ………… away.
(iii) Mahesh : We have to organise a class party for our teacher. ………… (Do) anyone play an instrument?
Vipul : Rohit ………… (play) the flute.
Mahesh : ………… (Do) he also act ?
Vipul : No, he ………… (compose) music.
Mahesh : That’s wonderful!
Answer:
1. sends, takes place, contracts, forces, expands
2. digs, encloses, dries, hardens, comes, dissolves, swims
3. Does, plays, Does, only composes.


Short answer type question ke answer to do