Notes For All Chapters Geography Class 8
Activities which are related to earning livelihood are called economic activities. There are three types of economic activities:
- Primary Activities
- Secondary Activities
- Tertiary Activities.
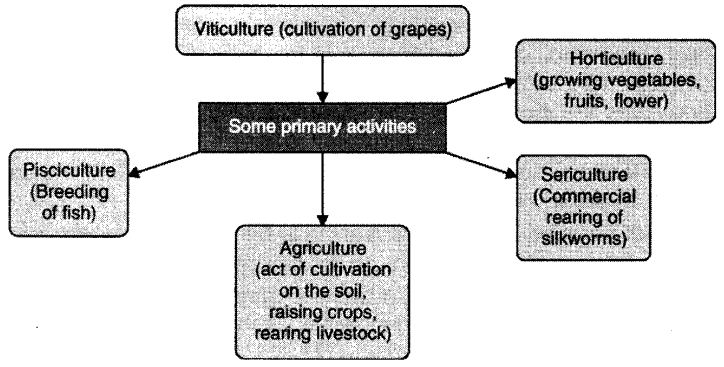
Agriculture is a primary activity. Nearly 2/3rd of India’s population is engaged in agricultural activities. Growing of crops, raising livestock, forestry and fishing all come under agricultural activities.
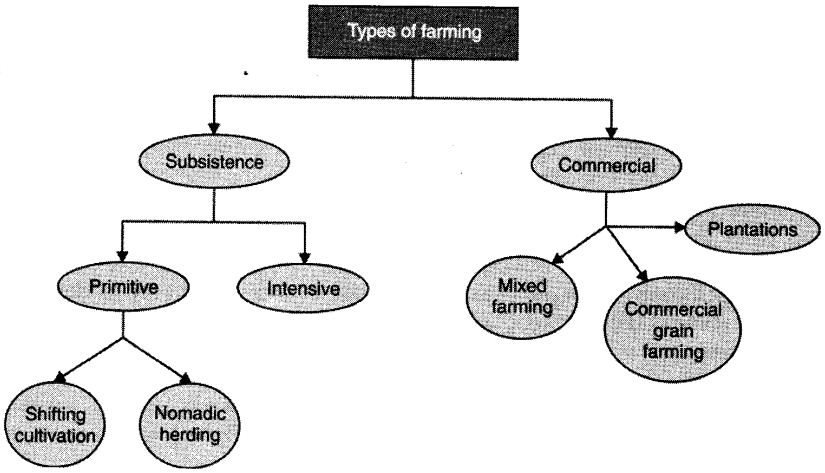
There are mainly two types of farming techniques:
- Subsistence Farming
- Commercial Farming.
When a farmer tills the land till the soil loses its fertility and then shifts to another fertile land, then this type of farming is known as shifting cultivation.
The efforts made to increase farm production in order to meet the growing demands of the increasing population is known as agricultural development. It varies in developed and developing countries.
We divide economic activities into three categories: primary, secondary and tertiary. Agriculture, an activity that is related directly to the extraction and production of natural resources, is a primary activity. Manufacturing of steel and baking of bread are secondary activities since they are not directly related to the extraction or production of natural resources, but their utilisation. Transport and trade are tertiary activities since they do not come in either category.
Two-thirds of India’s population depends on agriculture.
Some of the important inputs required in agriculture are seeds, fertilisers, machinery and labour. Operations involved are ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding and harvesting. Outputs include cops, wool, dairy and poultry products.
Two main types of farming practised are subsistence farming and commercial farming.
Subsistence farming is practised solely to meet the needs of the farmer’s family. Therefore, the practices involved are usually old-fashioned. Use of modern technology is minimum and most work is done by household labour.
In Intensive subsistence agriculture, simple tools and huge labour are used by a farmer to cultivate a small plot of land. More than one crop is grown annually in favourable conditions. Rioe is the major crop. This form of agriculture is seen in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of south, south-east and east Asia.
Shifting cultivation is a class of primitive subsistence agriculture. In this, a plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After some time, the land is abandoned and the farmers move to a different place. This type of farming is common in the thickly forested areas of the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of South-east Asia and north-east India. It’ is also called “slash and burn” agriculture.
Nomadic herding refers to the practice in which herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water. Animals usually reared are the yak, sheep, camel and goats.
Commercial farming is the practice in which crops are grown exclusively for commercial purpose, i.e. for sale in the market. A large area is cultivated and huge capital is involved unlike subsistence farming. Machines are used to a large extent.
Commercial grain farming is a class of commercial farming. Crops like wheat and maize are grown for commercial purpose. The temperate grasslands of North America, Europe and Asia are some common areas where it is seen.
Mixed farming is another type of commercial farming. The land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock. Some areas where it is followed are Europe, eastern USA, Argentina, south-east Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Plantations are a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton) is grown. Large amount of labour and capital are required. The produce is processed in the farm itself or nearby factories.
Rice is the major food crop of the world. It is the staple diet in tropical and sub-tropical parts. Its cultivation needs high temperature, humidity and rainfall. China and India are the largest producers of rice in the world.
Wheat thrives best in well-drained loamy soil. In addition, it needs moderate temperature and rainfall during growing season and bright sunshine at harvesting. USA is a major producer.
Millets are coarse grains. Jowar, bajra and ragi are major millets grown in India.
Maize requires moderate temperature, rainfall, good sunshine and well-drained fertile soils.
Cotton grows best on black and alluvial soils. It needs high temperature, light rainfall, 210 frost free days and bright sunshine.
Jute (called the Golden Fibre) is grown in tropical areas. India and Bangladesh are leading producers.
Coffee grows well on hill slopes. Brazil is the leading producer.
Tea is a beverage crop grow on plantations. It needs well-drained loamy soils ad gentle slopes. Large labour is required.
Agricultural development refers to the effort to increase farm production so as to meet growing demand of increasing population. Mechanisation, a part of agricultural development, means using more machines than human labour.
A typical Indian farm is about 1.5 hectares in area, whereas a typical USA farm is about 250 hectares.
In the USA, farmers use very modern methods for agriculture. In India, however, obsolete methods are used in most parts. Mechanisation is not seen much in India as compared to USA.
A farmer in India generally works as a “peasant” whereas in the USA, he works as a complete businessman.
Primary Activities: Activities which involve direct extraction and production of natural resources are called primary activities: For example agricultural farming, sericulture, pisciculture, etc.
Secondary Activities: Activities which are concerned with the processing of natural resources are called secondary activities.
Tertiary Activities: Activities which fall neither in the primary category nor the secondary category are called tertiary activities. They do not use natural resources directly.
Agriculture: Agriculture is the primary activity that involves cultivation of crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers and rearing of livestock.
Subsistence Farming: Subsistence farming is the form of agriculture practised solely to meet the needs of the farmer’s family: The practices involved are usually old- fashioned.
Intensive Subsistence Agriculture: In intensive, subsistence agriculture, simple tools and huge labour are used by a farmer to cultivate a small plot of land.
Shifting Cultivation: Shifting cultivation is the form of agriculture in which a plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After some time, the land is abandoned and the farmers move to a different place.
Nomadic Herding: Nomadic herding refers to the practice in which herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water.
Commercial Farming: Commercial farming is the practice in which crops are grown exclusively for commercial purpose, i.e. for sale in the market.
Commercial Grain Farming: It is a class of commercial farming in which crops like wheat and maize are grown for commercial purpose.
Mixed Farming: It is a type of commercial farming in which land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
Plantations: These are a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton) is grown.
Food Crops: Crops like rice, wheat, maize, millets are called food crops.
Fiber Crops: Crops like jute and cotton are called fibre crops. Their usage is not as food.
Beverage Crops: Tea and coffee are called beverage crops.
Agricultural Development: Agricultural development refers to the effort to increase farm production so as to meet the growing demand of the increasing population.
Mechanization: This refers to the process of using machines more than human labor.
Leave a Reply