Tangents (स्पर्श रेखाएँ) In Hindi
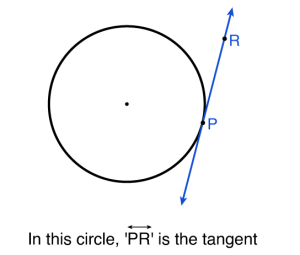
स्पर्श रेखाएँ (tangents) : एक वृत्त की स्पर्शरेखा रेखा वह रेखा होती है जो वृत्त को ठीक एक बिंदु पर स्पर्श करती है , कभी भी वृत्त के आंतरिक भाग में प्रवेश नहीं करती है।
स्पर्शरेखा के कुछ महत्वपूर्ण गुण:
स्पर्शरेखा रेखा कभी भी वृत्त को पार नहीं करती, वह केवल वृत्त को छूती है।
स्पर्शरेखा के बिंदु पर, यह त्रिज्या के लंबवत है।
एक जीवा और स्पर्शरेखा एक कोण बनाते हैं और यह कोण जीवा के विपरीत दिशा में अंकित स्पर्शरेखा के समान होता है।
एक ही बाह्य बिंदु से, वृत्त के स्पर्शरेखा खंड बराबर होते हैं।
Tangents In English
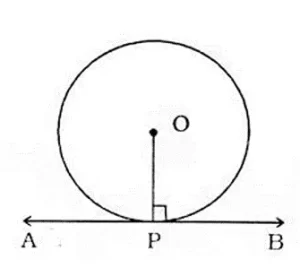
Tangents :- A tangent to a circle is a line that touches the circle at exactly one point, never entering the interior of the circle.
Condition of Tangency
1.When point lies inside the circle
2.When point lies on the circle
3.When point lies outside the circle
1.When point lies inside the circle, no tangent can be drawn passing through it.
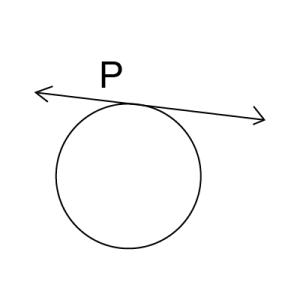
2.When point lies on the circle, one tangent can be drawn passing through it.
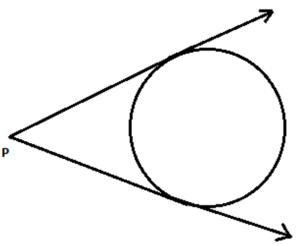
3. When point lies outside the circle, there are exactly two tangents to the circle.
Properties Of Tangency
1.Contact at a Single Point: The tangent line touches the circle at only one point. This point is called the point of tangency.
2.Perpendicularity: The tangent line is perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of tangency. This means that the angle between the tangent line and the radius at the point of tangency is 90 degrees.
3.No Intersecting: The tangent line does not intersect the circle except at the point of tangency. It lies entirely on one side of the circle.
4.Unique Tangent: At any point on a circle, there exists only one tangent line that is tangent to the circle at that point. This property is unique to the circle’s geometry.
Tangent Formula
- QT ² = RT × PT
Tangent Theories
1. The tangent to the circle is perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of contact.
2.The length of two tangents drawn from the circle’s external point is equal.



Leave a Reply