Mixture and Alligation (मिश्रण एवं एलीगेशन) In Hindi
मिश्रण:
1. दो या दो से अधिक पदार्थों का एक साथ मिलना, जिसमें उनकी अलग-अलग पहचान बनी रहती है।
2. यह एक भौतिक प्रक्रिया है, जिसमें ऊर्जा का उत्सर्जन या अवशोषण नहीं होता है।
3. नए पदार्थों का निर्माण नहीं होता है, केवल मूल पदार्थों का मिश्रण बनता है।
एलीगेशन:
1. मिश्रण की एक विशेष विधि, जिसमें दो या दो से अधिक पदार्थों को अलग-अलग अनुपात में मिलाकर एक निश्चित अनुपात का मिश्रण बनाया जाता है।
2. यह एक गणितीय तकनीक है, जिसका उपयोग मिश्रण की गणना करने के लिए किया जाता है।
Mixture and Alligation In English
Mixture:
1. A mixture refers to the combining of two or more substances together. In a mixture, the individual components retain their own chemical identities.
2. It’s a physical process, meaning no energy change (absorption or release) occurs during mixing.
3. No new substances are formed, just a physical combination of the original ingredients.
Alligation:
1. Alligation is a specific method used for mixtures. It involves combining two or more substances with different properties (like cost or concentration) in specific ratios to achieve a desired final mixture with a particular ratio.
2. It’s essentially a mathematical technique used for calculating the proportions needed to create a desired mixture.
Types of Mixture
Homogeneous Mixture: Also known as a solution, a homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout. In other words, the components are evenly distributed at the molecular level, and it is difficult to distinguish between them. Examples include saltwater, sugar dissolved in water, and air.
Heterogeneous Mixture: A heterogeneous mixture does not have a uniform composition throughout. In this type of mixture, the components are not evenly distributed and may be visible to the naked eye. Examples include a mixture of oil and water, sand and water, or a salad containing various vegetables.
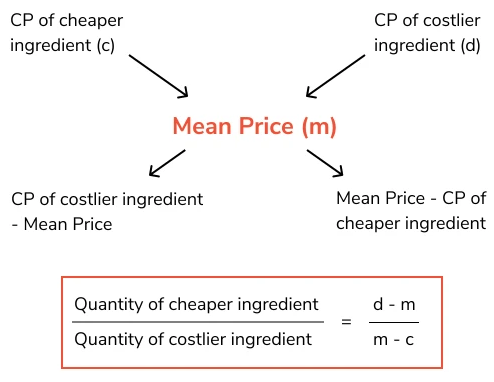
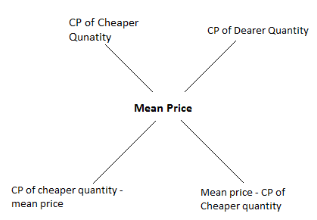
Rule of Alligation:
- \( \frac{Quantity of Cheaper}{Quantity of Dearer} \) = \( \frac{CP of Dearer – Mean Price}{Mean Price – CP of Cheaper} \)


Leave a Reply