Heights and Distances (ऊंचाई और दूरी) In Hindi
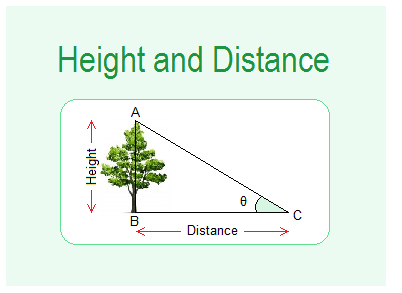
ऊंचाई: किसी वस्तु या बिंदु का जमीन या किसी आधार स्तर से ऊर्ध्वाधर दूरी को ऊंचाई कहते हैं। इसे मीटर (m), सेंटीमीटर (cm), या किलोमीटर (km) में मापा जाता है।
दूरी: दो बिंदुओं के बीच की सीधी रेखा की लंबाई को दूरी कहते हैं। इसे मीटर (m), सेंटीमीटर (cm), किलोमीटर (km), या इंच (in) में मापा जाता है।
Heights and Distances In English
Height: The vertical distance of an object or point from the ground or a reference level is called its height. It’s measured in meters (m), centimeters (cm), or kilometers (km).
Distance: The straight-line length between two points is called their distance. It’s measured in meters (m), centimeters (cm), kilometers (km), or inches (in).
Examples:
1. The height of a building is the distance from the ground to its roof.
2. The height of a tree is the distance from the ground to its top.
3. The distance between two cities is the straight-line length from one city to the other.
Heights and Distances – Important Terms
Line of Sight – The imaginary horizontal straight line drawn from the observer’s eye to the objects to be viewed. It gives an accurate idea of where the observers view.
Horizontal line – The line passing parallel to the ground or surface is called a horizontal line. The horizontal line is shown in the above figure.
The angle of Elevation – The angle formed by the light of sight with the horizontal line when observers view the object situated upward over the horizontal line. It is formed only when the observer views the upward-placed object.
The angle of Depression – The angle of depression is the inclination of light of sight and horizontal line when observers view the downward object. It is formed only when the observer views the object at the ground from any height.
We know that the ratio of the Tan function is tan = \( \frac{Height}{Distance} \)
= \( \frac{Perpendicular}{Base} \)


Leave a Reply