Complementary angles (पूरक कोण) In Hindi
पूरक कोण दो ऐसे कोण होते हैं जिनके मापों का योग 90° होता है।
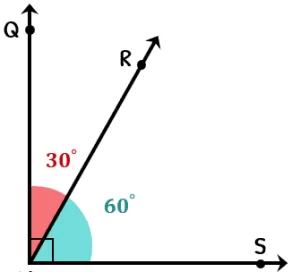
उदाहरण – मान लीजिए कोण A का माप 30° है, तो कोण A का पूरक कोण 60° होगा क्योंकि 30° + 60° = 90°
Complementary angles In English
Complementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. In other words, if you have two angles, and when you add their degree measures, the result is 90 degrees, then those angles are complementary. Each angle is considered the complement of the other.
For Example – if one angle measures 30 degrees, the complementary angle would measure 60 degrees because 30 degrees + 60 degrees = 90 degrees. Complementary angles are commonly encountered in geometry and trigonometry.
Complementary Angles Formula
Complementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. The formula for complementary angles is:
- ∠A + ∠B = 90°
Complementary Angles Types
There are two types of complementary angles:
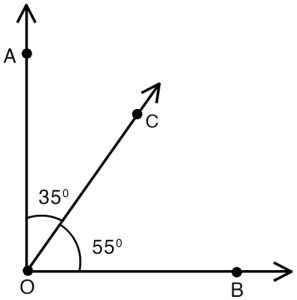
1. Adjacent complementary angles : These are two angles that share a common vertex and a common side, but do not overlap, and together form a right angle (90 degrees).
Example : Angles ∠A and ∠B are adjacent complementary angles. Their sum is 90 degrees.
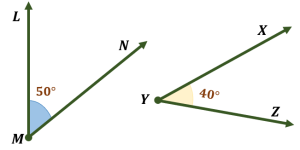
2. Non-adjacent complementary angles: These are two angles that share a common vertex but do not share any sides. They can also be formed by two angles from different shapes, as long as their sum is 90 degrees.
Example : Angles ∠M and ∠Y are non-adjacent complementary angles. Their sum is also 90 degrees.
Complementary Angles Properties
1. Two angles are complementary if they add up to 90 degrees.
2. Complementary angles can be adjacent or non-adjacent.
3. Three or more angles cannot be complementary even if their sum is equal to 90 degrees.
4. If two angles are complementary, each angle is called the “complement” or “complementary angle” of the other angle.
5. Two acute angles of a right triangle are complementary.
Difference between Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Complementary Angles:
1. Sum is equal to 90 degrees
2. Two angles complement each other
3. These angles do not form linear pair of angles
4. Meant only for right angles
Supplementary Angles
1. Sum is equal to 180 degrees
2. Two angles supplement each other
3. These angles form linear pair of angles
4. Meant only for straight angles
Here’s an easy way to remember the difference:
Complementary angles – C for Corner (like a right angle) – add up to 90 degrees.
Supplementary angles – S for Straight line – add up to 180 degrees.


Leave a Reply