Questions Answers For All Chapters – Civics Class 8
The Indian Judicial System
Q 1. Choose the correct option and complete the statements.
(1) Laws are made by …………… .
(a) Legislature
(b) Council of Ministers
(c) Judiciary
(d) Executive
Answer: Laws are made by (a) Legislature
(2) The Chief Justice of Supreme Court is appointed by ……………
(a) The Prime Minister
(b) The President
(c) The Home Minister
(d) The Chief Justice
Answer: The Chief Justice of Supreme Court is appointed by (b) The President
Q 2. Explain the concepts.
(1) Judicial Review
Answer: Judicial Review is the power of the Supreme Court to protect the Constitution. If any law passed by the Legislature or any act of the Executive violates the Constitution, the court can declare it illegal and strike it down. This ensures that all laws and acts are consistent with the Constitution.
(2) Public Interest Litigation
Answer: Public Interest Litigation (PIL) refers to cases filed on issues of public importance by individual citizens, social organisations, or NGOs on behalf of the public. The court considers the issues raised and gives a decision to protect the interests of society.
Q 3. Write short notes on.
(1) Civil and Criminal Law
Answer:
- Civil Law: Deals with conflicts that affect the rights of a person, such as land and property disputes, rent agreements, and divorce. A petition is filed in the relevant court, which gives a decision.
- Criminal Law: Deals with serious crimes such as theft, robbery, dowry, and murder. A First Information Report (FIR) is filed with the police, which investigates the matter, and if the charges are proved, severe punishment is given.
(2) Judicial Activism
Answer: Judicial Activism refers to the active role of the judiciary in ensuring justice and equality. Courts have become proactive in providing legal protection to marginalised sections of society, including women, children, tribal communities, and workers. Public Interest Litigations (PIL) have played a significant role in this process.
Q 4. Answer in brief.
(1) Why are laws necessary in society?
Answer: Laws are necessary to maintain order, resolve conflicts, and protect the rights of individuals. They help prevent the emergence of authoritarian groups and ensure that justice, equality, and freedom are maintained in society.
(2) Enumerate the functions of the Supreme Court.
Answer:
- Settles disputes between the Union and the States.
- Protects the fundamental rights of citizens.
- Reviews decisions of lower courts and its own decisions.
- Advises the President on legal matters of public importance.
(3) Which are the provisions that preserve the independence of the judiciary?
Answer:
- Judges are appointed by the President to avoid political pressure.
- Judges enjoy security of tenure and cannot be removed for trivial reasons.
- Salaries are drawn from the Consolidated Fund of India, without parliamentary discussion.
- Personal criticisms on judges are not allowed; contempt of court is punishable.
- Parliament cannot discuss judicial decisions but can remove judges through impeachment.
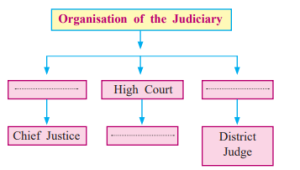
Q 5. Complete the table.
Answer:
| Organisation of the Judiciary |
|---|
| Supreme Court → High Court → District Court |
| Chief Justice → Judge → District Judge |

Leave a Reply