Questions Answers For All Chapters – Civics Class 8
The Union Executive
Q 1. Choose the correct option and rewrite the statement.
(1) In India, the executive power is vested with the …………… . (President, Prime Minister, Speaker)
Answer: In India, the executive power is vested with the President.
(2) The tenure of the President is of ………… years. (Three, Four, Five)
Answer: The tenure of the President is of five years.
(3) The Council of Ministers is led by the ………. .(Party chief, Prime Minister, President)
Answer: The Council of Ministers is led by the Prime Minister.
Q 2. Find and write.
(1) The President, the Prime Minister, the Council of Minister are called the –
Answer: The President, the Prime Minister, and the Council of Ministers are called the Union Executive.
(2) During the parliamentary session the period around 12 noon is known as –
Answer: During the parliamentary session, the period around 12 noon is known as Zero Hour.
Q 3. Write on following concepts in your own words.
(1) Impeachment procedure
Answer: If the President violates the Constitution, the Parliament has the authority to remove him through the process of impeachment. Any one House of Parliament can lay the charge of violation of the Constitution, and the other House investigates the charge. The resolution for removal has to be passed by a special (two-thirds) majority of both Houses of Parliament.
(2) No-confidence motion
Answer: The government remains in power as long as it enjoys the majority support in the Lok Sabha. If the members of the Parliament withdraw their support, the government may lose its majority. A no-confidence motion is moved by the members of the House to express that they do not have confidence in the government. If the motion is passed with a majority, the Council of Ministers has to resign.
(3) Jumbo ministry
Answer: A “Jumbo ministry” refers to a large Council of Ministers. Earlier, there was a trend of appointing a large number of ministers. However, a constitutional amendment was introduced to limit the size of the Council of Ministers to 15% of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Q 4. Answer in brief.
(1) Enumerate the functions of the Council of Ministers.
Answer:
The Council of Ministers takes the initiative in the law-making process.
It drafts and discusses schemes, policy plans, and decisions.
It introduces these policies in Parliament for approval.
It handles key sectors like education, agriculture, health, and foreign relations.
After Parliament’s approval, the Council of Ministers is responsible for the implementation of these policies.
(2) How does the Parliament keep a check on the Council of Ministers ?
Answer:
Discussions and Debates: Parliament members scrutinize and debate policy proposals.
Question Hour: Ministers are required to answer questions from members of the House.
Zero Hour: Members can raise issues of public importance around 12 noon.
No-confidence motion: If the government loses the support of the majority in Lok Sabha, the Council of Ministers must resign.
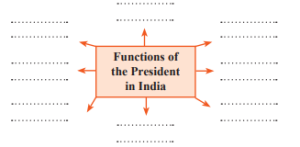
Q 5. Complete the concept picture.
Answer:
Executive Powers – The President is the head of the executive branch and appoints the Prime Minister and other ministers.
Legislative Powers – The President summons, prorogues, and dissolves Parliament sessions and gives assent to bills.
Judicial Powers – The President has the power to grant pardons, reprieves, and respites under Article 72.
Military Powers – The President is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces.
Diplomatic Powers – The President appoints ambassadors and receives foreign diplomats.
Financial Powers – The President causes the Union Budget to be presented and authorizes money bills.
Emergency Powers – The President can declare National, State, and Financial emergencies under Articles 352, 356, and 360.
Ordinance-Making Power – The President can promulgate ordinances when Parliament is not in session.

Leave a Reply