Question Answers For All Chapters – General Science Class 7
Cell Structure and Micro-organisms
Exercise
1. Answer the following questions.
(a) What is a ‘cell’?
→ A cell is the basic unit of life that makes up all living organisms. It carries out all necessary functions of life.
(b) Name the different organelles in a cell.
→ The main cell organelles are nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, ribosomes, Golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, and lysosomes.
(c) What are micro-organisms?
→ Micro-organisms are tiny living organisms that are too small to see with the naked eye, such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, and algae.
(d) Which are the different types of micro-organisms?
→ The five main types of micro-organisms are bacteria, fungi, protozoa, algae, and viruses.
2. Fill in the blanks with the proper word.
(a) The organelle called the chloroplast is present in plant cells only.
(b) Garbage is converted into compost by micro-organisms.
(c) In the cell, photosynthesis is carried out with the help of chloroplasts.
(d) An electron microscope is necessary for the study of viruses.
3. What is the difference between us?
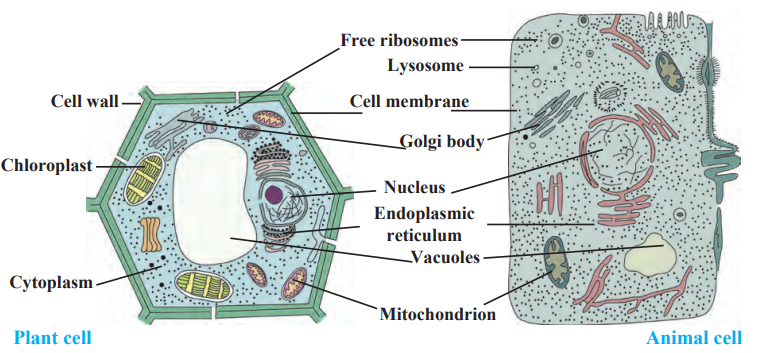
(a) Difference between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|
| Has a cell wall for support. | No cell wall present. |
| Has chloroplasts for photosynthesis. | Does not have chloroplasts. |
| Contains large vacuoles for storing nutrients. | Contains small vacuoles. |
| Fixed, rectangular shape. | Irregular, round shape. |
(b) Difference between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
|---|---|
| Does not have a nucleus. | Has a well-defined nucleus. |
| DNA is present in the cytoplasm. | DNA is inside the nucleus. |
| Example: Bacteria. | Example: Plant and Animal Cells. |
4. Sketch and describe the plant cell and animal cell.
(a) Plant Cell Diagram and Description
- The plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, a large vacuole, and a nucleus.
- Chloroplasts help in photosynthesis by converting sunlight into food.
- The cell wall provides structure and strength to the cell.
(b) Animal Cell Diagram and Description
- The animal cell has a cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, and small vacuoles.
- Mitochondria provide energy to the cell.
- Animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts.
5. Explain the uses and harmful effects of micro-organisms.
Uses of Micro-organisms:
✔ Food Production – Yeast is used in bread and alcohol production.
✔ Medicine – Bacteria and fungi help make antibiotics and vaccines.
✔ Agriculture – Some bacteria increase soil fertility by fixing nitrogen.
✔ Decomposition – Microbes help break down waste into compost.
Harmful Effects of Micro-organisms:
✘ Cause diseases – Bacteria cause tuberculosis, viruses cause flu.
✘ Spoil food – Fungi and bacteria cause food poisoning.
✘ Damage crops – Pests and fungi destroy crops, leading to food shortages.
6. Give reasons.
(a) Diseases spread on a large scale during periods of heavy rainfall and floods.
→ Stagnant water allows bacteria, viruses, and mosquitoes to breed, spreading diseases like cholera and malaria.
(b) There is a possibility of food poisoning if we eat stale food.
→ Stale food develops harmful bacteria and fungi that release toxins, causing food poisoning.
(c) Soil is turned over during tilling.
→ Turning soil exposes insects and bacteria to sunlight, improves aeration, and increases soil fertility.
(d) Fungus grows quickly in moist or humid conditions.
→ Fungi need warm and damp conditions to grow, which is why they spread faster in humid areas.
(e) A refrigerator is used in almost every home.
→ Refrigeration slows down bacterial growth, keeping food fresh for longer.
(f) Bread ‘rises’ during baking.
→ Yeast produces carbon dioxide gas, which forms air bubbles, making the dough rise.
(g) Fodder is soaked in water before offering to cattle.
→ Soaking softens the fodder, making it easier to digest and improving nutrient absorption.
7. When will you use a simple microscope and when, a compound microscope? Explain in detail how you will use them.
✔ Simple Microscope:
- Used for observing small objects, like insects and plant parts.
- Works with a single lens and magnifies small objects up to 10x.
- Used by jewelers and watchmakers.
✔ Compound Microscope:
- Used for studying cells and micro-organisms.
- Has two lenses (eyepiece and objective lens) for higher magnification (100x to 1000x).
- Used in laboratories, schools, and hospitals.
✔ How to Use a Microscope:
- Place the slide on the stage.
- Adjust the focus knob to get a clear view.
- Start with low magnification and then increase.
- Observe cells, bacteria, or plant tissues.

Leave a Reply