Questions Answers For All Chapters – Geography Class 7
Winds
Q.1. Rewrite the following statements after choosing the correct option.
(1) When the air expands, it ………….. .
(a) becomes solid
(b) becomes thinner
(c) gets lost
(d) becomes humid
Answer: (b) becomes thinner.
(2) From high air pressure regions, winds ………… .
(a) blow to regions of still higher pressure.
(b) blow towards regions of cooler air.
(c) blow towards regions of low air pressure.
(d) remain still.
Answer: (c) blow towards regions of low air pressure.
(3) In the northern hemisphere, winds blowing towards the equator ………. due to the rotation of the earth.
(a) turn to the south
(b) turn to the east
(c) turn to the west
(d) turn to the north
Answer: (c) turn to the west.
(4) The direction of seasonal winds blowing over the Indian subcontinent during winter is from the ……. .
(a) south-east to north-west.
(b) south-west towards north-east.
(c) north-east to south-west.
(d) north-west to south-east.
Answer: (c) north-east to south-west.
(5) The Roaring Forties in the southern hemisphere
(a) blow towards the equator.
(b) blow in the areas around 40° S parallel.
(c) blow from the subpolar region of low pressure.
(d) blow around 40° N parallel.
Answer: (b) blow in the areas around 40° S parallel.
Q.2. Identify the type of winds from the description given below.
(1) These winds from the south-west bring rains to the Indian subcontinent. During June to September, India gets rains. After this period these winds retreat.
Answer: South-West Monsoon Winds
(2) These winds blowing from the north pole region towards 60° N parallel cause cold wave conditions in extensive areas covering North America, Europe and Russia.
Answer: Polar Winds
(3) Hilltops get heated quickly during the day. The air in this part becomes hot, light and starts ascending. Hence, a low pressure area forms in this region. At the same time the air at the foothills being cooler, and that area experiences high pressure. Air in that area blows towards low pressure.
Answer: Valley Breeze
Q.3. Given below are the values of air pressure in millibars. Using the same, draw diagrams to show a cyclone and an anticyclone.
- 990, 994, 996, 1000
- 1030, 1020, 1010, 1000
Answer:
Cyclone: Air pressure values – 990, 994, 996, 1000
Explanation: Cyclones are formed in low-pressure areas where air moves towards the center in a circular manner.
Anticyclone: Air pressure values – 1030, 1020, 1010, 1000
Explanation: Anticyclones are formed in high-pressure areas where air moves outward from the center in a circular manner.
Q.4. State one reason why.
(1) A belt of calm exists near the equator.
Answer: The equator has a low-pressure belt known as the Doldrums, where warm air rises, and there is minimal horizontal movement of air, resulting in calm conditions.
(2) The winds coming from the north-west in the southern hemisphere have greater velocities than the winds coming from the south-west in the northern hemisphere.
Answer: In the southern hemisphere, there is a larger expanse of ocean and fewer land barriers, so winds can blow at greater speeds without obstruction.
(3) The monsoon winds in the summer come from the sea but the retreating monsoon winds in winter come from land.
Answer: During summer, land heats up faster than water, creating a low-pressure zone over land, causing moist winds to blow from the sea. In winter, the land cools faster, creating a high-pressure zone, causing dry winds to blow from the land towards the sea.
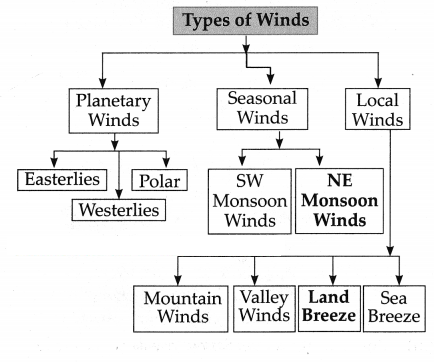
Q.5. Complete the flow chart:
Answer:
Q.6. Answer in short:
(1) Why is the air pressure high in polar areas in both the hemispheres?
Answer: Cold temperatures at the poles cause air to contract and become dense, increasing the air pressure. This creates polar high-pressure belts in both hemispheres.
(2) What effect does the rotation of the earth have on the winds?
Answer: The rotation of the Earth causes the Coriolis Effect, which deflects winds to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere.
(3) Why do the cyclonic winds blow in a circular manner?
Answer: Due to the Coriolis Effect, winds moving towards the low-pressure center of a cyclone are deflected, making them spiral in a counterclockwise direction in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere.
(4) State the reasons that lead to the formation of cyclones and describe the effects of cyclones.
Answer:
Reasons for Formation:
- Cyclones form due to low-pressure areas surrounded by high-pressure regions.
- High temperatures over oceans lead to evaporation and moisture accumulation.
- The Coriolis Effect makes the winds rotate in a circular manner.
Effects of Cyclones:
- Heavy rainfall and flooding
- Strong winds causing destruction
- Storm surges leading to coastal damage
- Disruption of communication and transport

Leave a Reply