Questions Answers For All Chapters – Geography Class 7
Human Settlements
Q.1. Answer in short.
(1) Explain the various types of human settlements.
Answer: Human settlements are classified into rural and urban settlements. Rural settlements include villages and hamlets, while urban settlements include towns and cities. They can also be classified as nucleated (clustered) or scattered (dispersed) settlements based on their layout.
(2) Differentiate between nucleated and scattered settlements.
Answer:
- Nucleated settlements are those where houses are closely packed together, often around a central point like a market or water source. These settlements have strong social interactions.
- Scattered settlements have houses spread apart, often found in hilly, forested, or agricultural areas. These settlements provide more privacy and open spaces.
(3) Explain the natural factors affecting the location of human settlements.
Answer: The location of human settlements is influenced by water availability, land fertility, climate, relief (terrain), and natural resources. People prefer to settle near rivers, fertile plains, and areas with moderate climate and resources for survival and development.
(4) Explain how human settlements have evovled.
Answer: Early human settlements began near water sources and fertile lands for agriculture. Over time, settlements expanded into villages and towns due to trade, industrialization, and transportation. Today, urbanization and technology have led to modern cities with advanced infrastructure.
(5) Differentiate between a hamlet and a village.
Answer:
- A hamlet is a small group of houses with a very low population and limited facilities. It is smaller than a village.
- A village is a larger rural settlement with basic facilities like schools, markets, and healthcare, and it often has a governing body.
Q. 2. Identify the types of human settlements from the follwing statements.
(1) Their money and time is saved by living on the farm.
Answer: Scattered settlement (since houses are located near farms, saving time and money).
(2) There is a lot of social life in this settlement.
Answer: Nucleated settlement (houses are close to each other, leading to more social interaction).
(3) Shops are located on both the sides of the road.
Answer: settlement (developed along roads, railways, or rivers).
(4) This settlement is found at the foothills of mountains or along the coast.
Answer: Dispersed settlement (houses are spread out due to terrain and natural conditions).
(5) Each house is located away from the other.
Answer: Scattered settlement (houses are far apart, often in hilly or forested areas).
(6) This settlement is good from a security point of view.
Answer: Nucleated settlement (people live close together, making it safer from attacks).
(7) Having houses away from each other is good for health.
Answer: Scattered settlement (provides fresh air, less pollution, and open space).
(8) The houses are too close to each other.
Answer: Nucleated settlement (houses are built close together, common in villages and towns).
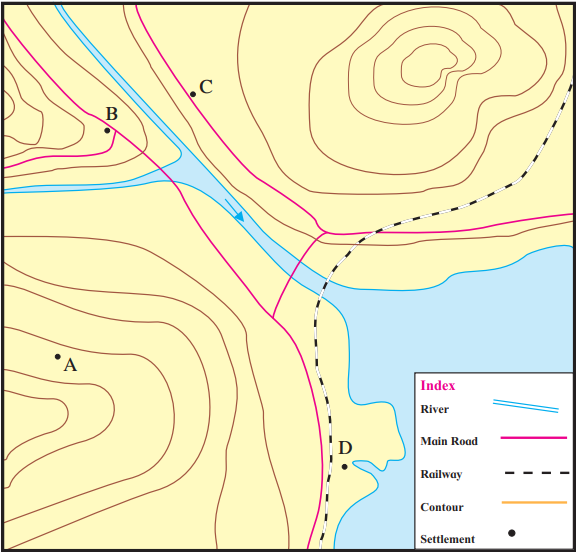
Q.3. Study the diagram and identify the types of settlements.
Question 1. Settlement ‘A’ has 5-6 houses and the place does not have other facilities.
Answer: Scattered settlement.
Question 2. ‘B’ has a high school, a big market and a small theatre.
Answer: Nucleated settlement.
Question 3. ‘C’ has houses, farmers, many shops and small industries.
Answer: Linear settlement.
Question 4. ‘D’ has a natural harbour. Many industries have been established here.
Answer: Linear settlement.
Question 5. ‘C’ is a settlement that has developed along the road side. Give two reasons of its location here.
Answer: The reasons for settlement ‘C’ developing along the roadside are:
- It has direct & easy access to the main road which helps in easy movement of people & agricultural & industrial goods as houses, farms & small industries are found here.
- It is located at the foothill close to the main river.

Leave a Reply