Question Answers For All Chapters – Political Science Class 12
Contemporary India: Good Governance
Exercise
Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative and complete the statements.
Answer: 1. The concept of Lokpal has been taken from Sweden.
2. Right to Information is one of the important aspects of Good Governance.
(B) State the appropriate concept for the given concept.
Person investigating complaints against government officials –
Answer: Ombudsman (or Lokpal/Lokayukta in the Indian context)
Explanation: An Ombudsman, such as the Lokpal at the national level or Lokayukta at the state level, is responsible for investigating complaints against government officials.
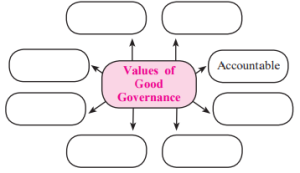
Q.2 (A) Compete the concept map.
Answer : Values of Good Governance
Participatory
Transparent
Responsive
Accountable
Follows Rule of Law
Consensus Oriented
Equitable and Inclusive
Effective and Efficient
(B) State whether the following statements are true or false with reason.
(1) Lokayukta can investigate complaints against political executives.
Answer : True – Lokayukta has the authority to investigate complaints against public servants, including political executives.
(2) Good Governance aims at efficient use of natural resources.
Answer : True – One of the values of Good Governance is “effectiveness and efficiency”, which includes sustainable use of resources.
Q.3 Explain co-relation between the following.
Good Governance and E-Governance.
Answer : Good governance and e-governance are closely related as e-governance serves as a tool to achieve the objectives of good governance. Good governance emphasizes values like transparency, accountability, responsiveness, and citizen participation in administration. E-governance, through the use of Information and Communications Technology (ICT), enhances these values by speeding up governmental processes, improving access to services, and increasing transparency. For instance, e-governance initiatives like online applications for certificates or the National e-Governance Plan make administration more efficient and citizen-centric, aligning with good governance goals. It reduces delays, minimizes corruption, and ensures that citizens can interact with the government more effectively, thus strengthening the principles of good governance.
Q.4 Express your opinion.
(a) E-governance speeds up governmental processes.
Answer : Yes, E-Governance allows for quick communication, easy storage and retrieval of data, and faster decision-making. This makes administrative work more efficient.
(b) E-governance brought administration closer to people.
Answer : Yes, with services like online applications for documents (PAN, Aadhaar, Birth Certificates), citizens can access government services easily from home, making administration more accessible.
Q.5 Answer the following in 80 to 100 words.
Explain various institutions protecting rights of different sections in India.
Answer : In India, several institutions safeguard the rights of different sections of society. The National Commission for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes protect the constitutional rights of SCs and STs, addressing deprivation complaints. The National Human Rights Commission ensures protection of life, liberty, and dignity for all. The National Commission for Women promotes women’s socio-economic development, while the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights defends child rights (0-18 years). The National Commission for Minorities safeguards minority communities (e.g., Muslims, Sikhs), and the National Commission for Backward Classes focuses on the welfare of backward classes. These bodies ensure inclusivity and justice.
Q.6 Answer the following question in detail with help of given points.
Explain in detail the following values of Good Governance.
(a) Participation:
Participation is a cornerstone of good governance, ensuring that citizens actively engage in decision-making and implementation processes. It strengthens democracy by giving people a voice in policies affecting them. The document emphasizes that effective governance requires people’s involvement, as seen in initiatives like citizen participation programs, which transform traditional representative democracy into a participative one. This “bottom-up” approach empowers citizens to influence development.
(b) Transparency:
Transparency means openness in government functioning, allowing public scrutiny. The document notes that the Right to Information Act, 2005, challenges the culture of secrecy by enabling citizens to access information about policies and actions. This fosters trust, reduces corruption, and ensures that administrative decisions are predictable and objective, aligning with good governance principles.
(c) Responsiveness:
Responsiveness requires institutions to address stakeholders’ needs promptly. According to the document, good governance demands that the government listens to citizens’ problems and designs timely policies. For example, quick grievance redressal and efficient service delivery (e.g., through e-governance) reflect responsiveness, ensuring administration meets public expectations effectively.
(d) Accountability:
Accountability ensures that government, private sector, and civil society organizations are answerable to the public. The document explains that it depends on transparency and the rule of law. For instance, the Lokpal and Citizens’ Charters hold officials accountable by setting service standards and investigating corruption. This ensures decisions benefit citizens and promotes trust in governance.

Leave a Reply