Question Answers For All Chapters – Political Science Class 12
Contemporary India: Challenges to Peace, Stability and National Integration
Exercise
Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative and complete the following statements.
Answer : (1) Rajiv Gandhi was assassinated for having taken decision of the Tamil question in Sri Lanka.
(2) The first national integration conference was held in 1961.
(B) Identify incorrect pair in every set, correct it and rewrite.
Answer : 1. Incorrect Pair: (iii) Basque Fatherland and Liberty (CTA) – Portugal
Correct Pair: (iii) Basque Fatherland and Liberty (ETA) – Spain
2. Incorrect Pair: (i) Boko Haram – Bangladesh
Correct Pair: (i) Boko Haram – Nigeria
(C) Complete the following statements by using appropriate reason.
(1) The left wing extemists prevent execution and implementation of developmental work, because –
Answer : (iii) they want to show that the government structure at field level is ineffective.
(2) In 1990’s Kashmiri Pandits migrated from Kashmir valley, because –
Answer : (ii) there was growth in Islamic militancy.
Q.2 (A) Find the odd word in the given set.
Terrorism, Naxalism, Nationalism, Extremism
Answer : Nationalism (Because the others involve violent or extremist ideologies.)
(B) State the appropriate concept for the given statement.
Answer : (1) Threat use violence with an intention to create panic in the society – Terrorism
(2) Involvement of people in decision making process of state – Governance
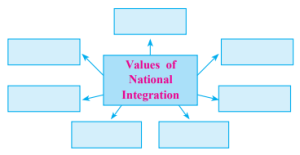
Q.3 (A) Complete the concept map.
Answer : Common Citizenship
Unity in Diversity
Loyalty to the Nation
Sense of Fraternity
Secularism
Socio-Economic and Political Justice
Equality
(B) State whether the following statements are true or false with reason.
(1) Democracy is required to establish national integration and social transformation.
Answer : True – Democracy ensures participation of all communities, promoting unity and reducing inequality.
(2) National movement in India played an important role in national integration.
Answer : True – The freedom struggle helped unite people with diverse backgrounds under the identity of being Indian.
Q.4 Explain the co-relation between the following.
National Unity and Regional Aspirations
Answer : National unity aims to bring diverse communities under a common identity, while regional aspirations reflect the desire for recognition and development of specific cultural, linguistic, or ethnic groups. A strong democracy accommodates these aspirations through federalism, ensuring that unity does not mean uniformity but mutual respect and cooperation.
Q.5 Express your opinion.
Peace and stability are needed for the nation’s progress.
Answer : Peace and stability are essential for any nation’s development. Without them, there can be no sustained economic growth, political governance, or social justice. Public disorder hampers productivity and weakens institutions, making it harder to address issues like poverty, inequality, and education. Stability builds trust and encourages investment and innovation.
Q.6 Answer the following in 80 to 100 words.
(1) What is left wing extremism in India?
Answer : Left Wing Extremism (LWE), also known as Naxalism or Maoism, is an armed insurgency aimed at overthrowing the government. Originating in 1967 at Naxalbari, West Bengal, it draws support from landless laborers, Dalits, and tribals who feel neglected by the state. Inspired by Marxist-Leninist-Maoist ideology, it gained momentum with the formation of the CPI (Maoist) in 2004. Operating in rural, underdeveloped areas, LWE disrupts development projects to weaken governance, using violence, propaganda, and mobilization of marginalized groups, posing a significant challenge to India’s stability.
(2) Explain cross border terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir.
Answer : Cross-border terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir refers to violence sponsored by Pakistan to destabilize the region. It began in 1947 with tribal raiders, escalating in the 1980s-90s with groups like JKLF and Hizb-ul-Mujahideen, backed by Pakistan’s ISI. The insurgency turned Islamic, causing the Kashmiri Pandit migration. Tactics include infiltration, attacks on security forces, stone-throwing, and school burnings. Key events include the 2016 Uri attack and 2019 Pulwama bombing by Pakistan-based Jaish-e-Mohammed. India views this as a core issue in Indo-Pak relations, impacting regional peace.
Q.7 Answer the following in 150 to 200 words.
Explain the role of the State with help of given points.
Answer : (a) Peace and Order: The primary role of the State is to maintain peace, law, and order within its territory. A peaceful society provides the foundation for all other aspects of development – political, economic, and social. Without peace, governance becomes ineffective, and citizens suffer from insecurity and fear.
Maintaining public order involves preventing riots, communal violence, terrorism, and insurgency. The State achieves this by enforcing laws, using police and security forces, and promoting justice. A secure environment encourages investment, boosts productivity, and helps ensure social harmony.
Peace is not only about the absence of conflict, but also about resolving disputes through dialogue, negotiations, and constitutional means. When citizens believe in the justice system and the rule of law, they are less likely to resort to violence.
The Indian Constitution empowers the State to protect its people and uphold democratic values. During times of crisis—like terrorism in Jammu & Kashmir or Left-Wing Extremism—the State uses both preventive and corrective measures to restore peace.
Thus, peace and order are crucial responsibilities of the State, and their successful maintenance ensures national integration, unity, and progress.
(b) Economic Development: Economic development is one of the most vital responsibilities of the State. It ensures the overall progress and prosperity of the nation by improving living standards, generating employment, and reducing poverty and inequality. The State plays the role of a facilitator and regulator in the economy, providing infrastructure, formulating policies, and supporting industries, agriculture, and services.
After independence, India adopted a mixed economy, where both the public and private sectors contribute to growth. The Planning Commission (now replaced by NITI Aayog) was established to guide economic planning through Five-Year Plans. The government invested heavily in industries, transport, energy, and education to lay the foundation for self-reliance.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation (LPG), allowing more private and foreign investment. The State still plays a key role by launching schemes like Skill India, Make in India, and Digital India to boost employment and innovation.
Additionally, the State aims to reduce regional imbalances by promoting development in backward areas and encouraging public-private partnerships. Inclusive economic development not only strengthens the economy but also contributes to social stability and national integration.
(c) National Building: Nation building refers to the process of uniting diverse groups of people into a single national identity. In a country like India, with its vast diversity in language, religion, ethnicity, and culture, the role of the State in nation building becomes extremely important.
The State ensures that diversity does not lead to division. It does this by promoting values such as unity in diversity, secularism, democracy, and social justice. Nation building is closely linked to national integration, which means creating a sense of belonging and loyalty among all citizens, regardless of their background.
The Indian Constitution plays a vital role in nation building by guaranteeing fundamental rights, equality, and justice to all. Through the democratic process, the State involves people in governance, enabling every group to express its identity within a shared national framework.
Policies like language recognition, state reorganization, reservation for marginalized communities, and the establishment of institutions like the National Integration Council have helped India preserve unity.
In essence, the State fosters a national identity that respects regional and cultural diversity while promoting a shared sense of belonging. This is the true spirit of nation building.
(d) Governance: Governance refers to the process of decision-making and the way those decisions are implemented in a democratic system. Good governance ensures transparency, accountability, responsiveness, and participation of citizens in the functioning of the State.
In India, democratic governance allows people to elect their representatives and be part of policymaking. The State is responsible for creating structures and institutions that empower citizens and encourage their involvement. This includes decentralisation of power through Panchayati Raj Institutions, urban local bodies, and participatory planning processes.
Good governance means more than just functioning government—it includes the delivery of public services, protection of rights, and ensuring social and economic justice. Initiatives like Digital India, RTI (Right to Information), e-governance, and citizen charters have been launched to bring the government closer to the people.
Governance is crucial for addressing the needs of different sections of society, especially the marginalised. When people feel heard and respected, it strengthens their trust in the system and promotes national unity.
Therefore, governance is not only about administration but about involving citizens in building a better and more inclusive nation.
(e) Welfare: Welfare refers to the well-being of the citizens, and the State plays a crucial role in ensuring the social and economic welfare of its people. The State’s role in welfare is grounded in the principles of social justice, equality, and fairness, ensuring that every citizen, particularly the marginalized and vulnerable groups, has access to essential services like education, healthcare, housing, and employment.
In India, welfare is enshrined in the Constitution, which provides for fundamental rights and directive principles to promote the welfare of the people. Various social welfare schemes are implemented by the State to reduce poverty, inequality, and unemployment. Programs like National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA), Mid-Day Meal Scheme, Public Distribution System (PDS), and Right to Education (RTE) aim to improve the quality of life for citizens, especially those in rural and economically backward areas.
The welfare State also ensures that the resources of the nation are distributed equitably, and no group is left behind. This fosters social harmony and promotes national integration by reducing disparities.
Thus, the welfare function of the State is critical for ensuring a just society where every individual has the opportunity to lead a dignified life.

Leave a Reply