Social Change
1. (A) Choose the correct alternative and complete the statements.
(1) Social change as a term is ___. (value loaded, ethically neutral, prejudiced)
Answer: ethically neutral.
(2) The effects of an earthquake on people is a ___ factor of change. (geographical, biological, cultural)
Answer: geographical
(3) The study of sex ratio is a ___ factor of change. (biological, technological, natural)
Answer: biological
(4) The Slum Rehabilitation programme within a city is an example of ___ social change. (planned, unplanned, revolutionary)
Answer: planned
1. (B) Correct the incorrect pair.
(1) (i) Earthquake – Physical
(ii) Fundamentalism – Biological
(iii) Growing urbanization – Economic
(iv) E-governance – Technological
Answer: (ii) Fundamentalism – Socio-cultural
1. (C) Identify the appropriate term from the given options.
Physical factor, Educational factor, Economic factor
1. Impact of rising sea water level on coastal regions: Physical factor
2. Creating awareness about the problem of sexual abuse: Educational factor
1. (D) Correct underlined words and complete the sentence.
1. Social change is not always a linear process.
Answer: Social change can be linear, multilinear, or cyclical process.
2. All teachers are expected to think about how they will teach a unit in the classroom. This is an example of unplanned change.
Answer: All teachers are expected to think about how they will teach a unit in the classroom. This is an example of planned change.
2. Write differences.
(1) Planned change and Unplanned Change.
| Aspect | Planned Change | Unplanned Change |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate and intentional changes promoted by governments or agencies. | Changes that occur suddenly without deliberate intent. |
| Nature | Purposeful, with specific goals and structured implementation. | Spontaneous, often triggered by unexpected events. |
| Example | Development of planned cities with designated areas for residences, parks, etc. | Natural calamities like earthquakes or floods causing societal disruptions. |
| Control | Controlled and directed by human intervention or policy. | Uncontrolled, often a reaction to external forces like natural disasters. |
| Outcome Predictability | Outcomes are generally anticipated and designed. | Outcomes are uncertain and may lead to unforeseen consequences. |
(2) Short-term and Long-term change
| Aspect | Short-term Change | Long-term Change |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changes that produce immediate or quick results. | Changes that take years or decades to show significant results. |
| Time Frame | Occurs over a short period, often noticeable instantly or within months. | Occurs over an extended period, sometimes spanning generations. |
| Example | Purchasing new gadgets like a home theatre for entertainment. | Eradicating social evils like dowry or early marriage. |
| Impact Depth | Often superficial or limited to specific areas of life. | Deep-rooted, affecting societal structures and cultural norms. |
| Effort Required | Requires less sustained effort, often driven by immediate resources or decisions. | Requires continuous effort and systemic changes to achieve lasting impa |
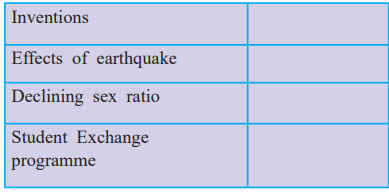
4. (A) Complete the concept map.
Identify the significant factor of change for each:
| Item | Significant Factor of Change |
|---|---|
| Inventions | Technological factor |
| Effects of earthquake | Physical factor |
| Declining sex ratio | Biological factor |
| Student Exchange programme | Educational factor |
4. (B) State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons.
1. Prejudice and fear of the unknown is an obstacle to change.
Answer: True
- Reason: The document mentions negative consequences of ideologies like superstitious beliefs and blind faith, which can hinder social progress. Prejudice and fear resist new ideas, making change difficult.
2. Social change can be predicted accurately.
Answer: False
- Reason: Social change is complex and influenced by multiple interdependent factors (physical, biological, socio-cultural, etc.). While trends can be observed, the document does not suggest that social change can be predicted with precision due to its dynamic nature.
5. Give your personal response.
1. Do you think people accept social change easily? Why?
Answer: People do not always accept social change easily. Resistance often stems from fear of the unknown, attachment to traditions, or perceived threats to identity, as highlighted by socio-cultural factors in the document. For example, changes like the adoption of e-governance may face pushback from those unfamiliar with technology. However, younger generations or those exposed to education may embrace change faster due to awareness and adaptability.
2. Do you think the ‘Swachh Bharat Abhiyan’ has had a positive impact on society? Justify your response.
Answer: Yes, the ‘Swachh Bharat Abhiyan’ has had a positive impact on society. As a planned change initiative, it aligns with the document’s description of government-driven efforts to improve societal conditions. It has raised awareness about cleanliness, improved sanitation infrastructure, and encouraged community participation. For instance, the construction of toilets in rural areas has enhanced public health and dignity, especially for women. However, challenges like sustaining behavioral change remain, indicating it is a long-term process.

Leave a Reply