Unemployment in India
EXERCISE
Q. 1. Find the odd word out:
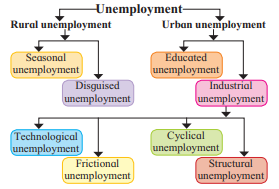
1. Urban unemployment – Educated unemployment, Industrial unemployment, Disguised unemployment, Technological unemployment
Answer: Disguised unemployment
Reason: Educated unemployment, Industrial unemployment, and Technological unemployment are types of urban unemployment, whereas Disguised unemployment is a type of rural unemployment.
2. States with high rates of unemployment – Goa, Punjab, Maharashtra, Tripura
Answer: Goa
Reason: Punjab, Maharashtra, and Tripura have relatively higher unemployment rates, while Goa typically has a lower unemployment rate due to its tourism-driven economy.
3. Employment Guarantee Scheme 1972, Jawahar Rozgar Yojana 1989, Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana 1999, Development of Tourism
Answer: Development of Tourism
Reason: The first three are specific government schemes aimed at reducing unemployment, while Development of Tourism is a general measure, not a specific scheme.
Q. 2. Identify and explain the concepts from the given illustrations:
1. Hussain Shaikh employed seven workers less than the usual number of workers on his farm, in spite of this, output remained the same.
Concept: Disguised Unemployment
Explanation: This refers to a situation where more workers are employed than required, and removing some workers does not affect output. In this case, the farm’s output remained the same despite employing fewer workers, indicating surplus labor.
2. Use of new technology in the printing industry has led to unemployment among several workers.
Concept: Technological Unemployment
Explanation: This occurs when workers lose jobs due to the introduction of new technology that reduces the need for labor. Here, new printing technology displaced workers.
3. Satish has completed his post-graduation and is desperately expecting a job.
Concept: Educated Unemployment
Explanation: This refers to educated individuals (like graduates or post-graduates) who are willing to work but cannot find jobs. Satish, being a post-graduate, is facing this issue.
4. In certain agricultural areas of Maharashtra, only kharif crops are grown, therefore employment is available till the month of October.
Concept: Seasonal Unemployment
Explanation: This occurs when workers are employed only during specific seasons (e.g., kharif crop season) and remain unemployed for the rest of the year. In this case, employment is limited to the kharif season, ending in October.
Q. 3. Complete the correlation:
1. Seasonal unemployment: Tourist guides; ____: Graduates
Answer: Educated unemployment
Explanation: Seasonal unemployment affects tourist guides who work only during tourist seasons, while educated unemployment affects graduates who cannot find jobs despite their qualifications.
2. ____: Disguised unemployment; Urban unemployment: Industrial unemployment
Answer: Rural unemployment
Explanation: Disguised unemployment is a type of rural unemployment, while industrial unemployment is a type of urban unemployment.
3. Frictional unemployment: Shortage of raw materials; ____: Fluctuations in business activity
Answer: Cyclical unemployment
Explanation: Frictional unemployment is caused by temporary issues like shortage of raw materials, while cyclical unemployment results from fluctuations in business activity, such as during economic depression.
4. MGNREGS: guaranteed wage employment; TRYSEM: ____
Answer: Training for self-employment
Explanation: MGNREGS provides guaranteed wage employment, while TRYSEM (Training Rural Youth for Self-Employment) focuses on training rural youth for self-employment.
5. ____: Waste of resources; Social effect: Loss of human dignity
Answer: Economic effect
Explanation: Waste of resources is an economic effect of unemployment, while loss of human dignity is a social effect.
Q. 4. Observe the following chart and answer the following questions.
1. Production does not increase if an additional worker is employed and production does not decrease if a worker is reduced from the work. Mention the type of unemployment.
Answer: Disguised unemployment
2. A worker is thrown out of a job because of computerization. Name this type of unemployment?
Answer: Technological unemployment
3. Sharad was forced to return back to India from the USA due to depression in the IT sector.
Answer: Cyclical unemployment
4. In spite of being a graduate, Vasant is sitting idle at home.
Answer: Educated unemployment
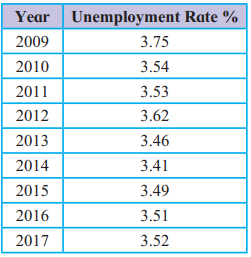
Q. 5. Find out Q1 and Q3 using unemployment rates as numerical data :
Answer:
| Year | Unemployment Rate (%) | Cumulative Frequency (cf) |
|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 3.75 | 3.75 |
| 2010 | 3.54 | 7.29 |
| 2011 | 3.53 | 10.82 |
| 2012 | 3.62 | 14.44 |
| 2013 | 3.46 | 17.9 |
| 2014 | 3.41 | 21.31 |
| 2015 | 3.49 | 24.8 |
| 2016 | 3.51 | 28.31 |
| 2017 | 3.52 | 31.83 |
| Total (N) | 31.83 | |
Q. 6. Answer the following in detail:
1. Explain the types of Industrial unemployment in India.
Answer: Industrial unemployment refers to unemployment in the industrial sector, affecting both skilled and unskilled workers.
The types of industrial unemployment in India are:
i) Technological Unemployment: This occurs when workers lose jobs due to the introduction of new technology. For example, computerization or robotic technology reduces the need for manual labor, displacing workers who lack training in new methods.
ii) Frictional Unemployment: This is temporary unemployment caused by factors like machinery breakdowns, power failures, raw material shortages, or workers’ strikes. It disrupts production briefly, leading to short-term joblessness.
iii) Cyclical Unemployment: This results from fluctuations in business activity, particularly during economic depression. A fall in demand reduces production, leading to lower profits and investment, which causes layoffs. For example, workers lose jobs during economic downturns.
iv) Structural Unemployment: This arises due to long-term changes in the economy, such as shifts in government policies, capital shortages, or relocation of industries. It occurs when workers’ skills do not match available jobs, e.g., manual typists becoming unemployed due to computerized typing.
2. Explain the causes of unemployment in India.
Answer: The major causes of unemployment in India are:
i) Jobless Growth: Economic growth in India has not created enough jobs to absorb the growing labor force. The rate of employment growth lags behind economic growth, leading to unemployment.
ii) Increase in Labour Force: Rapid population growth, due to a declining death rate without a corresponding fall in birth rate, has expanded the labor force, outpacing job creation.
iii) Excessive Use of Machinery: Despite abundant manpower, industries and agriculture increasingly use capital-intensive techniques (e.g., automated machines), reducing job opportunities for labor.
iv) Lack of Skill Development Programmes: There is a shortage of vocational training programs tailored to industry needs, resulting in a lack of skilled workers.
v) Expectations Towards Employment: Educated youth prefer white-collar jobs and lack entrepreneurial spirit, choosing to remain unemployed rather than take up self-employment or less-preferred jobs.
vi) Seasonal Nature of Agriculture: Agriculture depends on monsoons, and factors like poor irrigation, outdated techniques, and lack of quality seeds limit year-round employment, leaving workers jobless for months.
vii) Slow Rate of Economic Development: Slow industrial and infrastructural growth limits job creation, especially in rural areas, failing to absorb the growing labor force.
viii) Migration of Rural Population: Rural-to-urban migration in search of jobs increases urban unemployment, as cities cannot accommodate the influx of workers.
3. Explain the measures taken by the government to reduce unemployment.
Answer: The government has implemented both general and specific measures to reduce unemployment:
General Measures:
i) Development of the agricultural sector to create year-round employment.
ii) Promoting alternative occupations like animal husbandry or cottage industries.
iii) Improving infrastructure to generate jobs in construction and related sectors.
iv) Reforming education to align with industry needs.
v) Developing tourism to create seasonal and permanent jobs.
vi) Using labor-intensive techniques to employ more workers.
vii) Expanding IT and communication sectors for job creation.
viii) Providing vocational training and skill development programs.
ix) Promoting rural industrialization to reduce migration.
x) Encouraging self-employment through motivation and support.
Specific Measures (Government Schemes):
i) Employment Guarantee Scheme (EGS) (1972): Provides productive employment to rural populations, first introduced in Maharashtra and later adopted elsewhere.
ii) Swarnjayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY) (1999): Promotes self-employment for rural poor through skill training and financial support.
iii) Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rozgar Yojana (SJSRY) (1997): Offers employment to urban unemployed/underemployed through self-employment and skill training programs.
iv) Pradhan Mantri Rozgar Yojana (PMRY) (1993): Creates self-employment opportunities for educated unemployed youth.
v) Training Rural Youth for Self-employment (TRYSEM) (1979): Trains rural youth for self-employment, now merged with SGSY.
vi) Jawahar Rozgar Yojana (JRY) (1989): Generates wage employment in rural areas, later renamed Jawahar Gram Samrudhi Yojana (JGSY).
vii) Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) (2009): Guarantees 100 days of wage employment per year to rural households for unskilled manual work.
viii) Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (2014): Provides skill training and placement for rural youth aged 15-35.
ix) National Policy for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (2015): Promotes entrepreneurship and skill development through private sector participation.
x) Start-up India Initiative (2016): Encourages young entrepreneurs to start businesses.
xi) Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (2016-20): Offers monetary rewards for completing skill training programs to encourage youth skill development.



Leave a Reply