Population in India
EXERCISE
Q. 1. Choose the correct option :
1) Stages of the theory of demographic transition.
a) High birth rate and high death rate
b) High birth rate and low death rate
c) Low birth rate and low death rate
d) Economic developme
Options:
1. a and b
2. a and c
3. a, b, and c
4. a, b, c, and d
Answer: 3) a, b, and c
Explanation: The theory of demographic transition includes three stages:
a) High birth rate and high death rate (First stage)
b) High birth rate and low death rate (Second stage)
c) Low birth rate and low death rate (Third stage). Economic development (d) is not a stage but a factor influencing the transition.
2. Incorrect reasons for the population explosion in India.
a) Illiteracy
b) Universalization of Marriage
c) Joint family system
d) Upliftment in lifestyle
Options:
1. a and b
2. c and d
3. a, b, and c
4. d
Answer: 4) d
Explanation: Illiteracy (a), universalization of marriage (b), and joint family system (c) are listed as causes of high birth rate leading to population explosion. Upliftment in lifestyle (d) is not mentioned as a reason for population explosion in the document.
3. Remedies are undertaken to check population explosion.
a) To provide employment
b) To improve women’s quality of life
c) National Population Policy
d) Disaster management
Options:
1. d
2. a and c
3. c and d
4. a, b, and c
Answer: 4) a, b, and c
Explanation: Remedies to check population explosion include economic measures like providing employment (a), social measures like improving women’s quality of life (b), and the National Population Policy (c). Disaster management (d) is related to reducing death rates, not directly to controlling population explosion.
4) Choose the correct option.
| Group A | Group B |
|---|---|
| Year of Great Divide | Stable population till 2045 |
| A. J. Coale and E. M. Hoover | 1921 |
| Social Reforms | Demographic Transition |
| National population policy, 2000 | Spread of education |
Options:
1-d, 2-c, 3-a, 4-b
1-b, 2-c, 3-d, 4-a
1-b, 2-a, 3-c, 4-d
1-c, 2-d, 3-a, 4-b
Answer: 2) 1-b, 2-c, 3-d, 4-a
Explanation:
Year of Great Divide (1) refers to 1921 (b), when population growth turned positive after a decline.
A. J. Coale and E. M. Hoover (2) proposed the Demographic Transition theory (c).
Social Reforms (3) involve measures like spread of education (d).
National Population Policy, 2000 (4) aims for a stable population by 2045 (a).
Q. 2. Give economic terms:
1. Increase in population is faster than economic growth and development.
Answer: Population Explosion
2. Difference between birth rate and death rate.
Answer: Survival Rate
3. Balance between natural resources and population growth.
Answer: Optimum Population
4. Programme introduced to reduce the birth rate in 1952.
Answer: Family Planning Programme
Q. 3. Identify and explain the concepts from the given illustrations:
1. There were 40 births per 1000 in country ‘A’ during a year.
Concept: Birth Rate
Explanation: Birth rate refers to the number of births per 1000 people in a population during a year. In this case, 40 births per 1000 indicates the birth rate of country ‘A’.
2. In Mumbai city, public transport service is largely affected due to the growing population.
Concept: Population Explosion
Explanation: Population explosion occurs when population growth exceeds the capacity of infrastructure and resources, leading to issues like overburdened public transport in Mumbai.
3. In country ‘B’, there are 15 deaths taking place per 1000 during a year.
Concept: Death Rate
Explanation: Death rate is the number of deaths per 1000 people in a population during a year. Here, 15 deaths per 1000 represents the death rate in country ‘B’.
4. For a certain period of time China had adopted the policy of ‘One child per family’.
Concept: Family Planning
Explanation: Family planning involves measures to control birth rates, such as China’s ‘One Child Policy’, which aimed to limit population growth by restricting families to one child.
Q. 4. Answer the following:
1. Explain the causes of high birth rate.
Answer: The causes of high birth rate in India include:
- Illiteracy: Illiterate people have rigid attitudes toward marriage and childbirth, contributing to high birth rates. Low female literacy worsens this issue.
- Universalization of Marriage: Marriage is a social and religious obligation, and attitudes toward it remain unchanged despite education.
- Low Age of Marriage: Legal marriage ages (18 for females, 21 for males) are lower than in many countries, leading to early pregnancies.
- Preference for Male Child: Many parents continue having children until they have a son, increasing birth rates.
- Joint Family System: Lack of individual financial responsibility in joint families encourages larger families.
- Dependence on Agriculture: More children mean more labor for agricultural work, incentivizing higher birth rates.
- Widespread Poverty: Poor families see more children as economic support.
- Lack of Awareness about Family Welfare Services: Ignorance about family planning methods contributes to high birth rates.
2. Explain the causes of low death rate.
Answer: The causes of low death rate in India include:
- Improvement in Medical and Health Facilities: Epidemics like plague, cholera, and malaria have been largely eradicated due to better healthcare.
- Decline in Maternal Mortality Rate: Improved medical facilities have reduced deaths during childbirth.
- Fall in Infant Mortality Rate: Better healthcare and female literacy have lowered infant mortality from 146 per 1000 in 1951 to 47 per 1000 in 2011.
- Increase in Literacy: Education promotes better health practices and reduces ignorance.
- Use of Nutritious Food: Awareness of health and nutrition, along with programs like mid-day meals, has reduced deaths due to malnutrition.
- Disaster Management: The National Disaster Management Authority (2005) mitigates disasters, reducing loss of life.
- Other Factors: Education, social reforms, urbanization, and awareness campaigns improve living standards and reduce death rates.
3. Explain the role of Human Resource in Economic Development.
Answer: Human resources play a crucial role in economic development as follows:
- Human Development as an End: Human development improves living conditions, which is the ultimate goal, while economic growth is a means to achieve it.
- Reduces Civil Disturbances: Human development promotes political stability by improving living conditions.
- Widens Choices: It covers economic, social, cultural, and political aspects, enriching human lives.
- Education and Population Control: Increased literacy, especially among women, reduces birth and infant mortality rates, aiding population control.
- Improves Quality of Life: Human resource development enhances life expectancy and literacy, improving overall well-being.
- Promotes Research and Development: Educated human resources drive innovation and research.
- Increases Productivity: Investments in health, education, and nutrition boost human productivity.
- Universal Application: Human development benefits both developing and developed countries, fostering inclusive growth.
Q. 5. State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements:
1. India is experiencing population explosion.
Answer: Agree
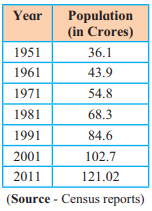
Reason: India’s population grew rapidly from 36.1 crores in 1951 to 121.02 crores in 2011, with high birth rates and declining death rates, especially between 1971–2001, when the annual growth rate exceeded 2%. This indicates a population explosion, as growth outpaces economic development.
2. Death rate is falling rapidly in India.
Answer: Agree
Reason: The death rate in India has declined significantly, from 42.6 per 1000 in 1901 to 7.48 per 1000 in 2011, due to improved medical facilities, reduced maternal and infant mortality, better nutrition, and disaster management.
3. Optimum population contributes to economic development of a country.
Answer: Agree
Reason: Optimum population maintains a balance between population growth and natural resources, ensuring sustainable economic development without overburdening infrastructure or resources.
4. Human resources play an important role in economic development.
Answer: Agree
Reason: Human resources drive economic growth through education, innovation, and productivity. Investments in health and education improve quality of life, reduce population growth, and foster research, contributing to overall development.
5. Birth rate is declining due to changes in the standard of living.
Answer: Agree
Reason: Improvements in education, urbanization, and awareness about family planning, along with better living standards, have led to a decline in birth rates, from 49.2 per 1000 in 1901 to 20.97 per 1000 in 2011.
Q. 6. Solve the following :
1. To find Q₃ from the given data.
Step-by-step Calculation:
Q₃ (Third Quartile) represents the 75th percentile.
Arrange data in ascending order: 36.1, 43.9, 54.8, 68.3, 84.6, 102.7, 121.02
Number of data points (n) = 7
Q₃ position = (3/4) * (n + 1) = (3/4) * (7 + 1) = (3/4) * 8 = 6
Q₃ is the 6th value in the ordered data: 102.7
Answer: Q₃ = 102.7 crores
2) Draw a population growth curve from the given data.
Answer:


Leave a Reply