Question 1.
(a) Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the statement.
(1) The earliest museum in the world was discovered in the excavations at the city of ……………..………. .
(a) Delhi
(b) Harappa
(c) Ur
(d) Kolkata
Answer:
(c) Ur
(2) The National Archives of India is in ……………..………. .
(a) New Delhi
(b) Kolkata
(c) Mumbai
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(a) New Delhi
(b) Identify and write the wrong pair in the following set.
(1) Kootiyattam- Sanskrit theatre, Kerala
(2) Ramman- Dance form in West Bengal
(3) Ramlila- Traditional Performance of the Ramayana in Uttar Pradesh
(4) Kalbelia- Folk songs and dances of Rajasthan.
Answer:
(2) Wrong pair: Ramman – Dance form in West Bengal
2. Write short notes.
(1) Applied History
- Applied History, also known as Public History, is the use of historical knowledge to benefit people in the present and future.
- It connects history to everyday life by solving contemporary social issues.
- It promotes public participation in conservation projects and tourism.
- It creates awareness about preserving cultural and natural heritage.
- Example: Universities abroad and Srushti Institute in Bengaluru offer courses in Public History.
(2) Archives
- Archives are places where old documents, official records, and films are preserved.
- They store valuable historical materials for research and future generations.
- The National Archives of India is located in New Delhi.
- Every state in India maintains its own archives.
- Example: The National Film Archives in Pune preserves rare Indian films and promotes film culture.
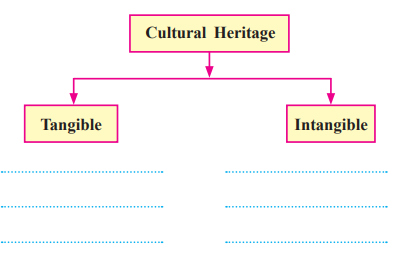
3. Complete the following concept map.
Cultural Heritage
Tangible
- Ancient sites
- Buildings
- Artefacts
- Manuscripts
- Sculptures
- Paintings
Intangible
- Oral traditions and their language
- Traditional knowledge
- Social customs and rituals of celebrating festivals
- Styles of performing arts
- Certain traditional skills
- Communities, groups who represent such traditions, customs, and skills
4. Explain the following statements with reasons.
(1) It is essential to study the history of technology.
- The history of technology helps understand changes in fields like agriculture, production, and architecture.
- It explains the causes of technological advancements and their impact on society.
- It shows the mutual dependence between scientific discoveries and technological progress.
- Example: Knowledge of stone tools to mechanized production highlights human evolution.
- Thus, studying the history of technology is essential to understand development and innovation.
(2) The list of World Heritage Sites is announced by UNESCO.
- UNESCO aims to promote and preserve cultural and natural heritage globally.
- It announces World Heritage Sites to recognize their universal value and importance.
- This ensures conservation efforts and awareness for future generations.
- Example: Western Ghats and Ajanta Caves in India are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
- Therefore, UNESCO’s list helps protect and promote global heritage.
5. Write elaborate answers.
(1) How is the method of history useful in the research of (a) Science
- The history of science helps understand the chronological order of discoveries and inventions.
- It explains the cause-effect relationships leading to scientific advancements.
- It highlights how human needs and curiosity drive scientific progress.
- Example: Studying the history of the steam engine shows its role in the Industrial Revolution.
- Thus, historical methods provide context for scientific research and innovation.
(b) Arts
- The history of arts traces the development of various art forms and their styles.
- It reveals the emotional and cultural traditions behind artistic expressions.
- It helps understand the artist’s temperament and the evolution of art forms.
- Example: Studying Mughal miniature paintings shows cultural influences of the period.
- Therefore, historical methods enrich the understanding of artistic heritage.
(c) Management Studies
- The history of management helps understand past production and market systems.
- It provides insights into human resources, production processes, and marketing strategies.
- It highlights the role of social and economic institutions in industrial processes.
- Example: Studying historical trade guilds shows early management practices.
- Thus, historical knowledge improves modern management techniques.
(2) How can we correlate applied history with our present?
- Applied history connects the past with the present by preserving heritage.
- It helps understand our identity through the creative thoughts of ancestors.
- It addresses present social issues using historical knowledge.
- It promotes conservation of cultural and natural heritage for future generations.
- Example: Managing heritage sites like Taj Mahal creates jobs and boosts tourism.
- Thus, applied history makes history relevant to our present and future.
(3) Suggest at least 10 solutions for preservation of the sources of history.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean and repair historical sites to prevent decay.
- Legal Protection: Enforce laws to protect heritage sites from vandalism.
- Public Awareness: Educate people about the importance of preserving history.
- Expert Involvement: Involve archaeologists and historians in conservation projects.
- Use of Technology: Use digital archiving to preserve documents and artefacts.
- Restricted Access: Limit visitor access to fragile sites to avoid damage.
- Funding: Provide government and private funds for heritage preservation.
- Training Programs: Train locals in conservation techniques to ensure sustainability.
- Documentation: Create detailed records of historical sources for future reference ¬.
- Community Participation: Encourage local communities to protect nearby heritage sites.
(4) What objectives can be fulfilled through the heritage projects?
- Preservation: Protect cultural and natural heritage for future generations.
- Awareness: Educate people about the importance of historical sites and traditions.
- Economic Growth: Create job opportunities through tourism and conservation projects.
- Cultural Identity: Strengthen community identity by connecting people to their heritage.
- Research: Support studies in history, archaeology, and related fields.
- Sustainable Development: Promote eco-friendly practices in heritage management.
- Social Unity: Foster unity by celebrating shared cultural heritage.
- Global Recognition: Gain UNESCO World Heritage status for significant sites.
- Skill Development: Train locals in conservation and tourism-related skills.
- Tourism Boost: Attract tourists to heritage sites, boosting local economies.

Leave a Reply