Historiography : Indian Tradition
Q.1. (A) Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the statement.
1. Alexander Cunningham was the first Director General of the Archaeological Survey of India.
Correct option: (a) Alexander Cunningham
2. Friedrich Max Muller translated the Sanskrit text of ‘Hitopadesh’ in German language.
Correct option: (b) Friedrich Max Muller
Q.1. (B) Identify and write the wrong pair in the following set.
- ‘Who were the Shudras’ – Subaltern History
- ‘Stri-Purush Tulana’ – Feminist Writing
- ‘The Indian War of Independence 1857’ – Marxist History
- Grant Duff – Colonial History
Wrong pair: ‘The Indian War of Independence 1857’ – Marxist History
Reason: ‘The Indian War of Independence 1857’ by Vinayak Damodar Savarkar is associated with Nationalistic Historiography, not Marxist History.
Q.2. Explain the following statements with reasons.
1. Writing of the regional history received a momentum.
- Nationalistic historiography inspired historians to focus on India’s glorious past.
- This led to increased interest in regional histories, such as those of South India.
- Historians studied geographic conditions and local histories to highlight regional contributions.
- For example, V.K. Rajwade emphasized writing Maratha history, boosting regional historical research.
2. Bakhar is an important type of historical document.
- Bakhars are medieval Marathi historical documents that record events, battles, and lives of great men.
- They provide valuable insights into the social, political, and cultural aspects of the time.
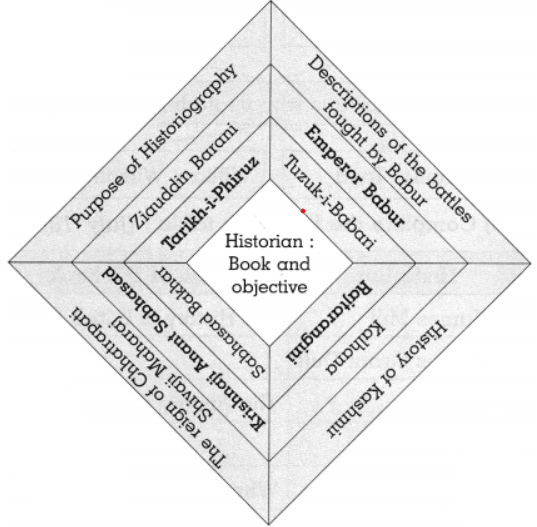
- Examples include ‘Sabhasad Bakhar’, which details Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s reign, and ‘Bhausahebanchi Bakhar’, describing the Battle of Panipat.
- They are authentic sources for understanding Maratha history and other regional events.
Q.3. Write detailed answers to the following questions in detail.
1. What is Marxist History?
- Marxist History is an approach to historiography based on the theories of Karl Marx.
- It focuses on the means of production, modes of production, and class relations in society.
- Marxist historians analyze social events to understand their impact on economic and social structures.
- In India, historians like Damodar Dharmanand Kosambi and Shripad Amrut Dange adopted this framework.
- For example, Dange’s book ‘Primitive Communism to Slavery’ represents Marxist historiography.
- It emphasizes the role of economic factors and class struggles in shaping historical events.
What is the contribution of Itihasacharya V.K. Rajwade to historiography?
- V.K. Rajwade was a prominent nationalistic historian who emphasized writing Indian history by Indians.
- He founded the ‘Bharat Itihas Samshodhak Mandal’ in Pune in 1910 to promote historical research.
- Rajwade compiled and edited 22 volumes of ‘Marathyanchya Itihasachi Sadhane’, a collection of historical documents.
- He wrote scholarly prefaces to these volumes, defining history as an all-inclusive image of past societies.
- He insisted on using authentic documentary sources for historical writing.
- Rajwade’s work inspired regional historiography, particularly Maratha history, and emphasized the importance of time, space, and personalities in historical narratives.
Q.4. (a) Complete the following chart.
| Historian | Name of the Book |
| James Mill | ‘The History of British India’ |
| James Grant Duff | …………………………………………… |
| …………………………………………… | ‘The History of India’ |
| S.A. Dange | …………………………………………… |
| …………………………………………… | ‘Who were the Shudras’ |
Answer:
| Historian | Name of the Book |
| James Mill | The History of British India |
| James Grant Duff | A History of Mahrattas |
| Mountstuart Elphinstone | The History of India |
| S. A. Dange | Primitive Communism to Slavery |
| Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar | Who Were the Shudras |
(b) Complete the following concept chart.
Answer :

Q.5. Write short notes.
1. Orientalist Historiography
- Orientalist historiography was developed by European scholars curious about Eastern civilizations.
- Scholars like Friedrich Max Muller studied Sanskrit and Vedic traditions.
- They explored similarities between Sanskrit and European languages, suggesting a common ancient language.
- The Asiatic Society, founded by William Jones in 1784, promoted research in Indian literature and history.
- However, some orientalist writings were influenced by imperialistic interests, as noted by Edward Said.
2. Nationalistic Historiography
- Nationalistic historiography aimed to restore pride in India’s ancient glory.
- Historians like V.K. Rajwade, M.G. Ranade, and V.D. Savarkar wrote to counter British biases.
- They focused on India’s golden past but sometimes ignored critical analysis of historical truth.
- In Maharashtra, Vishnushastri Chiplunkar inspired nationalistic writings.
- This approach also boosted regional histories, such as Maratha and South Indian history.
3. Subaltern History
- Subaltern history focuses on the history of marginalized groups, like the lower castes and oppressed communities.
- It emerged from Marxist historiography and was influenced by Antonio Gramsci’s ideas.
- Ranjit Guha played a key role in establishing it as an academic school.
- Mahatma Phule and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar wrote about the exploitation of shudras and atishudras.
- Folklore is a key source for writing subaltern histories, highlighting the role of Dalit communities.


Leave a Reply